Related Research Articles

Eta Sculptoris, Latinized from η Sculptoris, is a single, variable star in the central part of the southern constellation of Sculptor. It is visible to the naked eye as a faint, red-hued star with an apparent visual magnitude that fluctuates around 4.81. The star is located approximately 460 light years from the Sun based on parallax, and is drifting further away with a radial velocity of +12 km/s.
21 Aquarii is a single star in the zodiac constellation of Aquarius. 21 Aquarii is the Flamsteed designation. It is visible to the naked eye as a dim, orange-hued star with an apparent visual magnitude of 5.48. This object is a member of the HR 1614 moving group, and is moving closer to the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of −24.5 km/s.
BE Camelopardalis is a solitary variable star in the northern circumpolar constellation of Camelopardalis. It is visible to the naked eye as a faint, red-hued point of light with an apparent visual magnitude that fluctuates around 4.39. The star is located roughly 800 light years away from the Sun based on stellar parallax.

24 Capricorni or A Capricorni is a single star in the southern constellation of Capricornus. This object is visible to the naked eye as a faint, red-hued star with an apparent visual magnitude of +4.49. It is approximately 460 light years from the Sun, based on parallax. The star is moving further from the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of +32 km/s.
Upsilon Capricorni, Latinized from υ Capricorni, is a solitary star in the southern constellation of Capricornus. It has a reddish hue and is dimly visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 5.17. The star is located at a distance of approximately 730 light years from the Sun based on parallax, but is drifting closer with a radial velocity of −12 km/s. As it is positioned near the ecliptic, the star is subject to lunar occultations.
HD 80230 is a single star in the southern constellation of Carina, near the northern constellation border with Vela. It has the Bayer designation g Carinae, while HD 80230 is the star's identifier in the Henry Draper catalogue. This is a suspected variable star with a brightness that has been measured varying from magnitude 4.31 down to 4.35, both of which is bright enough for the star to be visible to the naked eye. The distance to this object is approximately 490 light years based on parallax, but it is drifting closer to the Sun with a radial velocity of −5 km/s.
HD 56618 is a single star in the southern constellation of Canis Major. It is a red-hued star that is faintly visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.66. This object is located at a distance of approximately 390 light years from the Sun based on parallax measurements. It is drifting further away with a radial velocity of +41.5 km/s, having come to within 203 light-years some 2.2 million years ago. Olin J. Eggen listed it as a probable member of the Hyades supercluster.
36 Comae Berenices is a single star in the northern constellation of Coma Berenices. It is faintly visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.76. The distance to this star, as determined from an annual parallax shift of 9.3 mas, is 349 light years. It is moving closer to the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of −1.5 km/s.
HD 24160 is a single star in the equatorial constellation of Eridanus. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.17. The distance to HD 24160 can be estimated from its annual parallax shift of 15.0 mas, yielding a separation of 217 light years. It is moving further from the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of +2 km/s. This object is a coronal member of the Ursa Major Moving Group of stars that share a common motion through space.
54 Eridani is a suspected astrometric binary star system located around 400 light years from the Sun in the equatorial constellation of Eridanus. It is visible to the naked eye as a faint, reddish hued star with a baseline apparent visual magnitude of 4.32. The object is moving closer to the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of −33 km/s.
42 Herculis is a single star located around 450 light years away from the Sun in the northern constellation of Hercules. It is visible to the naked eye as a faint, red-hued star with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.86. The star is moving closer to the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of −56 km/s.
98 Herculis is a single star located approximately 590 light years from the Sun in the northern constellation Hercules. It is visible to the naked eye as a dim, red-hued point of light with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.96. The brightness of the star is diminished by an extinction of 0.19 due to interstellar dust. The star is moving closer to the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of −19 km/s.
104 Herculis is a solitary variable star located around 560 light years away from the Sun in the northern constellation of Hercules. It has the variable star designation V669 Herculis and the Bayer designation A Herculis, while 104 Herculis is the Flamsteed designation. This object is visible to the naked eye as a dim, red-hued point of light with a baseline apparent visual magnitude of 4.96. It is moving closer to the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of −1.2 km/s.
32 Ophiuchi is a single star located 410 light years away from the Sun in the constellation Hercules. It is visible to the naked eye as a dim, red-hued star with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.97. This is an aging red giant star on the asymptotic giant branch with a stellar classification of M3−III. Having exhausted the supply of hydrogen at its core it has expanded to 60 times the girth of the Sun. The star is radiating 614 times the luminosity of the Sun from its swollen photosphere at an effective temperature of around 3,712 K. It is moving further away from the Sun with a heliocentric radial velocity of +43 km/s.
HD 211073 is a triple star system in the northern constellation Lacerta, located around 580 light years from the Sun. It is visible to the naked eye as a faint orange-hued star with a baseline apparent visual magnitude of 4.50. The system is moving closer to the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of −11.7 km/s.
Mu Coronae Borealis, Latinized from μ Coronae Borealis, is a solitary, ruby-hued star located in the northern constellation of Corona Borealis. It is faintly visible to the naked eye, having an apparent visual magnitude of 5.12. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 5.27 mas, it is located roughly 620 light years from the Sun. This is an evolved red giant star with a stellar classification of M1.5 IIIb. It is currently on the asymptotic giant branch and is a variable star of uncertain type, showing a change in brightness with an amplitude of 0.0147 magnitude and a frequency of 0.02455 cycles per day, or 40.7 days/cycle. On average, it is radiating 932 times the Sun's luminosity from its enlarged photosphere at an effective temperature of 3,889 K.

