
Sandalwood is a class of woods from trees in the genus Santalum. The woods are heavy, yellow, and fine-grained, and, unlike many other aromatic woods, they retain their fragrance for decades. Sandalwood oil is extracted from the woods for use. Sandalwood is the second-most expensive wood in the world, after African blackwood. Both the wood and the oil produce a distinctive fragrance that has been highly valued for centuries. Consequently, species of these slow-growing trees have suffered overharvesting in past centuries.

Santalum acuminatum, the Desert Quandong, is a hemiparasitic plant in the sandalwood family, Santalaceae, which is widely dispersed throughout the central deserts and southern areas of Australia. The species, especially its Edible fruit, is also commonly referred to as Quandong or Native Peach. The use of the fruit as an exotic flavouring, one of the best known Bush tucker, has led to the attempted domestication of the species.

Acacia acuminata, known as mangart and jam, is a tree in the family Fabaceae. Endemic to Western Australia, it occurs throughout the south west of the State. It is common in the Wheatbelt, and also extends into the semi-arid interior.

Acer spicatum, also known as dwarf maple, moose maple, and white maple, is a species of maple native to northeastern North America from Saskatchewan to Newfoundland, and south to Pennsylvania. It also grows at high elevations in the southern Appalachian Mountains to northern Georgia.

Santalum spicatum, the Australian sandalwood, is a tree native to semiarid areas at the edge of Southwest Australia. It is traded as sandalwood, and its valuable oil has been used as an aromatic, a medicine, and a food source. S. spicatum is one of four high-value Santalum species occurring in Australia.
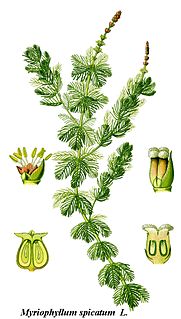
Myriophyllum spicatum is native to Europe, Asia, and north Africa, but has a wide geographic and climatic distribution among some 57 countries, extending from northern Canada to South Africa. It is a submerged aquatic plant, grows in still or slow-moving water, and is considered to be a highly invasive species.

Santalum album, or Indian sandalwood, is a small tropical tree, and is the most commonly known source of sandalwood. It is native to southern India and Southeast Asia. Certain cultures place great significance on its fragrant and medicinal qualities. It is also considered sacred in some religions and is used in different religious traditions. The high value of the species has caused its past exploitation, to the point where the wild population is vulnerable to extinction. Indian sandalwood still commands high prices for its essential oil, but due to lack of sizable trees it is no longer used for fine woodworking as before. The plant is widely cultivated and long lived, although harvest is only viable after many years. Etymologically it is derived from Sanskrit चन्दनं chandanam.

Philotheca spicata, commonly known as pepper and salt, is a species of flowering plant in the family Rutaceae and is endemic to the south-west of Western Australia. It is a small shrub with linear to narrow elliptical leaves and pink, mauve or blue flowers arranged in a raceme on the ends of branchlets.

Schenkia australis is a species of annual herb in the Gentianaceae family. It is endemic to Australia.

Pterocaulon is a genus of flowering plants in the sunflower family, native to North and South America and to Australasia. Blackroot is a common name for species native to North America.

Blancoa is a monotypic genus of perennial herbs in the family Haemodoraceae; the single species is Blancoa canescens, commonly known as the winter bell. It is endemic to the southwestern corner of Western Australia. It has nodding red to pink flowers, a clumping habit and grows to be 10 to 40 cm in height. The genus is named in honour of Francisco Manuel Blanco, a Spanish friar and botanist who compiled the first comprehensive flora of the Philippines.

In general use, herbs are plants with savory or aromatic properties that are used for flavoring and garnishing food, for medicinal purposes, or for fragrances; excluding vegetables and other plants consumed for macronutrients. Culinary use typically distinguishes herbs from spices. Herbs generally refers to the leafy green or flowering parts of a plant, while spices are usually dried and produced from other parts of the plant, including seeds, bark, roots and fruits.

Haemodorum is a genus of herbs in the family Haemodoraceae, first described as a genus in 1798. It is native to New Guinea and Australia. The type species is Haemodorum corymbosum Vahl.
Grevillea parallelinervis is a shrub of the genus Grevillea native to South Australia.

Conospermum huegelii, commonly known as the slender smokebush, is a plant endemic to Western Australia.
Stirlingia seselifolia is a herb or shrub endemic to Western Australia.
Stirlingia tenuifolia is a herb or shrub endemic to Western Australia.
Cartonema parviflorum, commonly known in wiridjagu, is a herb in the Commelinaceae family.

Cartonema philydroides is a herb in the Commelinaceae family.
Prasophyllum spicatum, commonly known as the dense leek orchid, is a species of orchid endemic to southern mainland Australia. It has a single tubular, green leaf and up to fifty brownish and white or greenish and white flowers crowded in a cylinder-shaped spike.















