Cerradomys marinhus, also known as Marinho's rice rat, is a rodent species from South America. It is found in Minas Gerais, Brazil. It was formerly known as Oryzomys marinhus, but was transferred to the new genus Cerradomys in 2006.
Oligoryzomys chacoensis, also known as the Chacoan colilargo or Chacoan pygmy rice rat, is a rodent species from South America. It is found in the Gran Chaco region of southeastern Bolivia, southwestern Brazil, Paraguay, and northeastern Argentina. Its karyotype has 2n = 58 and FNa = 74.

Oligoryzomys flavescens, also known as the flavescent colilargo or yellow pygmy rice rat is a species of rodent in the genus Oligoryzomys of family Cricetidae. It is found in southern South America, occurring in southern Brazil, Paraguay, Uruguay, and northeastern Argentina. Its karyotype has 2n = 64-66 and FNa = 66–70.

Oligoryzomys fulvescens, also known as the fulvous colilargo, fulvous pygmy rice rat, or northern pygmy rice rat, is a species of rodent in the genus Oligoryzomys of family Cricetidae. It is found from southern Mexico through Central America into South America, where it occurs south into Peru and Brazil, and includes numerous synonyms, including the type species of the genus, Oryzomys navus Bangs, 1899. The taxonomy of this species is unresolved, and it may be found to contain more than one species. Its karyotype has 2n = 54-60 and FNa = 68–74.
Oligoryzomys microtis, also known as the small-eared colilargo or small-eared pygmy rice rat, is a species of rodent in the genus Oligoryzomys of family Cricetidae. It is found in western Brazil, eastern Peru, Bolivia, and northern Paraguay.

Oligoryzomys nigripes, also known as the black-footed colilargo or the black-footed pygmy rice rat, is a rodent in the genus Oligoryzomys of family Cricetidae. Oligoryzomys nigripes is a species that has been further divided into different sister taxa throughout history. It is found in different countries in South America. It is a large species with long ears, dark yellow to dark brown upperparts, sharply delimited from the whitish underparts, and often a pink girdle on the chest. This species of rat spends much of its life among the trees. The karyotype is 2n = 62, FNa = 78–82.
Oligoryzomys stramineus, also known as the straw-colored colilargo or straw-colored pygmy rice rat, is a species of rodent in the genus Oligoryzomys of the family Cricetidae. It occurs only in the cerrado and caatinga ecoregions of northeastern Brazil. Its karyotype has 2n = 52 and FNa = 68-70.
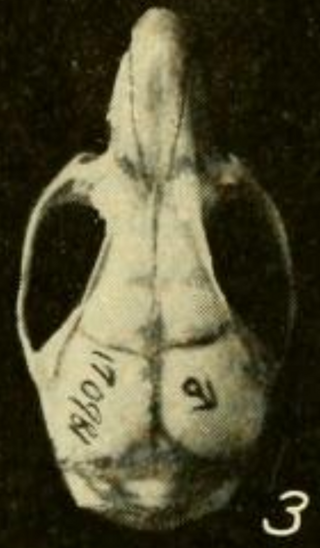
The Tocantins vesper mouse is a South American rodent species of the family Cricetidae. It is found in Brazil. Its karyotype has 2n = 46 and FNa = 66.

Lundomys molitor, also known as Lund's amphibious rat or the greater marsh rat, is a semiaquatic rat species from southeastern South America.

