
Copepods are a group of small crustaceans found in nearly every freshwater and saltwater habitat. Some species are planktonic, some are benthic, a number of species have parasitic phases, and some continental species may live in limnoterrestrial habitats and other wet terrestrial places, such as swamps, under leaf fall in wet forests, bogs, springs, ephemeral ponds, puddles, damp moss, or water-filled recesses of plants (phytotelmata) such as bromeliads and pitcher plants. Many live underground in marine and freshwater caves, sinkholes, or stream beds. Copepods are sometimes used as biodiversity indicators.

Siphonostomatoida is an order of copepods, containing around 75% of all the copepods that parasitise fishes. Their success has been linked to their possession of siphon-like mandibles and of a "frontal filament" to aid attachment to their hosts. Most are marine, but a few live in fresh water. There are 40 recognised families:

Peristediidae, the armored sea robins or armoured gurnards, is a family of ray-finned fishes belonging to the suborder Platycephaloidei in the order Scorpaeniformes. They are found in the deep water in the tropical and warm temperate of the world's oceans.

The Japanese angelshark is a species of angelshark, family Squatinidae, found in the northwestern Pacific Ocean off China, Japan, and Korea. It is a bottom-dwelling shark found in sandy habitats down to 300 m (980 ft) deep. This species has the flattened shape with wing-like pectoral and pelvic fins typical of its family, and grows to 1.5 m (4.9 ft) or more in length. Its two dorsal fins are placed behind the pelvic fins, and a row of large thorns occurs along its dorsal midline. Its upper surface is cryptically patterned, with numerous squarish dark spots on a brown background.
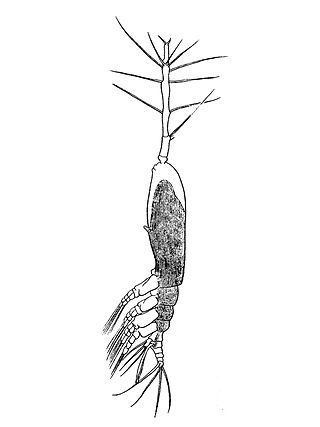
Monstrilloida is an order of copepods with a cosmopolitan distribution in the world's oceans. The order contains a single family, Monstrillidae. The name of the first ever described genus Monstrilla is derived from latin, meaning "tiny monster", because the lack of usual diagnostic features of copepods puzzled early taxonomists.

Pennellidae is a family of parasitic copepods. When anchored on a host, they have a portion of the body on the outside of the host, whereas the remaining anterior part of the parasite is hidden inside tissues of the host.

Lernaeocera branchialis, sometimes called cod worm, is a parasite of marine fish, found mainly in the North Atlantic. It is a marine copepod which starts life as a small pelagic crustacean larva. It is among the largest of copepods, ranging in size from 2 to 3 millimetres when it matures as a copepodid larva to more than 40 mm as a sessile adult.

Stephanolepis cirrhifer, commonly known as the thread-sail filefish, is a species of marine fish in the family Monacanthidae. It is found in the western Pacific, in an area that ranges from northern Japan to the East China Sea, to Korea. The fish grows to a maximum length of about 12 inches, and consumes both plant material and small marine organisms like skeleton shrimp. S. cirrhifer is host of the parasite Peniculus minuticaudae. Some minor genetic differentiation between S. cirrhifer born in the wild and those bred in a hatchery for consumer use has been shown. The fish is edible and sold commercially for culinary purposes in many Asian countries.

Lernaeopodidae is a family of parasitic copepods. The females are typically large and fleshy, and attach to the host permanently using a plug made of chitin called the bulla. The males cling on to the females using their antennae. They parasitize both marine and freshwater fish. Some lernaeopodids, including Clavella and Salmincola, can have negative impacts on fish in aquaculture.
Pennella is a genus of large copepods which are common parasites of large pelagic fishes. They begin their life cycle as a series of free-swimming planktonic larvae. The females metamorphose into a parasitic stage when they attach to a host and enter into its skin. The males are free swimming. Due to their large size and mesoparasitic life history there have been a number of studies of Pennella, the members of which are among the largest of the parasitic Copepoda. All species are found as adults buried into the flesh of marine bony fish, except for a single species, Pennella balaenopterae which can be found in the muscles and blubber of cetaceans and occasionally other marine mammals, and is the largest species of copepod.
Pennella balaenopterae is a large ectoparasitic copepod specialising in parasitising marine mammals. It is the largest member of the genus Pennella, the other species of which are parasites of larger marine fish.

Trimma is a genus of fish in the family Gobiidae native to the Indian and Pacific Ocean. Together with members of the genus Eviota, they are known commonly as pygmygobies or dwarfgobies.

Lethrinus nebulosus, the spangled emperor, green snapper, morwong, north-west snapper, sand bream, sand snapper, sixteen-pounder, sharie, sheri and yellow sweetlip, is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Lethrinidae, the emperors and emperor breams. This species is found the Indo-West Pacific region.

Peniculisa is a genus of marine parasitic copepods in the family Pennellidae.
Cardiodectes bellottii is a species of copepods in the family Pennellidae. It is a parasite of fish. It is found in the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans as well as the Mediterranean Sea; specimens from the Pacific were formerly treated as a separate species, Cardiodectes medusaeus.

Protosarcotretes is a genus of marine copepods in the family Pennellidae. Its type-species is Protosarcotretes nishikawai. This genus exhibits the most plesiomorphic states in the first to fourth legs of pennellids, and is differentiated from two closely related pennellid genera Sarcotretes and Lernaeenicus by the morphology of the oral appendages.

Peniculus is a genus of marine copepods in the family Pennellidae. They occur worldwide and typically parasitize coastal or epipelagic fish, with the exception of Peniculus hokutoae that was found parasitizing a mesopelagic myctophid, Symbolophorus evermanni.
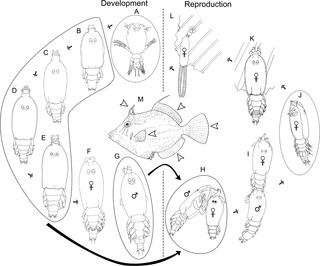
Peniculus minuticaudae is a species of parasitic pennellid copepod. It is known from the northeast Pacific Ocean. It was originally described in 1956, redescribed in 2012, and its complete life cycle has been elucidated on the cultured threadsail filefish, Stephanolepis cirrhifer in 2013.

Symbolophorus evermanni is a species of fish in the family Myctophidae. It is widely distributed in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. The specific name evermanni honors ichthyologist Barton Warren Evermann. It is also known as Evermann's lanternfish or Evermann's lantern fish.















