
R Hydrae, abbreviated R Hya, is a single star in the equatorial constellation of Hydra, about 2.7° to the east of Gamma Hydrae. It is a Mira-type variable that ranges in apparent visual magnitude from 3.5 down to 10.9 over a period of 389 days. At maximum brightness the star can be seen with the naked eye, while at minimum a telescope of at least 5 cm is needed. This star is located at a distance of approximately 410 light-years from the Sun but is drifting closer with a radial velocity of −10 km/s.

U Antliae is a variable star in the constellation Antlia. It is a carbon star surrounded by two thin shells of dust.

R Horologii is a red giant star approximately 760 light-years away in the southern constellation of Horologium. It is a Mira variable with a period of 404.83 days, ranging from apparent magnitude 4.7 to 14.3—one of the largest ranges in brightness known of stars in the night sky visible to the unaided eye. The star is losing mass at the rate of 5.9×10−7 M☉·y−1.

Iota Centauri, Latinized from ι Centauri, is a star in the southern constellation of Centaurus. Based upon parallax measurements, it lies at a distance of approximately 58.6 light-years from Earth. Iota Centauri has an apparent visual magnitude of +2.73, making it easily visible to the naked eye.
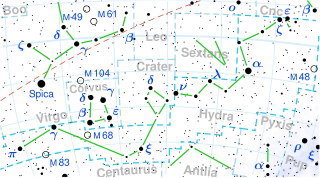
Epsilon Hydrae is a multiple star system of a combined third magnitude in the constellation of Hydra. Based upon parallax measurements obtained during the Hipparcos mission, it is located roughly 129 light-years distant from the Sun.

V Hydrae is a carbon star in the constellation Hydra. To date perhaps uniquely in our galaxy it has plasma ejections/eruptions on a grand scale that could be caused by its near, unseen companion.

HD 33579 is a white/yellow hypergiant and one of the brightest stars in the Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC). It is a suspected variable star.
μ Hydrae, Latinised as Mu Hydrae, is a solitary, orange-hued star in the equatorial constellation of Hydra. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 3.83. Positioned just 1.8° to the south-southwest is the planetary nebula NGC 3242. Mu Hydrae has an annual parallax shift of 13.93 mas, which yields a distance estimate of 234 light years.

Rho Hydrae, equally written ρ Hydrae, is a binary star in the equatorial constellation of Hydra. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.34. The distance to this system, based upon an annual parallax shift of 9.21 mas, is about 354 light years. At that distance, the visual magnitude is diminished by an interstellar extinction of 0.06 magnitudes, due to intervening dust.
58 Hydrae is a single star in the equatorial constellation of Hydra, located around 290 light years away from the Sun based on parallax. It has the Bayer designation E Hydrae; 58 Hydrae is the Flamsteed designation − a later designation of 6 Librae. It is visible to the naked eye as a faint, orange-hued star with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.42. This object is moving closer to the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of −9 km/s.
Phi3 Hydrae is a binary star in the equatorial constellation of Hydra. It originally received the Flamsteed designation of 2 Crateris before being placed in the Hydra constellation. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 15.49 mas as seen from Earth, it is located around 211 light years from the Sun. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.90. It forms a triangle with the fainter φ1 Hydrae and φ2 Hydrae, between μ Hydrae and ν Hydrae.

Phi2 Hydrae, Latinized from φ2 Hydrae, is a star in the constellation Hydra. It originally received the Flamsteed designation of 1 Crateris before being placed in the Hydra constellation. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 4.31 mas as seen from Earth, it is located roughly 760 light years from the Sun. The star is faintly visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 6.09. It forms a triangle with the fainter φ1 Hydrae and the brighter φ3 Hydrae, between μ Hydrae and ν Hydrae.
HD 96819 is a star in the equatorial constellation of Hydra. It was formerly known by its designation 10 Crateris, but that name fell into disuse after constellations were redrawn and the star was no longer in Crater. It is visible to the naked eye as a dim, white-hued star with an apparent visual magnitude of 5.43. Parallax measurements put it at a distance of 182 light years away from the Sun. This is most likely a member of the TW Hydrae association.

3 Puppis is a supergiant star in the constellation Puppis. It is a very rare A[e] supergiant, referred to as a B[e] star despite its spectral classification, and its apparent magnitude is 3.93.

Chi2 Hydrae, Latinised from χ2 Hydrae, is a binary star system in the equatorial constellation of Hydra. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 4.6 mas as seen from Earth, it is located roughly 685 light years from the Sun. It is visible to the naked eye with a combined apparent visual magnitude of about 5.7.

TW Horologii is a carbon star and semiregular variable in the southern constellation of Horologium, near the eastern constellation border with Reticulum. It has a ruddy hue and, with an apparent visual magnitude that ranges from 5.52 down to 5.95, is visible to the naked eye and one of the brightest carbon stars. Based on parallax measurements, it is located at a distance of approximately 1,370 light years from the Sun. It is drifting further away with a radial velocity of +14 km/s. In the past this star has been considered a member of the open cluster NGC 1252, but this now seems unlikely.

S Scuti is a carbon star located in the constellation Scutum. Parallax measurements by Hipparcos put it at a distance of approximately 1,300 light-years. Its apparent magnitude is 6.80, making it not quite bright enough to be seen with the naked eye.
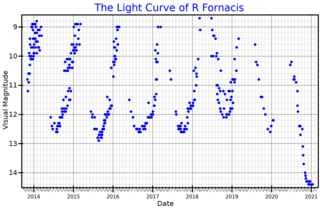
R Fornacis is a Mira variable and carbon star located in the constellation Fornax. It is around 1,800 light years away based on parallax measurements.

HS Hydrae is a triple star system in the equatorial constellation of Hydra. The inner pair were an eclipsing binary during the period 1920 until 2019, with HS Hya being the variable star designation. With a base apparent visual magnitude of 8.08, HS Hya is too dim to be viewed with the naked eye. During the primary eclipse, the magnitude dropped to 8.61; the secondary eclipse lowered the magnitude to 8.55. Based on parallax measurements, the system is located at a distance of approximately 335 light years from the Sun. It is drifting closer with a mean radial velocity of −7 km/s.

LQ Hydrae is a single variable star in the equatorial constellation of Hydra. It is sometimes identified as Gl 355 from the Gliese Catalogue; LQ Hydrae is the variable star designation, which is abbreviated LQ Hya. The brightness of the star ranges from an apparent visual magnitude of 7.79 down to 7.86, which is too faint to be readily visible to the naked eye. Based on parallax measurements, this star is located at a distance of 59.6 light years from the Sun. It is drifting further away with a radial velocity of 7.6 km/s.
















