
Seyfert galaxies are one of the two largest groups of active galaxies, along with quasar host galaxies. They have quasar-like nuclei with very high surface brightnesses whose spectra reveal strong, high-ionisation emission lines, but unlike quasars, their host galaxies are clearly detectable.

Messier 95, also known as M95 or NGC 3351, is a barred spiral galaxy about 33 million light-years away in the zodiac constellation Leo. It was discovered by Pierre Méchain in 1781, and catalogued by compatriot Charles Messier four days later. In 2012 its most recent supernova was discovered.

NGC 7319 is a highly distorted barred spiral galaxy that is a member of the compact Stephan's Quintet group located in the constellation Pegasus, some 311 megalight-years distant from the Milky Way. It was discovered on 27 September 1873 by French astronomer Édouard Stephan.

NGC 7469 is an intermediate spiral galaxy in the constellation of Pegasus. NGC 7469 is located about 200 million light-years away from Earth, which means, given its apparent dimensions, that NGC 7469 is approximately 90,000 light-years across. It was discovered by William Herschel on November 12, 1784.

NGC 3367 is a barred spiral galaxy located in the constellation Leo. It is located at a distance of about 120 million light years from Earth, which, given its apparent dimensions, means that NGC 3367 is about 85,000 light years across. It was discovered by William Herschel on March 19, 1784.

NGC 7130 is a spiral galaxy located in the constellation Piscis Austrinus. It is located at a distance of about 220 million light years from Earth, which, given its apparent dimensions, means that NGC 7130 is about 100,000 light years across. It was discovered by John Herschel on September 25, 1834, and discovered independently by Lewis Swift on September 17, 1897. The location of the galaxy given in the New General Catalogue was off by 30 arcminutes in declination from the location of the galaxy.

NGC 985 is a ring galaxy in the constellation of Cetus. It is located about 550 million light years away from Earth, which means, given its apparent dimensions, that NGC 985 is approximately 160,000 light years across. It was discovered by Francis Leavenworth in 1886. It is a type 1 Seyfert galaxy.

NGC 6951 is a barred spiral galaxy located in the constellation Cepheus. It is located at a distance of about 75 million light-years from Earth, which, given its apparent dimensions, means that NGC 6951 is about 100,000 light-years across. It was discovered by Jérôme Eugène Coggia in 1877 and independently by Lewis Swift in 1878.

NGC 1386 is a spiral galaxy located in the constellation Eridanus. It is located at a distance of circa 53 million light years from Earth, which, given its apparent dimensions, means that NGC 1386 is about 50,000 light years across. It is a Seyfert galaxy, the only one in Fornax Cluster.

IC 1459 is an elliptical galaxy located in the constellation Grus. It is located at a distance of circa 85 million light-years from Earth, which, given its apparent dimensions, means that IC 1459 is about 130,000 light-years across. It was discovered by Edward Emerson Barnard in 1892.

NGC 2273 is a barred spiral galaxy located in the constellation Lynx. It is located at a distance of circa 95 million light years from Earth, which, given its apparent dimensions, means that NGC 2273 is about 100,000 light years across. It was discovered by Nils Dunér on September 15, 1867.

NGC 4800 is an isolated spiral galaxy in the constellation Canes Venatici, located at a distance of 95 megalight-years from the Milky Way. It was discovered by William Herschel on April 1, 1788. The morphological classification of this galaxy is SA(rs)b, indicating a spiral galaxy with no visual bar at the nucleus (SA), an incomplete ring structure (rs), and moderately-tightly wound spiral arms (b). The galactic plane is inclined to the line of sight by an angle of 43°, and the long axis is oriented along a position angle of 25°. There is a weak bar structure at the nucleus that is visible in the infrared.

NGC 1241 is a spiral galaxy located in the constellation Eridanus. It is located at a distance of circa 150 million light years from Earth, which, given its apparent dimensions, means that NGC 1241 is about 140,000 light years across. It was discovered by William Herschel on January 10, 1785. It is classified as a Seyfert galaxy.

NGC 1142 is a distorted spiral galaxy in the constellation of Cetus. It is located about 370 million light years away from Earth, which means, given its apparent dimensions, that NGC 1142 is approximately 170,000 light years across. It is a type 2 Seyfert galaxy. It interacts with the elliptical galaxy NGC 1141.

NGC 7592 is an interacting galaxy system located 300 million light years away in the constellation Aquarius. It was discovered by William Herschel on September 20, 1784. The total infrared luminosity is 1011.33 L☉, and thus it is categorised as a luminous infrared galaxy. One of the galaxies hosts a type 2 Seyfert nucleus.

NGC 7679 is a lenticular galaxy with a peculiar morphology in the constellation Pisces. It is located at a distance of about 200 million light years from Earth, which, given its apparent dimensions, means that NGC 7679 is about 60,000 light years across. It was discovered by Heinrich d'Arrest on September 23, 1864. The total infrared luminosity is 1011.05 L☉, and thus it is categorised as a luminous infrared galaxy. NGC 7679 is both a starburst galaxy and a Seyfert galaxy.

NGC 7172 is a spiral galaxy located in the constellation Piscis Austrinus. It is located at a distance of about 110 million light years from Earth, which, given its apparent dimensions, means that NGC 7172 is about 100,000 light years across. It was discovered by John Herschel on September 23, 1834.
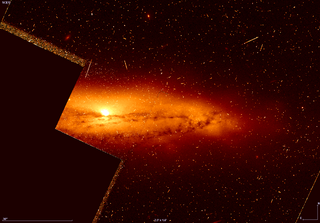
NGC 5506 is a spiral galaxy located in the constellation Virgo. It is located at a distance of about 75 million light years from Earth, which, given its apparent dimensions, means that NGC 5506 is about 80,000 light years across. It was discovered by William Herschel on April 15, 1787. It is a Seyfert galaxy.

NGC 4593 is a barred spiral galaxy located in the constellation Virgo. It is located at a distance of about 120 million light years from Earth, which, given its apparent dimensions, means that NGC 4593 is about 125,000 light years across. It was discovered by William Herschel on April 17, 1784. It is a Seyfert galaxy.

NGC 5953 is a peculiar spiral galaxy in the constellation Serpens. The galaxy lies about 80 million light years away from Earth, which means, given its apparent dimensions, that NGC 5953 is approximately 35,000 light years across. It was discovered by William Herschel on April 17, 1784. NGC 5953 interacts with NGC 5954 forming a pair known as Arp 91.





