55 Pegasi is a single star in the northern constellation of Pegasus. It is visible to the naked eye as a faint, reddish-hued point of light with a baseline apparent visual magnitude of 4.51. The star is located approximately 302 light years away from the Sun based on parallax, but it is moving closer with a radial velocity of −5 km/s.

Chi Pegasi, Latinized from χ Pegasi, is a single star in the northern constellation of Pegasus, along the eastern constellation border with Pisces. It has a reddish hue and is faintly visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.80. The distance to this star is approximately 368 light years based on parallax, but it is drifting closer with a radial velocity of -46 km/s.
DU Lyncis is a single variable star in the constellation Lynx. It is a faint star but visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 5.15. With an annual parallax shift of 9.2 mas, it is located some 350 light years from the Sun. The star is moving closer with a heliocentric radial velocity of −37 km/s.
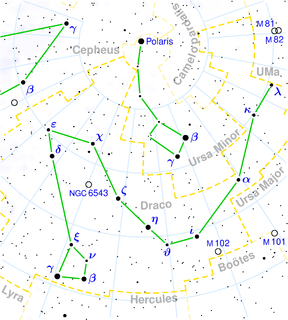
64 Draconis is a single star in the northern circumpolar constellation of Draco, located 452 light years away. It has the Bayer designation of e Draconis; 64 Draconis is the Flamsteed designation. The object is visible to the naked eye as a dim, red-hued star with an apparent visual magnitude of 5.27. It is moving closer to the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of −36 km/s, and it is predicted to come as close as 204 ly in around 4.3 million years.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Brown, A. G. A.; et al. (Gaia collaboration) (August 2018). "Gaia Data Release 2: Summary of the contents and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics . 616. A1. arXiv: 1804.09365 . Bibcode: 2018A&A...616A...1G . doi: 10.1051/0004-6361/201833051 . Gaia DR2 record for this source at VizieR.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Anderson, E.; Francis, Ch. (2012), "XHIP: An extended hipparcos compilation", Astronomy Letters, 38 (5): 331, arXiv: 1108.4971 , Bibcode:2012AstL...38..331A, doi:10.1134/S1063773712050015.
- 1 2 Eggen, Olin J. (July 1992), "Asymptotic giant branch stars near the sun", Astronomical Journal, 104 (1): 275–313, Bibcode:1992AJ....104..275E, doi:10.1086/116239.
- 1 2 Keenan, Philip C.; McNeil, Raymond C. (1989), "The Perkins catalog of revised MK types for the cooler stars", Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series, 71: 245, Bibcode:1989ApJS...71..245K, doi:10.1086/191373.
- ↑ "HD 92036". SIMBAD . Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg . Retrieved 2020-01-30.
- ↑ Eggleton, P. P.; Tokovinin, A. A. (September 2008), "A catalogue of multiplicity among bright stellar systems", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society , 389 (2): 869–879, arXiv: 0806.2878 , Bibcode:2008MNRAS.389..869E, doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2008.13596.x.
| This giant-star-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |