Related Research Articles
In genetics, an operon is a functioning unit of DNA containing a cluster of genes under the control of a single promoter. The genes are transcribed together into an mRNA strand and either translated together in the cytoplasm, or undergo splicing to create monocistronic mRNAs that are translated separately, i.e. several strands of mRNA that each encode a single gene product. The result of this is that the genes contained in the operon are either expressed together or not at all. Several genes must be co-transcribed to define an operon.

The lactose operon is an operon required for the transport and metabolism of lactose in E.coli and many other enteric bacteria. Although glucose is the preferred carbon source for most bacteria, the lac operon allows for the effective digestion of lactose when glucose is not available through the activity of beta-galactosidase. Gene regulation of the lac operon was the first genetic regulatory mechanism to be understood clearly, so it has become a foremost example of prokaryotic gene regulation. It is often discussed in introductory molecular and cellular biology classes for this reason. This lactose metabolism system was used by François Jacob and Jacques Monod to determine how a biological cell knows which enzyme to synthesize. Their work on the lac operon won them the Nobel Prize in Physiology in 1965.

Tryptophan repressor is a transcription factor involved in controlling amino acid metabolism. It has been best forstudied in Escherichia coli, where it is a dimeric protein that regulates transcription of the 5 genes in the tryptophan operon. When the amino acid tryptophan is plentiful in the cell, it binds to the protein, which causes a conformational change in the protein. The repressor complex then binds to its operator sequence in the genes it regulates, shutting off the genes.

The nucleoid is an irregularly shaped region within the prokaryotic cell that contains all or most of the genetic material. The chromosome of a prokaryote is circular, and its length is very large compared to the cell dimensions needing it to be compacted in order to fit. In contrast to the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell, it is not surrounded by a nuclear membrane. Instead, the nucleoid forms by condensation and functional arrangement with the help of chromosomal architectural proteins and RNA molecules as well as DNA supercoiling. The length of a genome widely varies and a cell may contain multiple copies of it.
Charles Yanofsky was an American geneticist on the faculty of Stanford University who contributed to the establishment of the one gene-one enzyme hypothesis and discovered attenuation, a riboswitch mechanism in which messenger RNA changes shape in response to a small molecule and thus alters its binding ability for the regulatory region of a gene or operon.

The bacterial outer membrane is found in gram-negative bacteria. Its composition is distinct from that of the inner cytoplasmic cell membrane - among other things, the outer leaflet of the outer membrane of many gram-negative bacteria includes a complex lipopolysaccharide whose lipid portion acts as an endotoxin - and in some bacteria such as E. coli it is linked to the cell's peptidoglycan by Braun's lipoprotein.
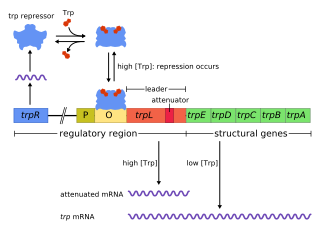
The trp operon is an operon—a group of genes that is used, or transcribed, together—that codes for the components for production of tryptophan. The trp operon is present in many bacteria, but was first characterized in Escherichia coli. The operon is regulated so that, when tryptophan is present in the environment, the genes for tryptophan synthesis are not expressed. It was an important experimental system for learning about gene regulation, and is commonly used to teach gene regulation.
The gene rpoS encodes the sigma factor sigma-38, a 37.8 kD protein in Escherichia coli. Sigma factors are proteins that regulate transcription in bacteria. Sigma factors can be activated in response to different environmental conditions. rpoS is transcribed in late exponential phase, and RpoS is the primary regulator of stationary phase genes. RpoS is a central regulator of the general stress response and operates in both a retroactive and a proactive manner: it not only allows the cell to survive environmental challenges, but it also prepares the cell for subsequent stresses (cross-protection). The transcriptional regulator CsgD is central to biofilm formation, controlling the expression of the curli structural and export proteins, and the diguanylate cyclase, adrA, which indirectly activates cellulose production. The rpoS gene most likely originated in the gammaproteobacteria.

Amino acid synthesis is the set of biochemical processes by which the amino acids are produced. The substrates for these processes are various compounds in the organism's diet or growth media. Not all organisms are able to synthesize all amino acids. For example, humans can only synthesize 11 of the 20 standard amino acids, and in time of accelerated growth, histidine can be considered an essential amino acid.
The L-arabinose operon, also called the ara or araBAD operon, is an operon required for the breakdown of the five-carbon sugar L-arabinose in Escherichia coli. The L-arabinose operon contains three structural genes: araB, araA, araD, which encode for three metabolic enzymes that are required for the metabolism of L-arabinose. AraB (ribulokinase), AraA, AraD produced by these genes catalyse conversion of L-arabinose to an intermediate of the pentose phosphate pathway, D-xylulose-5-phosphate.

The acetolactate synthase (ALS) enzyme is a protein found in plants and micro-organisms. ALS catalyzes the first step in the synthesis of the branched-chain amino acids.

fis is an E. coli gene encoding the Fis protein. The regulation of this gene is more complex than most other genes in the E. coli genome, as Fis is an important protein which regulates expression of other genes. It is supposed that fis is regulated by H-NS, IHF and CRP. It also regulates its own expression (autoregulation). Fis is one of the most abundant DNA binding proteins in Escherichia coli under nutrient-rich growth conditions.

