
Uncinia is a genus of flowering plants in the family Cyperaceae, known as hook-sedges in Australia and as hook grasses or bastard grasses in New Zealand. The genus is characterised by the presence of a long hook formed by an extension of the rachilla, which is used to attach the fruit to passing animals (epizoochory), especially birds, and it is this feature which gives the genus its name, from the Latin uncinus, meaning a hook or barb.
Carex acutata is a species of sedge, a flowering plant in the family Cyperaceae. It was first formally named by Francis Boott in 1846. Carex acutata is native to South America. In Bolivia it occurs at elevations of 3,500–4,000 m (11,500–13,100 ft).

Carex alligata, the Hawaiʻi sedge, is a species of sedge that is endemic to Hawaii.
Carex amicta is a species of sedge that was first formally named by Francis Boott in 1867. It is native to South America, from Venezuela to Peru.
Carex andersonii is a species of sedge that was first described by Francis Boott in 1846. It is native to Chile and Argentina.
Carex aperta, known as Columbian sedge, is a species of sedge that was first described by Francis Boott in 1839. It is native to eastern Russia, northern China, western Canada, and the northwestern United States. It grows in wet meadows, along shorelines, and in other wet habitats.

Carex arctata, known as drooping woodland sedge, is a species of sedge native to eastern North America. It is sometimes called black sedge, compressed sedge, or drooping wood sedge. It occurs from Manitoba to the Maritimes in Canada, south to northwestern North Carolina, and west to Minnesota. Carex arctata grows in bogs, hardwood forests, and spruce forests.

Carex banksii is a species of flowering plant in the sedge family, Cyperaceae. Carex banksii is native to South America and was first formally named by Francis Boott in 1839.
Carex barbata is a Tasmanian species of sedge that was first formally named by Francis Boott in 1858, in his Illustrations of the genus Carex. A specimen collected in February 1839 by R. C. Gunn is the only known collection of this species. In 1909, it was reclassified as a variety of Carex gunniana, but Kew's Plants of the World Online maintains it as a separate species.
Carex bichenoviana, the plains sedge, is a species of sedge that was first formally named by Francis Boott in 1858. It is native to eastern Australia and has been introduced to New Zealand. It has previously been considered a variety of Carex pumila.

Carex capillacea, common name yellowleaf sedge in Tasmania, is a species of sedge found in Assam, the far east of Russia, New Guinea, south east Australia, New Zealand, Malesia, China, Japan and India.
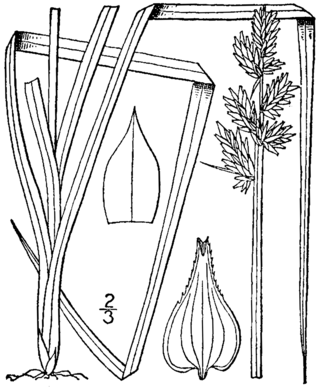
Carex conjuncta, known as soft fox sedge, is a species of sedge that was first formally named by Francis Boott in 1862. It is endemic to the central and eastern United States.
Carex gunniana is an Australia species of sedge that was first described in 1845 by Boott in the Proceedings of the Linnean Society of London. It is native to eastern Australia and Tasmania.

Carex lanceolata is a species of sedge, native to the eastern half of China, Mongolia, eastern Siberia, Korea, Sakhalin, and Japan. Its seeds are dispersed by ants.
Carex purdiei is a tussock-forming species of perennial sedge in the family Cyperaceae. It is native to southern parts of Central America and northern parts of South America.
Carex vicinalis is a species of sedge that was first described by Francis Boott in 1867. It is native to southern India. The type specimen was collected at the Nilghiri Hills.

Carex colchica is a species of perennial plant in the family Cyperaceae.
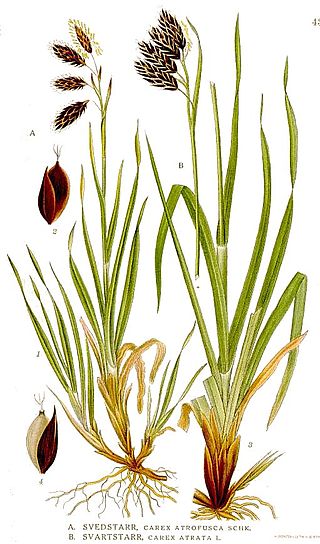
Carex atrata, called black alpine sedge, is a widespread species of flowering plant in the genus Carex, native to Greenland, Iceland, and most of Europe, plus scattered locations across temperate Asia, including Anatolia, Siberia and the Himalaya, as far as Taiwan and Japan. Its chromosome number is 2n=52, with some variants reported, e.g. n2=54 for Greenland material.

Carex breviculmis, called the Asian shortstem sedge, is a species of flowering plant in the genus Carex, native to Asia from the Indian subcontinent to Southeast Asia, China, Taiwan, Korea, Japan, north as far as Khabarovsk Krai, and Malesia, New Guinea, Australia, Norfolk Island and New Zealand. It has been introduced to the US state of Mississippi. Typically found in forests, it is quite shade tolerant.










