Related Research Articles
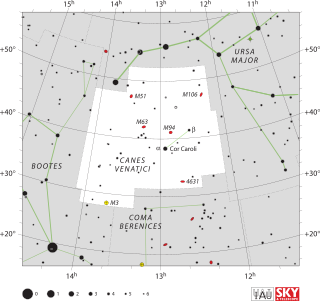
Canes Venatici is one of the 88 constellations designated by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It is a small northern constellation that was created by Johannes Hevelius in the 17th century. Its name is Latin for 'hunting dogs', and the constellation is often depicted in illustrations as representing the dogs of Boötes the Herdsman, a neighboring constellation.

The Virgo Supercluster or the Local Supercluster is a mass concentration of galaxies containing the Virgo Cluster and Local Group, which itself contains the Milky Way and Andromeda galaxies, as well as others. At least 100 galaxy groups and clusters are located within its diameter of 33 megaparsecs. The Virgo SC is one of about 10 million superclusters in the observable universe and is in the Pisces–Cetus Supercluster Complex, a galaxy filament.
The Catalogue of Galaxies and of Clusters of Galaxies was compiled by Fritz Zwicky in 1961–68. It contains 29,418 galaxies and 9,134 galaxy clusters.

Allan Rex Sandage was an American astronomer. He was Staff Member Emeritus with the Carnegie Observatories in Pasadena, California. He determined the first reasonably accurate values for the Hubble constant and the age of the universe.

NGC 4395 is a nearby low surface brightness spiral galaxy located about 14 million light-years from Earth in the constellation Canes Venatici. The nucleus of NGC 4395 is active and the galaxy is classified as a Seyfert Type I known for its very low-mass supermassive black hole. It is one of the lowest
The M94 Group is a loose, extended group of galaxies located about 13 million light-years away in the constellations Canes Venatici and Coma Berenices. The group is one of many groups that lies within the Virgo Supercluster and one of the closest groups to the Local Group.
The NGC 4631 Group is a poorly defined group of galaxies, about 25 million light-years from Earth in the Coma Berenices and Canes Venatici constellations.

The Great Diamond, also called the Diamond of Virgo, is an asterism that can be seen during spring evenings in the Northern Hemisphere. It is composed of the following stars:
Canes Venatici I or CVn I is a dwarf spheroidal galaxy situated in the Canes Venatici constellation and discovered in 2006 in the data obtained by Sloan Digital Sky Survey. It is one of the most distant known satellites of the Milky Way as of 2011 together with Leo I and Leo II. The galaxy is located at a distance of about 220 kpc from the Sun and is moving away from the Sun at a velocity of about 31 km/s. It is classified as a dwarf spheroidal galaxy (dSph) meaning that it has an elliptical shape with the half-light radius of about 550 pc.

NGC 5005, also known as Caldwell 29, is an inclined spiral galaxy in the constellation Canes Venatici. The galaxy has a relatively bright nucleus and a bright disk that contains multiple dust lanes. The galaxy's high surface brightness makes it an object that is visible to amateur astronomers using large amateur telescopes.

NGC 4618 is a distorted barred dwarf galaxy in the constellation Canes Venatici. The galaxy is formally classified as a Sm galaxy, which means that its structure vaguely resembles the structure of spiral galaxies. The galaxy is sometimes referred to as a Magellanic spiral because of its resemblance to the Magellanic clouds.

NGC 4625 is a distorted dwarf galaxy in the constellation Canes Venatici. The galaxy is formally classified as a Sm galaxy, which means that its structure vaguely resembles the structure of spiral galaxies. The galaxy is sometimes referred to as a Magellanic spiral because of its resemblance to the Magellanic clouds.

The M51 Group is a group of galaxies located in Canes Venatici. The group is named after the brightest galaxy in the group, the Whirlpool Galaxy (M51A). Other notable members include the companion galaxy to the Whirlpool Galaxy (M51B) and the Sunflower Galaxy (M63).

NGC 4449, also known as Caldwell 21, is an irregular Magellanic type galaxy in the constellation Canes Venatici, being located about 13 million light-years away. It is part of the M94 Group or Canes Venatici I Group that is relatively close to the Local Group hosting our Milky Way galaxy.

NGC 4244, also known as Caldwell 26, is an edge-on loose spiral galaxy in the constellation Canes Venatici, and is part of the M94 Group or Canes Venatici I Group, a galaxy group relatively close to the Local Group containing the Milky Way. In the sky, it is located near the yellow naked-eye star, Beta Canum Venaticorum, but also near the barred spiral galaxy NGC 4151 and irregular galaxy NGC 4214.
Canes Venatici II or CVn II is a dwarf spheroidal galaxy situated in the Canes Venatici constellation and discovered in 2006 in data obtained by the Sloan Digital Sky Survey. The galaxy is located at a distance of about 150 kpc from the Sun and moves towards the Sun with the velocity of about 130 km/s. It is classified as a dwarf spheroidal galaxy (dSph) meaning that it has an elliptical shape with a half-light radius of about 74+14
−10 pc.

The Giant Void is an extremely large region of space with an underdensity of galaxies and located in the constellation Canes Venatici. It is the second-largest-confirmed void to date, with an estimated diameter of 300 to 400 Mpc and its centre is approximately 1.5 billion light-years away. It was discovered in 1988, and was the largest void in the Northern Galactic Hemisphere, and possibly the second-largest ever detected. Even the hypothesized "Eridanus Supervoid" corresponding to the location of the WMAP cold spot is dwarfed by this void, although the Giant Void does not correspond to any significant cooling to the cosmic microwave background.

NGC 4490, also known as the Cocoon Galaxy, is a barred spiral galaxy in the constellation Canes Venatici. William Herschel discovered it in 1788. It is known to be of the closest interacting/merging galactic system. The galaxy lies at a distance of 25 million light years from Earth making it located in the local universe. It interacts with its smaller companion NGC 4485 and as a result is a starburst galaxy. NGC 4490 and NGC 4485 are collectively known in the Atlas of Peculiar Galaxies as Arp 269. The two galaxies has already made their closest approach and are rushing away from each other. It's been discovered that NGC 4490 has a double nucleus.

IC 883 is an irregular galaxy that is about 321 million light years away from Earth. It is located in the constellation Canes Venatici. Its largest radius is 1.4, and smallest 0.7 angular minutes. It was discovered by Rudolf Ferdinand Spitaler on May 1 1891.

NGC 4861, also known as Arp 266, is a galaxy in the constellation Canes Venatici. It was discovered by William Herschel on May 1, 1785.
References
- ↑ G. De Vaucouleurs, 1975. Nearby Groups of Galaxies, ch. 5. the nearer groups within 10 megaparsecs. Published in "Galaxies and the Universe," ed. by A. Sandage, M. Sandage and J. Kristian
- 1 2 3 "The Canes II Group". Atlas of the Universe. 2003. Retrieved 2009-08-06.