The JUMPstart RNA motif describes a conserved RNA-based secondary structure associated with JUMPstart elements. The 39-base-pair JUMPstart sequence describes a conserved element upstream of genes that participate in polysaccharide synthesis. The JUMPstart element has been shown to function as an RNA, and is present in the 5' untranslated regions of the genes it regulates.
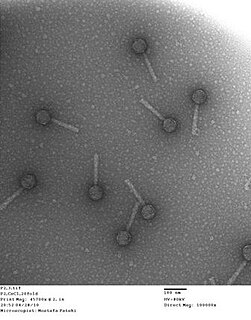
Bacteriophage P2, scientific name Escherichia virus P2, is a temperate phage that infects E. coli. It is a tailed virus with a contractile sheath and is thus classified in the genus Peduovirus, subfamily Peduovirinae, family Myoviridae within order Caudovirales. This genus of viruses includes many P2-like phages as well as the satellite phage P4.

In molecular biology, the ars operon is an operon found in several bacterial taxon. It is required for the detoxification of arsenate, arsenite, and antimonite. This system transports arsenite and antimonite out of the cell. The pump is composed of two polypeptides, the products of the arsA and arsB genes. This two-subunit enzyme produces resistance to arsenite and antimonite. Arsenate, however, must first be reduced to arsenite before it is extruded. A third gene, arsC, expands the substrate specificity to allow for arsenate pumping and resistance. ArsC is an approximately 150-residue arsenate reductase that uses reduced glutathione (GSH) to convert arsenate to arsenite with a redox active cysteine residue in the active site. ArsC forms an active quaternary complex with GSH, arsenate, and glutaredoxin 1 (Grx1). The three ligands must be present simultaneously for reduction to occur.

In molecular biology, the LuxR-type DNA-binding HTH domain is a DNA-binding, helix-turn-helix (HTH) domain of about 65 amino acids. It is present in transcription regulators of the LuxR/FixJ family of response regulators. The domain is named after Vibrio fischeri luxR, a transcriptional activator for quorum-sensing control of luminescence. LuxR-type HTH domain proteins occur in a variety of organisms. The DNA-binding HTH domain is usually located in the C-terminal region of the protein; the N-terminal region often containing an autoinducer-binding domain or a response regulatory domain. Most luxR-type regulators act as transcription activators, but some can be repressors or have a dual role for different sites. LuxR-type HTH regulators control a wide variety of activities in various biological processes.
EnvZ/OmpR is a two-component regulatory system widely distributed in bacteria and particularly well characterized in Escherichia coli. Its function is in osmoregulation, responding to changes in environmental osmolality by regulating the expression of the outer membrane porins OmpF and OmpC. EnvZ is a histidine kinase which also possesses a cytoplasmic osmosensory domain, and OmpR is its corresponding response regulator protein.
The multidrug/oligosaccharidyl-lipid/polysaccharide (MOP) flippase superfamily is a group of integral membrane protein families. The MOP flippase superfamily includes twelve distantly related families, six for which functional data are available:
- One ubiquitous family (MATE) specific for drugs - (TC# 2.A.66.1) The Multi Antimicrobial Extrusion (MATE) Family
- One (PST) specific for polysaccharides and/or their lipid-linked precursors in prokaryotes - (TC# 2.A.66.2) The Polysaccharide Transport (PST) Family
- One (OLF) specific for lipid-linked oligosaccharide precursors of glycoproteins in eukaryotes - (TC# 2.A.66.3) The Oligosaccharidyl-lipid Flippase (OLF) Family
- One (MVF) lipid-peptidoglycan precursor flippase involved in cell wall biosynthesis - (TC# 2.A.66.4) The Mouse Virulence Factor (MVF) Family
- One (AgnG) which includes a single functionally characterized member that extrudes the antibiotic, Agrocin 84 - (TC# 2.A.66.5) The Agrocin 84 Antibiotic Exporter (AgnG) Family
- And finally, one (Ank) that shuttles inorganic pyrophosphate (PPi) - (TC# 2.A.66.9) The Progressive Ankylosis (Ank) Family
CsgD is a transcription and response regulator protein referenced to as the master modulator of bacterial biofilm development. In E. coli cells, CsgD is tasked with aiding the transition from planktonic cell motility to the stationary phase of biofilm formation, in response to environmental growth factors. A transcription analysis assay illustrated a heightened decrease in CsgD's DNA-binding capacity when phosphorylated at A.A. D59 of the protein's primary sequence. Therefore, in the protein's active form (unphosphorylated), CsgD is capable of carrying out its normal functions of regulating curli proteins (fimbria) and producing ECM polysaccharides (cellulose). Following a promoter-lacZ fusion assay of CsgD binding to specific target sites on E. coli's genome, two classes of binding targets were identified: group I genes and group II genes. The group I genes, akin to fliE and yhbT, exhibit repressed transcription following their interaction with CsgD, whilst group II genes, including yccT and adrA, illustrated active functionality. Other group I operons that illustrate repressed transcription include fliE and fliEFGH, for motile flagellum formation. Other group II genes, imperative to the transition towards stationary biofilm development, include csgBA, encoding for curli fimbriae, and adrA, encoding for the synthesis of cyclic diguanylate. In this context, c-di-GMP functions as a bacterial secondary messenger, enhancing the production of extracellular cellulose and impeding flagellum production and rotation.

The Phosphate (Pho) regulon is a bacterial regulatory mechanism used for the conservation and management of inorganic phosphate within the cell. It was first discovered in Escherichia coli as an operating system for the bacterial strain, and was later identified in other species. The Pho system is composed of various components including extracellular enzymes and transporters that are capable of phosphate assimilation in addition to extracting inorganic phosphate from organic sources. This is an essential process since phosphate plays an important role in cellular membranes, genetic expression, and metabolism within the cell. Under low nutrient availability, the Pho regulon helps the cell survive and thrive despite a depletion of phosphate within the environment. When this occurs, phosphate starvation-inducible (psi) genes activate other proteins that aid in the transport of inorganic phosphate.
References
| This Enterobacterales article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
| This genetics article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |