
Goobang is a national park located in New South Wales, Australia, 296 kilometres (184 mi) northwest of Sydney. It protects the largest remnant forest and woodland in the central west region of the state, where interior and coastal New South Wales flora and fauna species overlap. Originally named Herveys Range by John Oxley in 1817, the area was reserved in 1897 as state forest because of its importance as a timber resource, and was designated a national park in 1995.

The Chiltern-Mt Pilot National Park is a national park that is located in the Hume region of Victoria, Australia. The 21,650-hectare (53,500-acre) national park is situated approximately 275 kilometres (171 mi) northeast of Melbourne, and extends west from Beechworth across the Hume Freeway and the Albury-Melbourne railway line to the west of Chiltern.

Cupressaceae is a conifer family, the cypress family, with worldwide distribution. The family includes 27–30 genera, which include the junipers and redwoods, with about 130–140 species in total. They are monoecious, subdioecious or (rarely) dioecious trees and shrubs up to 116 m (381 ft) tall. The bark of mature trees is commonly orange- to red- brown and of stringy texture, often flaking or peeling in vertical strips, but smooth, scaly or hard and square-cracked in some species.

Araucaria bidwillii, commonly known as the bunya pine and sometimes referred to as the false monkey puzzle tree, is a large evergreen coniferous tree in the plant family Araucariaceae. It is found naturally in south-east Queensland Australia and two small disjunct populations in north eastern Queensland's World Heritage listed Wet Tropics. There are many old planted specimens in New South Wales, and around the Perth, Western Australia metropolitan area. They can grow up to 30–45 m (98–148 ft). The tallest presently living is one in Bunya Mountains National Park, Queensland which was reported by Robert Van Pelt in January 2003 to be 169 feet (51.5 m) in height.

Fokienia is a genus of conifer tree belonging to the cypress family. In its characteristics, Fokienia is intermediate between the genera of Chamaecyparis and Calocedrus. Genetically Fokienia is much closer to Chamaecyparis, and not all researchers recognize Fokienia as a separate genus. The genus comprises only one living species, Fokienia hodginsii or Fujian cypress, and one fossil species.

Callitris is a genus of coniferous trees in the Cupressaceae. There are 16 recognized species in the genus, of which 13 are native to Australia and the other three native to New Caledonia. Traditionally, the most widely used common name is cypress-pine, a name shared by some species of the closely related genus Actinostrobus.

Actinostrobus pyramidalis, commonly known as swamp cypress, Swan River cypress and King George's cypress pine, is a species of coniferous tree in the Cupressaceae. Like the other species in the genus Actinostrobus, it is endemic to southwestern Western Australia.

Albert's lyrebird is a timid, pheasant-sized songbird which is endemic to subtropical rainforests of Australia, in a small area on the state border between New South Wales and Queensland. The rarer of the two species of lyrebirds, Albert's lyrebird is named after Prince Albert, the prince consort of Queen Victoria, queen of the United Kingdom. It lacks the elegant lyre-shaped tail feathers of the superb lyrebird and is found in a much more restricted range.

Cupressus funebris, the Chinese weeping cypress, is a species of cypress native to southwestern and central China. It may also occur naturally in Vietnam.

The Sierra Madre sparrow, also known as Bailey's sparrow, is an endangered, range-restricted, enigmatic American sparrow. It is endemic to Mexico and is threatened with extinction through habitat loss.

Callitris columellaris is a species of coniferous tree in the family Cupressaceae, native to most of Australia. Common names include White Cypress-pine, Murray River Cypress-pine, and Northern Cypress-pine. Callitris columellaris has become naturalised in Hawaii and in southern Florida.

Actinostrobus arenarius is a species of conifer in the cypress family, Cupressaceae. Its common names include sandplain cypress, Bruce cypress, Bruce cypress-pine, and tamin. It is endemic to Western Australia.

Callitris macleayana is a species of conifer in the family Cupressaceae, endemic to Australia. The tree is commonly known as stringybark pine, as well as brush cypress pine and Port Macquarie pine, although it does not belong to the pine genus or family. Stringybark pine is found in two regions of Australia's East coast, one in the centre and one in the North.

Callitris oblonga, also called South Esk pine, pigmy cypress pine, river pine, or Tasmanian cypress pine, is a species of conifer in the family Cupressaceae. It is endemic to Australia, and is threatened by habitat loss.

Callitris rhomboidea, or Oyster Bay pine, is a species of conifer in the family Cupressaceae.
Callitris roei, or Roe's cypress-pine, is a species of Callitris native to Australia, where it is endemic to southwestern Western Australia from Moora south to Albany and east to Cape Arid National Park.
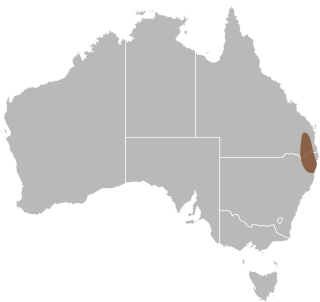
The collared delma or adorned delma is the smallest species of lizard in the Pygopodidae family endemic to Australia. Pygopopdids are legless lizards, so are commonly mistaken for snakes. They are distributed mainly across south-east Queensland and northern New South Wales, in both forests and some suburban areas. They are active during the day, seen foraging and hunting for small insects.

Eucalyptus albens, known as the white box, is a common tree of the western slopes and plains of New South Wales and adjacent areas in Queensland and Victoria. It has rough, fibrous bark on the base of its trunk and smooth, white bark above. The leaves are lance-shaped and groups of seven spindle-shaped flower buds are arranged in leaf axils or on the ends of the branches. White flowers are mostly present between August and February and the fruit are barrel-shaped to urn-shaped.
Angophora inopina, commonly known as the Charmhaven apple, is a species of small, often multi-stemmed tree that is endemic to the Central Coast of New South Wales. It has rough bark on the trunk and branches, lance-shaped adult leaves, flower buds in groups of three or seven, white or creamy white flowers and ribbed, cup-shaped fruit.

Dipodium hamiltonianum, commonly known as yellow hyacinth-orchid, is a leafless mycoheterotroph orchid that is endemic to eastern Australia. It has up to twenty five greenish flowers with dark red spots on a tall flowering stem.






















