
Pinus occidentalis, also known as the Hispaniolan pine, Hispaniola pine or pino criollo, is a pine tree endemic to the island of Hispaniola.

The Ash Meadows killifish is a species of killifish from the subfamily Empetrichthyinae, part of the family Goodeidae, which was first documented by C. H. Gilbert in 1893 and historically occupied numerous springs near Ash Meadows, Nye County, Nevada, United States. This species was last seen in 1948 and is believed to have gone extinct in the early 1950s, likely as a result of habitat alteration and competition with and predation by introduced crayfish Procambarus clarkii, mosquitofish, black mollies, and bullfrogs.

Juniperus occidentalis, known as the western juniper, is a shrub or tree native to the Western United States, growing in mountains at altitudes of 800–3,000 meters (2,600–9,800 ft) and rarely down to 100 m (330 ft). It is listed as Least Concern on the IUCN Red List because it is a widespread species with an increasing population.

The western woolly lemur or western avahi is a species of woolly lemur native to western Madagascar, where they live in dry deciduous forests. These nocturnal animals weigh 0.7–0.9 kg (1.5–2.0 lb). It is a folivorous species.

Cephalanthus occidentalis is a species of flowering plant in the family Rubiaceae that is native to eastern and southern North America. Common names include buttonbush, common buttonbush, button-willow, buck brush, and honey-bells.
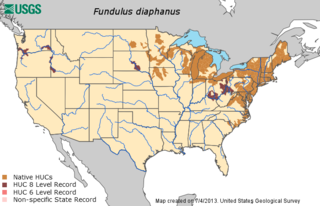
The banded killifish is a North American species of temperate freshwater killifish belonging to the genus Fundulus of the family Fundulidae. Its natural geographic range extends from Newfoundland to South Carolina, and west to Minnesota, including the Great Lakes drainages. This species is the only freshwater killifish found in the northeastern United States. While it is primarily a freshwater species, it can occasionally be found in brackish water.
The western shrew mouse is a species of rodent in the family Muridae. It is found in West Papua, Indonesia and Papua New Guinea.

The pine toad is a species of toad in the family Bufonidae. It is endemic to Mexico and found on the Central Mexican Plateau.
Dermophis occidentalis is a species of caecilian in the family Dermophiidae. It is endemic to south-western Costa Rica and occurs in the Pacific lowlands and premontane slopes, extending to the western part of the central valley. Its taxonomic status is unclear.

The Spanish mole is a species of mammal in the family Talpidae. It is found in Spain and Portugal.
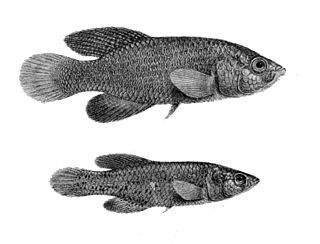
The spotted killifish is a small, short lived species of fish, an African rivuline from the family Nothobranchiidae. These fish are native to many isolated freshwater pools located in the savannah depressions of east Africa, specifically Malawi, Mozambique, Zimbabwe, and South Africa. This species of fish occurs in ephemeral waters and killifish eggs can survive long periods of dehydration. The word killifish likely comes from the Dutch kil for kill.
Nothobranchius kafuensis, known as the Caprivi killifish or Kafue killifish, is a species of killifish in the family Nothobranchiidae. This killifish is found in temporary pools, swamps and ditches in the floodplains of the Kafue and Upper Zambezi rivers in western Zambia and the Caprivi Strip in Namibia.

The blue lyretail, also known as the Gardner's killi and formerly as the steel-blue aphyosemion, is a species of killifish. It is endemic to freshwater habitats in Nigeria and Cameroon.

Nothobranchiidae are a family of bony fishes containing roughly 300 species, also known as African rivulines. They are small killifish, usually measuring about 5 centimetres (2.0 in). They are limited to Africa, living in fresh water but being also somewhat salt-tolerant. They are also found in muddy or brackish water. Some species are kept as aquarium pets. They have frilly fins and many are brightly colored. They were formerly included in the family Aplocheilidae ; a return to that broader family has recently been suggested.

Nothobranchius furzeri, the turquoise killifish, is a species of killifish from the family Nothobranchiidae native to Africa where it is only known from Zimbabwe and Mozambique. This annual killifish inhabits ephemeral pools in semi-arid areas with scarce and erratic precipitations and have adapted to the routine drying of their environment by evolving desiccation-resistant eggs that can remain dormant in the dry mud for one and maybe more years by entering into diapause.
The Guinean killifish is a species of African rivuline killifish from the family Nothobranchiidae native to the African nations of Guinea, Liberia, and Sierra Leone, where it is found in savanna streams and pools. This species grows to a length of 7 cm (2.8 in). It is found in the aquarium trade, where it has a reputation as being a difficult fish to keep.

Callopanchax is a genus of African rivulines endemic, as the name indicates, to Africa. Some of these species are popular aquarium fish.

Aphyosemion bivittatum is a species of freshwater fish belonging to the family Aplocheilidae. It is found in rivers in southeastern Nigeria and southwestern Cameroon. It was originally described as Fundulus bivittatus by Swedish zoologist Einar Lönnberg in 1895. The holotype was discovered near a waterfall in the Ndian River in Cameroon and currently is located in the Stockholm Museum.

The western round-eared bat is a bat species found only on the Pacific coast of northwestern Ecuador.
The Lake Afdera killifish is a species of fish in the family Aphaniidae. It is found in Lake Afdera in Ethiopia. The species was evaluated by the IUCN on 1 May 2009 and listed as endangered on the Red List.

