Pseudoryzomys simplex, also known as the Brazilian false rice rat or false oryzomys, is a species of rodent in the family Cricetidae from south-central South America. It is found in lowland palm savanna and thorn scrub habitats. It is a medium-sized species, weighing about 50 grams (1.8 oz), with gray–brown fur, long and narrow hindfeet, and a tail that is about as long as the head and body. The IUCN has assessed its conservation status as being of least concern, although almost nothing is known about its diet or reproduction.
Oligoryzomys andinus, also known as the Andean colilargo or Andean pygmy rice rat, is a species of rodent in genus Oligoryzomys of family Cricetidae. It is found in the Andes of southern Peru and western Bolivia, but may in fact include more than one species. Its karyotype has 2n = 60 and FNa = 70.
Oligoryzomys griseolus, also known as the grizzled colilargo or the grayish pygmy rice rat, is a species of rodent in the genus Oligoryzomys of family Cricetidae. It is found in the Andes of Venezuela and nearby Colombia. Its karyotype has 2n = 62 and FNa = 74–76.
Oligoryzomys magellanicus, also known as the Patagonian colilargo and the Magellanic pygmy rice rat, is a species of rodent in the genus Oligoryzomys of the family Cricetidae. It is found in the southernmost parts of Argentina and Chile, including Tierra del Fuego and other outlying islands. Its karyotype has 2n = 54 and FNa = 66.
Transandinomys talamancae is a rodent in the family Cricetidae that occurs from Costa Rica to southwestern Ecuador and northern Venezuela. Its habitat consists of lowland forests up to 1,500 m (5,000 ft) above sea level. With a body mass of 38 to 74 g, it is a medium-sized rice rat. The fur is soft and is reddish to brownish on the upperparts and white to buff on the underparts. The tail is dark brown above and lighter below and the ears and feet are long. The vibrissae (whiskers) are very long. In the skull, the rostrum is long and the braincase is low. The number of chromosomes varies from 34 to 54.
Oligoryzomys fornesi, also known as Fornes' colilargo, is a species of rodent in the genus Oligoryzomys of family Cricetidae. It is found from northeastern Brazil via Paraguay into northeastern Argentina. Its karyotype has 2n = 62 and FNa = 64.
Oligoryzomys moojeni is a species of rodent from South America in the genus Oligoryzomys of family Cricetidae. It is known only from central Brazil, where it is found in the cerrado and gallery forests. It is named after twentieth-century Brazilian zoologist João Moojen. Its karyotype has 2n = 70 and FNa = 84.
The caatinga vesper mouse is a rodent species in the family Cricetidae from South America. It is endemic to eastern Brazil, where it is found in open savanna (cerrado) and thorny scrub (caatinga) habitats. Its karyotype has 2n = 66 and FN = 68. It was formerly synonymized with C. callosus, but the latter has 2n = 50 and FN = 66. Karyologic analysis of C. expulsus has shown that the X chromosome is large and submetacentric while the Y chromosome is either acrocentric or submetacentric. Predators include the barn owl. Sexual dimorphism in shape and size occurs; the former is present mainly before the age of 20 days. Males are smaller before age 50 days and larger thereafter, which becomes less prominent after 200 days.
Oligoryzomys rupestris is a species of rodent in the genus Oligoryzomys of family Cricetidae. It is known only from eastern Brazil, where it has been found in several localities in the campos rupestres montane savanna ecoregion. This is a small Oligoryzomys species with a gray head, a yellow-brown back and gray belly and tail. Of the two karyotypic forms described by Silva & Yonenaga-Yassuda in 1998, species 1 is probably identical to O. rupestris, while the other is closely related. Its karyotype has 2n = 46 and FNa = 52.

Juliomys anoblepas is a rodent in the genus Juliomys of the subfamily Sigmodontinae known from a single broken skull. The specimen was collected by Peter Wilhelm Lund in the caves of Lagoa Santa, Minas Gerais, Brazil, in the first half of the 19th century and described by Herluf Winge in 1888 as Calomys anoblepas. The species remained unstudied and its affinities unclear until 2011, when it was recognized as a member of the genus Juliomys, which includes three other species from southern Brazil and nearby Argentina and Paraguay. J. anoblepas is probably a separate extinct species of the genus, which is no longer found at Lagoa Santa.
In mammals, ungual tufts are tufts of hairs at the base of claws of the forefeet and hindfeet. Their presence has been used as a character in cladistic studies of the Cricetidae, a large family of rodents.






