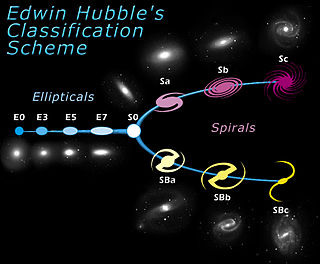
The Hubble sequence is a morphological classification scheme for galaxies invented by Edwin Hubble in 1926. It is often colloquially known as the Hubble tuning fork diagram because the shape in which it is traditionally represented resembles a tuning fork.

Hydra is the largest of the 88 modern constellations, measuring 1303 square degrees, and also the longest at over 100 degrees. Its southern end borders Libra and Centaurus and its northern end borders Cancer. It was included among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy. Commonly represented as a water snake, it straddles the celestial equator.

Messier 61 is an intermediate barred spiral galaxy in the Virgo Cluster of galaxies. It was first discovered by Barnaba Oriani on May 5, 1779, six days before Charles Messier discovered the same galaxy. Messier had observed it on the same night as Oriani but had mistaken it for a comet. Distance estimated to be 45.61 million light year from milky way galaxy.

The Whirlpool Galaxy, also known as Messier 51a, M51a, and NGC 5194, is an interacting grand-design spiral galaxy with a Seyfert 2 active galactic nucleus. It lies in the constellation Canes Venatici, and was the first galaxy to be classified as a spiral galaxy. Its distance is estimated to be 31 million light-years away from Earth.

NGC 3314 is a pair of overlapping spiral galaxies between 117 and 140 million light-years away in the constellation Hydra. This unique alignment gives astronomers the opportunity to measure the properties of interstellar dust in the face-on foreground galaxy. The dust appears dark against the background galaxy. Unlike interacting galaxies, the two components of NGC 3314 are physically unrelated. It was discovered in April 1999.

NGC 1300 is a barred spiral galaxy located about 61 million light-years away in the constellation Eridanus. The galaxy is about 110,000 light-years across. It is a member of the Eridanus Cluster, a cluster of 200 galaxies. It was discovered by John Herschel in 1835.

Interacting galaxies are galaxies whose gravitational fields result in a disturbance of one another. An example of a minor interaction is a satellite galaxy disturbing the primary galaxy's spiral arms. An example of a major interaction is a galactic collision, which may lead to a galaxy merger.

NGC 4414 is an unbarred spiral galaxy about 62 million light-years away in the constellation Coma Berenices. It is a flocculent spiral galaxy, with short segments of spiral structure but without the dramatic well-defined spiral arms of a grand design spiral. In 1974 a supernova, SN 1974G, was observed and was the only supernova in this galaxy to be recorded until June 7, 2013 when SN 2013df was discovered at magnitude 14 and January 1, 2021 when SN 2021J was discovered at magnitude 12.

NGC 1309 is a spiral galaxy located approximately 120 million light-years away, appearing in the constellation Eridanus. It is about 75,000 light-years across, and is about 3/4s the width of the Milky Way. Its shape is classified as SA(s)bc, meaning that it has moderately wound spiral arms and no ring. Bright blue areas of star formation can be seen in the spiral arms, while the yellowish central nucleus contains older-population stars. NGC 1309 is one of over 200 members of the Eridanus Group of galaxies.

NGC 1055 is an edge-on spiral galaxy located in the constellation Cetus. The galaxy has a prominent nuclear bulge crossed by a wide, knotty, dark lane of dust and gas. The spiral arm structure appears to be elevated above the galaxy's plane and obscures the upper half of the bulge. Discovered on December 19, 1783 by William Herschel from his home in Slough England.

Arp 87 is a pair of two interacting galaxies, NGC 3808A and NGC 3808B. They are situated in the Leo constellation. NGC 3808A, the brighter, is a peculiar spiral galaxy, while NGC 3808B is an irregular galaxy.

NGC 2775 is a spiral galaxy in the northern constellation of Cancer, located at a distance of 67 megalight-years from the Milky Way. It was discovered by William Herschel in 1783. NGC 2775 belongs to the Antlia-Hydra Cluster of galaxies and is the most prominent member of a small galaxy group known as NGC 2775 group, part of the Virgo Supercluster, along with the Local Group. Other members of the NGC 2775 group include NGC 2777 and UGC 4781.

NGC 3621 is a field spiral galaxy about 22 Mly (6.7 Mpc) away in the equatorial constellation of Hydra. It is comparatively bright and can be well seen in moderate-sized telescopes. The galaxy is around 93,000 ly (29,000 pc) across and is inclined at an angle of 25° from being viewed edge on. It shines with a luminosity equal to 13 billion times that of the Sun. The morphological classification is SA(s)d, which indicates this is an ordinary spiral with loosely wound arms. There is no evidence for a bulge. Although it appears to be isolated, NGC 3621 belongs to the Leo spur.

NGC 4183 is a spiral galaxy with a faint core and an open spiral structure located about 55 million light-years from the Sun. Spanning about eighty thousand light-years, it appears in the constellation of Canes Venatici. NGC 4183 was observed for the first time by British astronomer William Herschel on 14 January 1788.

NGC 428 is a barred spiral galaxy in the constellation of Cetus, with its spiral structure distorted and warped, possibly the result of the collision of two galaxies. There appears to be a substantial amount of star formation occurring within NGC 428 and lacks well defined arms — a telltale sign of a galaxy merger. In 2015 the Hubble Space Telescope made a close-up shot of the galaxy with its Advanced Camera for Surveys and its Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2. The structure of NGC 428 has been compared to NGC 5645.

NGC 672 is a spiral galaxy in the northern constellation of Triangulum, positioned around 2° to the southwest of the star Alpha Trianguli. The original object designated NGC 672 was discovered by the German-born astronomer William Herschel on 26 October 1786, but this was later cataloged as NGC 614. The object now identified as NGC 672 was discovered by John Herschel on 11 November 1827.

NGC 5264, also known as DDO 242, is an irregular galaxy in the constellation Hydra. It is part of the M83 subgroup of the Centaurus A/M83 Group, located some 15 million light years away. The galaxy was discovered on 30 March 1835 by John Herschel, and it was described as "very faint, pretty large, round, very little brighter middle" by John Louis Emil Dreyer, the compiler of the New General Catalogue.

NGC 522, also occasionally referred to as PGC 5218 or UGC 970, is a spiral galaxy located approximately 122 million light-years from the Solar System in the constellation Pisces. It was discovered on 25 September 1862 by astronomer Heinrich Louis d'Arrest.

NGC 3312 is a large and highly inclined spiral galaxy located about 194 million light-years away in the constellation Hydra. The galaxy was discovered by astronomer John Herschel on March 26, 1835. It was later rediscovered by astronomer Guillaume Bigourdan on February 26, 1887. NGC 3312 was later listed and equated with IC 629 because the two objects share essentially the same celestial coordinates. NGC 3312 is the largest spiral galaxy in the Hydra Cluster and is also classified as a LINER galaxy.

NGC 2936 is an interacting spiral galaxy located at a distance of 326 million light years, in the constellation Hydra. NGC 2936 is interacting with elliptical galaxy NGC 2937, located just beneath it. They were both discovered by Albert Marth on Mar 3, 1864. To some astronomers, the galaxy looks like a penguin or a porpoise. NGC 2936, NGC 2937, and PGC 1237172 are included in the Atlas of Peculiar Galaxies as Arp 142 in the category "Galaxy triplet".
![]() 13h 09m 10.082s, −28° 38′ 30.44″
13h 09m 10.082s, −28° 38′ 30.44″ 





















