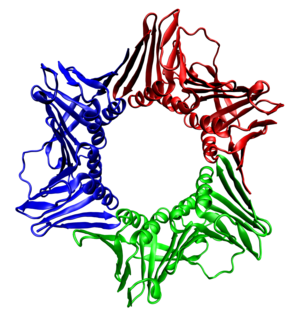
Proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) is a DNA clamp that acts as a processivity factor for DNA polymerase δ in eukaryotic cells and is essential for replication. PCNA is a homotrimer and achieves its processivity by encircling the DNA, where it acts as a scaffold to recruit proteins involved in DNA replication, DNA repair, chromatin remodeling and epigenetics.
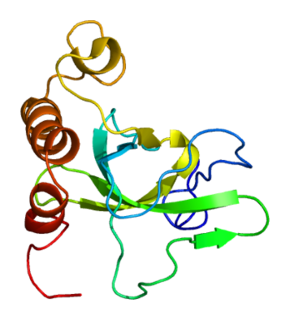
MSH6 or mutS homolog 6 is a gene that codes for DNA mismatch repair protein Msh6 in the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. It is the homologue of the human "G/T binding protein," (GTBP) also called p160 or hMSH6. The MSH6 protein is a member of the Mutator S (MutS) family of proteins that are involved in DNA damage repair.

Ku70 is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the XRCC6 gene.

Cell cycle checkpoint protein RAD17 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RAD17 gene.

Checkpoint protein HUS1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HUS1 gene.

Flap endonuclease 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the FEN1 gene.

Cell cycle checkpoint protein RAD1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RAD1 gene.
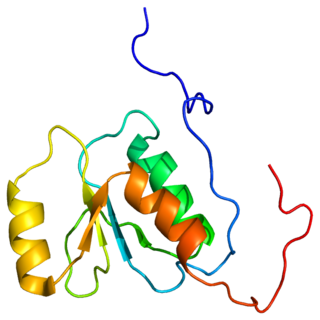
Replication factor C subunit 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RFC1 gene.

Cyclin-O is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CCNO gene.

Origin recognition complex subunit 2 is a protein that is encoded by the ORC2 (ORC2L) gene in humans.

DNA mismatch repair protein, MutS Homolog 3 (MSH3) is a human homologue of the bacterial mismatch repair protein MutS that participates in the mismatch repair (MMR) system. MSH3 typically forms the heterodimer MutSβ with MSH2 in order to correct long insertion/deletion loops and base-base mispairs in microsatellites during DNA synthesis. Deficient capacity for MMR is found in approximately 15% of colorectal cancers, and somatic mutations in the MSH3 gene can be found in nearly 50% of MMR-deficient colorectal cancers.

Replication factor C subunit 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RFC4 gene.

Replication factor C subunit 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RFC2 gene.

Replication factor C subunit 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RFC3 gene.

Replication factor C subunit 5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RFC5 gene.

DNA polymerase delta subunit 2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the POLD2 gene. It is a component of the DNA polymerase delta complex.

Sister chromatid cohesion protein DCC1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DSCC1 gene.
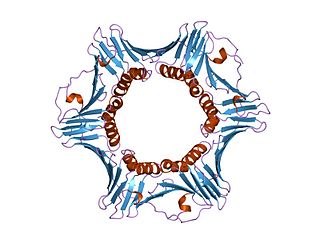
DNA polymerase delta subunit 3 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the POLD3 gene. It is a component of the DNA polymerase delta complex.

Chromosome transmission fidelity protein 8 homolog is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CHTF8 gene.
Sister chromatid cohesion refers to the process by which sister chromatids are paired and held together during certain phases of the cell cycle. Establishment of sister chromatid cohesion is the process by which chromatin-associated cohesin protein becomes competent to physically bind together the sister chromatids. In general, cohesion is established during S phase as DNA is replicated, and is lost when chromosomes segregate during mitosis and meiosis. Some studies have suggested that cohesion aids in aligning the kinetochores during mitosis by forcing the kinetochores to face opposite cell poles.




















