
Fucus vesiculosus, known by the common names bladder wrack, black tang, rockweed, bladder fucus, sea oak, cut weed, dyers fucus, red fucus, and rock wrack is a seaweed found on the coasts of the North Sea, the western Baltic Sea, and the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans. It was the original source of iodine, discovered in 1811 and was used extensively to treat goitre, a swelling of the thyroid gland related to iodine deficiency.

Ascophyllum nodosum is a large, common cold water seaweed or brown alga (Phaeophyceae) in the family Fucaceae, being the only species in the genus Ascophyllum. It is a seaweed that only grows in the northern Atlantic Ocean, also known in localities as feamainn bhuí, rockweed, Norwegian kelp, knotted kelp, knotted wrack or egg wrack. It is common on the north-western coast of Europe including east Greenland and the north-eastern coast of North America, its range further south of these latitudes being limited by warmer ocean waters.

Pelvetia canaliculata, the channelled wrack, is a very common brown alga (Phaeophyceae) found on the rocks of the upper shores of Europe. It is the only species remaining in the monotypic genus Pelvetia. In 1999, the other members of this genus were reclassified as Silvetia due to differences of oogonium structure and of nucleic acid sequences of the rDNA.
The brown topknot, Notoclinus compressus, is a triplefin of the family Tripterygiidae, endemic to New Zealand in rock pools and from low water to depths of about 5 m, in reef areas of broken rock and large brown seaweed of genera Carpophyllum and Cystophora. Its length is up to about 8.5 cm.

Durvillaea is a genus of brown algae in the monotypic family Durvillaeaceae. All members of the genus are found in the southern hemisphere, including Australia, New Zealand, South America, and various subantarctic islands.

Durvillaea antarctica, also known as cochayuyo and rimurapa, is a large, robust species of southern bull kelp found on the coasts of Chile, southern New Zealand, and Macquarie Island. D. antarctica, an alga, does not have air bladders, but floats due to a unique honeycomb structure within the alga's blades, which also helps the kelp avoid being damaged by the strong waves.
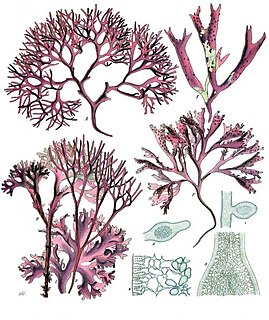
Red algae, or Rhodophyta, are one of the oldest groups of eukaryotic algae. The Rhodophyta also comprises one of the largest phyla of algae, containing over 7,000 currently recognized species with taxonomic revisions ongoing. The majority of species (6,793) are found in the Florideophyceae (class), and mostly consist of multicellular, marine algae, including many notable seaweeds. Red algae are abundant in marine habitats but are relatively rare in freshwaters. Approximately 5% of the red algae occur in freshwater environments with greater concentrations found in warmer areas. Except for two coastal cave dwelling species in the asexual class Cyanidiophyceae, there are no terrestrial species, which may be due to an evolutionary bottleneck where the last common ancestor lost about 25% of its core genes and much of its evolutionary plasticity.

Phlorotannins are a type of tannins found in brown algae such as kelps and rockweeds or sargassacean species, and in a lower amount also in some red algae. Contrary to hydrolysable or condensed tannins, these compounds are oligomers of phloroglucinol (polyphloroglucinols). As they are called tannins, they have the ability to precipitate proteins. It has been noticed that some phlorotannins have the ability to oxidize and form covalent bonds with some proteins. In contrast, under similar experimental conditions three types of terrestrial tannins apparently did not form covalent complexes with proteins.

Apophlaea is a genus of thalloid algae that is endemic to New Zealand. This genus has two species, both from the high intertidal zone on New Zealand's coasts. Specimens can reach around 15 cm in size. The thalli take a crustose form, but also contain upright, branching frond-like protrusions that reach 5–8 cm in height. Secondary pit connections and secondary pit connectionsare present in the organisms. Apophlaea reproduces by means of conceptacles; it produces tetraspores.
The epithallium or epithallus is the outer layer of a crustose coralline alga, which in some species is periodically shed to prevent organisms from attaching to and overgrowing the alga.

Codium fragile, known commonly as green sea fingers, dead man's fingers, felty fingers, forked felt-alga, stag seaweed, sponge seaweed, green sponge, green fleece, and oyster thief, is a species of seaweed in the family Codiaceae. It originates in the Pacific Ocean near Japan and has become an invasive species on the coasts of the Northern Atlantic Ocean.

Fucus gardneri is a species of seaweed, a brown alga living on the littoral shore of the Pacific coasts of North America. It has the common names of rockweed and bladderwrack.

Fucus radicans is a species of brown algae in the family Fucaceae, endemic to and recently evolved within the Baltic Sea. The species was first described by Lena Bergström and Lena Kautsky in 2005 from a location in Ångermanland, Sweden. The specific epithet is from the Latin and means "rooting", referring to the fact that this species primarily reproduces by the taking root of detached fragments.
Stypopodium zonale is a species of thalloid brown alga in the family Dictyotaceae. It is found in shallow waters in the Caribbean Sea and in various other tropical and sub-tropical seas around the world.
Lobophora variegata is a species of small thalloid brown alga which grows intertidally or in shallow water in tropical and warm temperate seas. It has three basic forms, being sometimes ruffled, sometimes reclining and sometimes encrusting, and each form is typically found in a different habitat. This seaweed occurs worldwide. It is the type species of the genus Lobophora, the type locality being the Antilles in the West Indies.

Spongites yendoi is a species of crustose red seaweed with a hard, calcareous skeleton in the family Corallinaceae. It is found on the lower shore as part of a diverse community in the southeastern Atlantic Ocean and the Indo-Pacific Ocean.

Ulvaria obscura is an intertidal and subtidal benthic marine algae found in temperate and Arctic ocean waters around the world.

Laminaria sinclairii is a species of brown algae, in the family Laminariaceae. It is native to the lower intertidal zone of the northeastern Pacific Ocean from British Columbia southwards to California.

Durvillaea poha is a large, robust species of southern bull kelp found in New Zealand.

Champia laingii is a marine red algal species endemic to New Zealand.
















