
Francis Boott was an American physician and botanist who was resident in Great Britain from 1820.

Carex rossii, commonly known as Ross's sedge, is a hardy species of sedge that is often a pioneer species in areas with little or no established vegetation, or in places where disturbance has occurred. Ross's sedge grows in a variety of habitats throughout much of western North America, from Alaska to Ontario, south to New Mexico and California. It flowers in May and June.

Carex archeri, known as Archer's sedge, is a species of sedge in the genus Carex, endemic to south-eastern Australia.

Carex alligata, the Hawaiʻi sedge, is a species of sedge that is endemic to Hawaii.
Carex amicta is a species of sedge that was first formally named by Francis Boott in 1867. It is native to South America, from Venezuela to Peru.
Carex andersonii is a species of sedge that was first described by Francis Boott in 1846. It is native to Chile and Argentina.
Carex aperta, known as Columbian sedge, is a species of sedge that was first described by Francis Boott in 1839. It is native to eastern Russia, northern China, western Canada, and the northwestern United States. It grows in wet meadows, along shorelines, and in other wet habitats.

Carex arctata, known as drooping woodland sedge, is a species of sedge native to eastern North America. It is sometimes called black sedge, compressed sedge, or drooping wood sedge. It occurs from Manitoba to the Maritimes in Canada, south to northwestern North Carolina, and west to Minnesota. Carex arctata grows in bogs, hardwood forests, and spruce forests.
Carex barbata is a Tasmanian species of sedge that was first formally named by Francis Boott in 1858, in his Illustrations of the genus Carex. A specimen collected in February 1839 by R. C. Gunn is the only known collection of this species. In 1909, it was reclassified as a variety of Carex gunniana, but Kew's Plants of the World Online maintains it as a separate species.
Carex bichenoviana, the plains sedge, is a species of sedge that was first formally named by Francis Boott in 1858. It is native to eastern Australia and has been introduced to New Zealand. It has previously been considered a variety of Carex pumila.
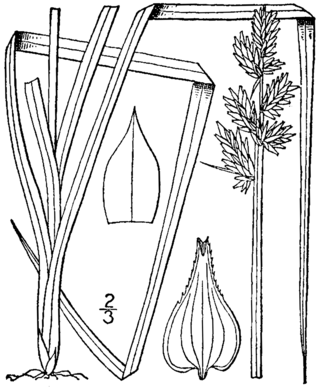
Carex conjuncta, known as soft fox sedge, is a species of sedge that was first formally named by Francis Boott in 1862. It is endemic to the central and eastern United States.
Carex gunniana is an Australia species of sedge that was first described in 1845 by Boott in the Proceedings of the Linnean Society of London. It is native to eastern Australia and Tasmania.
Carex hyalina, the tissue sedge, is a species of sedge that was first described by Francis Boott in 1847.

Carex lambertiana is a species of sedge that was first described by Francis Boott in 1853.

Carex senta, known as swamp carex, is a species of sedge that was first described by Francis Boott in 1867. It is found in western North America.

Carex solandri is a species of sedge that was first described by Francis Boott in 1853.
Carex vicinalis is a species of sedge that was first described by Francis Boott in 1867. It is native to southern India. The type specimen was collected at the Nilghiri Hills.
Carex wahlenbergiana is a species of sedge that was first described by Francis Boott in 1860.

Carex fascicularis, commonly known as tassel sedge, is a species of sedge of the family Cyperaceae that is native to Australia, New Zealand and New Guinea.









