| Mission type | Radar imaging |
|---|---|
| Operator | ASI/MDD |
| COSPAR ID | 2007-023A |
| SATCAT no. | 31598 |
| Spacecraft properties | |
| Bus | Thales Alenia Space |
| Manufacturer | Prima |
| Launch mass | 1,900 kilograms (4,200 lb) |
| Start of mission | |
| Launch date | 8 June 2007, 02:34:00 UTC |
| Rocket | Delta II 7420-10C D324 |
| Launch site | Vandenberg SLC-2W |
| Contractor | United Launch Alliance |
| Orbital parameters | |
| Reference system | Geocentric |
| Regime | Sun-synchronous |
| Semi-major axis | 7,000.53 kilometres (4,349.93 mi) [1] |
| Eccentricity | 0.0001316 [1] |
| Perigee | 628 kilometres (390 mi) [1] |
| Apogee | 630 kilometres (390 mi) [1] |
| Inclination | 97.88 degrees [1] |
| Period | 97.16 minutes [1] |
| Epoch | 25 January 2015, 04:25:20 UTC [1] |
COSMO-1 or COSMO-Skymed 1 is an Italian radar imaging satellite. Launched in 2007, it was the first of four COSMO-Skymed satellites to be placed into orbit. The spacecraft is operated by the Agenzia Spaziale Italiana, the Italian space agency, in conjunction with Italy's Ministry of Defence. It uses synthetic aperture radar to produce images for civilian, commercial and military purposes. [2]

Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern and Western Europe. Located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, Italy shares open land borders with France, Switzerland, Austria, Slovenia and the enclaved microstates San Marino and Vatican City. Italy covers an area of 301,340 km2 (116,350 sq mi) and has a largely temperate seasonal and Mediterranean climate. With around 61 million inhabitants, it is the fourth-most populous EU member state and the most populous country in Southern Europe.

The Italian Space Agency is a government agency established in 1988 to fund, regulate and coordinate space exploration activities in Italy. The agency cooperates with numerous national and international entities who are active in aerospace research and technology.

The Ministry of Defence is the government body of the Italian Republic responsible for military and civil defence matters and managing the Italian Armed Forces. It is led by the Italian Minister of Defence, a position occupied by Elisabetta Trenta since June 2018.
COSMO-1 was constructed by Thales Alenia Space, based on the Prima bus. It was the first Prima-based spacecraft to be launched. [3] Designed for a five-year mission, [4] the satellite remains operational As of 2013 [update] .

Thales Alenia Space is a Franco-Italian aerospace manufacturer formed after the Thales Group bought the participation of Alcatel in the two joint-ventures between Alcatel and Leonardo, Alcatel Alenia Space and Telespazio. The company is Europe's largest satellite manufacturer.
ASI awarded Boeing a contract to launch COSMO-1, with the launch being subcontracted to United Launch Alliance when it was formed to take over Delta launch operations. The launch took place at 02:34:00 UTC on 8 June 2007. A Delta II rocket in the 7420-10C configuration, flight number Delta 324, lifted off from Space Launch Complex 2W at Vandenberg Air Force Base, successfully injecting the satellite into low Earth orbit. Spacecraft separation occurred 58 minutes and 5 seconds after liftoff. [5]

The Boeing Company is an American multinational corporation that designs, manufactures, and sells airplanes, rotorcraft, rockets, satellites, and missiles worldwide. The company also provides leasing and product support services. Boeing is among the largest global aircraft manufacturers; it is the fifth-largest defense contractor in the world based on 2017 revenue, and is the largest exporter in the United States by dollar value. Boeing stock is included in the Dow Jones Industrial Average.

United Launch Alliance (ULA) is a provider of spacecraft launch services to the United States government. It was formed as a joint venture between Lockheed Martin Space Systems and Boeing Defense, Space & Security in December 2006 by combining the teams at the two companies. U.S. government launch customers include the Department of Defense and NASA, as well as other organizations. With ULA, Lockheed and Boeing held a monopoly on military launches for more than a decade until the US Air Force awarded a GPS satellite contract to SpaceX in 2016.

Delta II was an expendable launch system, originally designed and built by McDonnell Douglas. Delta II was part of the Delta rocket family and entered service in 1989. Delta II vehicles included the Delta 6000, and the two later Delta 7000 variants. The rocket flew its final mission ICESat-2 on September 15, 2018, earning the launch vehicle a streak of 100 successful missions in a row, with the last failure being GPS IIR-1 in 1997.
The satellite operates in a sun-synchronous low Earth orbit. As of 25 January 2015 it was located in an orbit with a perigee of 628 kilometres (390 mi), an apogee of 630 kilometres (390 mi), inclined at 97.88 degrees to the equator. It has an orbital period of 97.16 minutes, with right ascension of the ascending node of 211.26 degrees and an argument of perigee of 84.67 degrees. [1]

A Sun-synchronous orbit is a nearly polar orbit around a planet, in which the satellite passes over any given point of the planet's surface at the same local mean solar time. More technically, it is an orbit arranged so that it precesses through one complete revolution each year, so it always maintains the same relationship with the Sun.

A Low Earth Orbit (LEO) is an Earth-centered orbit with an altitude of 2,000 km (1,200 mi) or less, or with at least 11.25 periods per day and an eccentricity less than 0.25. Most of the manmade objects in space are in LEO. A histogram of the mean motion of the cataloged objects shows that the number of objects drops significantly beyond 11.25.
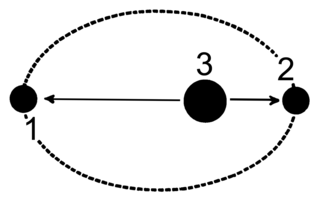
The term apsis refers to an extreme point in the orbit of an object. It denotes either the points on the orbit, or the respective distance of the bodies. The word comes via Latin from Greek, there denoting a whole orbit, and is cognate with apse. Except for the theoretical possibility of one common circular orbit for two bodies of equal mass at diametral positions, there are two apsides for any elliptic orbit, named with the prefixes peri- and ap-/apo- added to a reference to the body being orbited. All periodic orbits are, according to Newton's Laws of motion, ellipses: either the two individual ellipses of both bodies, with the center of mass of this two-body system at the one common focus of the ellipses, or the orbital ellipses, with one body taken as fixed at one focus, and the other body orbiting this focus. All these ellipses share a straight line, the line of apsides, that contains their major axes, the foci, and the vertices, and thus also the periapsis and the apoapsis. The major axis of the orbital ellipse is the distance of the apsides, when taken as points on the orbit, or their sum, when taken as distances.

