
The Cyperaceae are a family of graminoid (grass-like), monocotyledonous flowering plants known as sedges. The family is large, with some 5,500 known species described in about 90 genera, the largest being the "true sedges" genus Carex with over 2,000 species.

Ornamental grasses are grasses grown as ornamental plants. Ornamental grasses are popular in many colder hardiness zones for their resilience to cold temperatures and aesthetic value throughout fall and winter seasons.

Carex is a vast genus of more than 2,000 species of grass-like plants in the family Cyperaceae, commonly known as sedges. Other members of the family Cyperaceae are also called sedges, however those of genus Carex may be called true sedges, and it is the most species-rich genus in the family. The study of Carex is known as caricology.
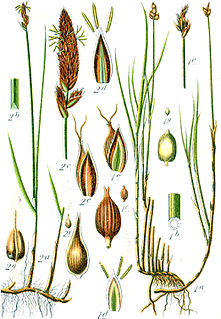
Carex chordorrhiza, commonly called creeping sedge or string sedge, is a species of perennial plant in the family Cyperaceae with Holarctic distribution growing in acidic bogs.

In botany, a perigynium, also referred to as a utricle, typically refers to a sac that surrounds the achene of plants in the genus Carex (Cyperaceae). The perigynium is a modified prophyll, tissue of leaf origin, that encloses the dry, one-seeded achene.

Carex siderosticta is a species of sedge native to East Asia. It is the only species of Carex known to produce "pseudo-lateral" culms, which appear to be lateral, but derive from the apical meristem. It is the type species of Carex subg. Siderosticta.

Carex tumulicola, the splitawn sedgefoothill sedge, or previously Berkeley sedge, is a sedge member of the family Cyperaceae.
Carex klamathensis is a rare species of sedge known by the common name Klamath sedge. It is known from 15 or fewer populations in southern Oregon and three populations in the Klamath Region of northern California. It was described to science only in 2007. Its habitat includes fens and other wet habitat, on serpentine soils. It was discovered independently by botanists Peter Zika and Lawrence Janeway.

Carex sect. Spirostachyae is a section of the genus Carex, containing 38 species of sedge. Species in Carex sect. Spirostachyae share a suite of features, including the short internodes of the primary rhizomes, the presence of an antiligule, the leaf-like, sheathing bract at the base of the inflorescence, the presence of three stigmas in female flowers, and the shape of the seeds.

Carex distans, commonly known as distant sedge, is a plant species in the sedge family, Cyperaceae. It is native to Europe and North Africa. It is part of a complex of similar species that occur across Eurasia. Its relatives include Carex diluta of central Asia, which has also introduced to North America in Montana. Carex distans has been introduced to the US states including Maryland and Pennsylvania. More recently, it was found in Oregon. There is a report from Victoria, Australia as well.
Carex aboriginum is a species of sedge endemic to Idaho in the western United States, known as Indian Valley sedge. It was not observed in the wild between 1910, when it was first described, and 1999. Until its rediscovery, C. aboriginum was considered the only plant native to Idaho to have become extinct, and it remains one of the state's rarest and most endangered plant species.

Carex subg. Carex is a subgenus of the sedge genus Carex. It is the largest of the four traditionally recognised subgenera, containing around 1400 of the 2000 species in the genus. Its members are characterised by the presence of one or more exclusively male (staminate) terminal spikes, quite dissimilar in appearance from the lateral female (pistillate) spikes below. In most species, the female flowers have three stigmas, but a few species, including Carex nigra, have female flowers with only two stigmas.
Carex lemmonii, or Lemmon's sedge, is a plant in the sedge family, and is endemic to California. Carex albida is now considered a synonym, but was previously thought to be a separate species; such plants have the common name white sedge.

Carex subg. Vignea is a subgenus of the sedge genus Carex, containing around 300 of the 2000 species in the genus. Its members are characterised by having bisexual, sessile spikes, where the female flowers have two stigmas each.

Carex kobomugi is a species of sedge, known as the Japanese sedge or Asiatic sand sedge, that lives in sandy coastal areas of eastern Asia, and has become an invasive species in the north-eastern United States.

Carex sect. Macrocephalae is a section of the genus Carex, containing two species. Both are coastal species of sandy areas beside the northern Pacific Ocean – Carex kobomugi from Taiwan to northern China and Japan, and Carex macrocephala from northern China to Oregon.

Carex viridula, known as little green sedge, green sedge, or greenish sedge, is a small flowering plant native to North America, Europe, Asia, and Morocco.
Carex arctogena is a member of the sedge family (Cyperaceae) which grows in high alpine areas. It is one of the few "bipolar" species; it has populations in Greenland, Scandinavia, Russia, Canada and southern South America. Plants in the far north and south appear to be genetically identical, having taken advantage of a similar niches on opposite ends of the globe.
Peter William Ball is an English-born botanist, plant collector, and plant taxonomist, specializing in caricology.

Carex remota, the remote sedge, is a species in the genus Carex, native to Europe, the Atlas Mountains in Africa, and western Asia. It is a riparian forest specialist. It is known as one of the most frequently hybridizing species of Carex, forming hybrids with C. appropinquata, C. arenaria, C. brizoides, C. canescens, C. divulsa, C. echinata, C. elongata, C. leporina, C. otrubae, C. paniculata, and C. spicata.













