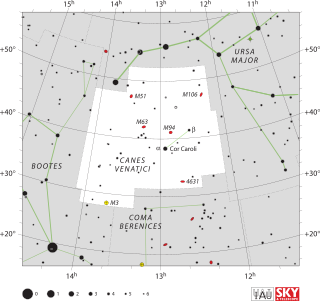
Canes Venatici is one of the 88 constellations designated by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It is a small northern constellation that was created by Johannes Hevelius in the 17th century. Its name is Latin for 'hunting dogs', and the constellation is often depicted in illustrations as representing the dogs of Boötes the Herdsman, a neighboring constellation.
NGC 4631 is a barred spiral galaxy in the constellation Canes Venatici about 30 million light years away from Earth. This galaxy's slightly distorted wedge shape gives it the appearance of a herring or a whale, hence its nickname. Because this nearby galaxy is seen edge-on from Earth, professional astronomers observe this galaxy to better understand the gas and stars located outside the plane of the galaxy.

NGC 55, is a Magellanic type barred spiral galaxy located about 6.5 million light-years away in the constellation Sculptor. Along with its neighbor NGC 300, it is one of the closest galaxies to the Local Group, probably lying between the Milky Way and the Sculptor Group. It has an estimated mass of (2.0 ± 0.4) × 1010M☉.

Messier 96 is an intermediate spiral galaxy about 31 million light-years away in the constellation Leo.

Messier 108 is a barred spiral galaxy about 28 million light-years away from Earth in the northern constellation Ursa Major. It was discovered by Pierre Méchain in 1781 or 1782. From the Earth, this galaxy is seen almost edge-on.

The Sculptor Galaxy is an intermediate spiral galaxy in the constellation Sculptor. The Sculptor Galaxy is a starburst galaxy, which means that it is currently undergoing a period of intense star formation.
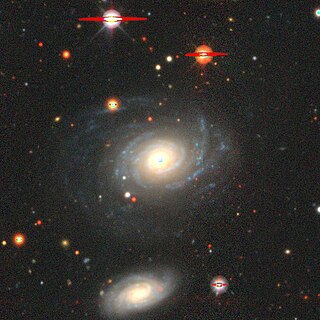
NGC 1 is an intermediate spiral galaxy of the morphological type Sbc, located in the constellation of Pegasus. It was discovered on 30 September 1861 by Heinrich d'Arrest.

NGC 1532, also known as Haley's Coronet, is an edge-on barred spiral galaxy located approximately 50 million light-years from the Solar System in the constellation Eridanus. The galaxy was discovered by James Dunlop on 29 October 1826.

NGC 1531 is a dwarf galaxy in the constellation Eridanus that is interacting with the larger spiral galaxy NGC 1532. It was discovered by John Herschel on 19 October 1835. Although technically classified as a peculiar lenticular galaxy, the galaxy's structure is better described as amorphous.

NGC 4656/57 is a highly warped edge-on barred spiral galaxy located in the local universe 30 million light years away from earth in the constellation Canes Venatici. This galaxy is sometimes called the Hockey Stick Galaxy or the Crowbar Galaxy. Its unusual shape is thought to be due to an interaction between NGC 4656, NGC 4631, and NGC 4627. The galaxy is a member of the NGC 4631 Group.
The NGC 4631 Group is a poorly defined group of galaxies, about 25 million light-years from Earth in the Coma Berenices and Canes Venatici constellations.

NGC 278 is an isolated spiral galaxy in the northern circumpolar constellation of Cassiopeia, near the southern constellation boundary with Andromeda. It lies at a distance of approximately 39 megalight-years from the Milky Way, giving it a physical scale of 190 ly (58 pc) per arcsecond. The galaxy was discovered on December 11, 1786 by German-born astronomer William Herschel. J. L. E. Dreyer described it as, "considerably bright, pretty large, round, 2 stars of 10th magnitude near".

NGC 4236 is a barred Magellanic spiral galaxy located in the constellation Draco.

NGC 1410 is a peculiar lenticular galaxy in the constellation Taurus. It was discovered on January 17, 1855, by English astronomer R. J. Mitchell. NGC 1410 is located in close proximity to the larger lenticular galaxy NGC 1409, and the two are strongly interacting. Their respective nuclei have a separation of just 23 kly, and they share a diffuse stellar envelope with a radius extending out to 49 kly.

NGC 7552 is a barred spiral galaxy in the constellation Grus. It is at a distance of circa 60 million light years from Earth, which, given its apparent dimensions, means that NGC 7552 is about 75,000 light years across. It forms with three other spiral galaxies the Grus Quartet.

The Coma I Group is a group of galaxies located about 14.5 Mpc (47.3 Mly) away in the constellation Coma Berenices. The brightest member of the group is NGC 4725. The Coma I Group is rich in spiral galaxies while containing few elliptical and lenticular galaxies. Coma I lies in the foreground of the more distant Coma and Leo clusters and is located within the Virgo Supercluster.

NGC 7674 is a spiral galaxy located in the constellation Pegasus. It is located at a distance of circa 350 million light years from Earth, which, given its apparent dimensions, means that NGC 7674 is about 125,000 light years across. It was discovered by John Herschel on August 16, 1830.

NGC 4278 is an elliptical galaxy located in the constellation Coma Berenices. It is located at a distance of circa 55 million light years from Earth, which, given its apparent dimensions, means that NGC 4278 is about 65,000 light years across. It was discovered by William Herschel on March 13, 1785. NGC 4278 is part of the Herschel 400 Catalogue and can be found about one and 3/4 of a degree northwest of Gamma Comae Berenices even with a small telescope.

NGC 5363 is a lenticular galaxy located in the constellation Virgo. It is located at a distance of circa 65 million light years from Earth, which, given its apparent dimensions, means that NGC 5363 is about 100,000 light years across. It was discovered by William Herschel on January 19, 1784. It is a member of the NGC 5364 Group of galaxies, itself one of the Virgo III Groups strung out to the east of the Virgo Supercluster of galaxies.

The Virgo III Groups, or Virgo III Cloud, are a series of at least 75 galactic clusters and individual galaxies stretching approximately 40 megalight-years off the eastern edge of the Virgo Supercluster. Parts of it are in the constellations Virgo, Libra, and Serpens Caput. It is located approximately 65 Mly (19,929,090.60 pc) to 85 Mly (26,061,118.47 pc) from the Solar System, at a right ascension of 13h 30m to 15h 20m.

















