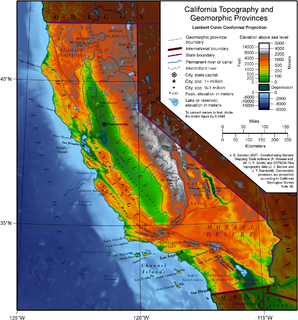
California is a U.S. state on the western coast of North America. Covering an area of 163,696 sq mi (423,970 km2), California is among the most geographically diverse states. The Sierra Nevada, the fertile farmlands of the Central Valley, and the arid Mojave Desert of the south are some of the major geographic features of this U.S. state. It is home to some of the world's most exceptional trees: the tallest, most massive, and oldest. It is also home to both the highest and lowest points in the 48 contiguous states. The state is generally divided into Northern and Southern California, although the boundary between the two is not well defined. San Francisco is decidedly a Northern California city and Los Angeles likewise a Southern California one, but areas in between do not often share their confidence in geographic identity. The US Geological Survey defines the geographic center of the state at a point near North Fork, California.
Interstate 15 (I-15) is a major Interstate Highway in the western United States, running through Southern California and the Intermountain West. I-15 begins near the Mexico–US border in San Diego County and stretches north to Alberta, Canada, passing through the states of California, Nevada, Arizona, Utah, Idaho, and Montana. The Interstate serves the cities of San Diego, San Bernardino, Las Vegas, St. George, Provo, Salt Lake City, Ogden, Pocatello, Idaho Falls, Butte, Helena, and Great Falls. It also passes close to the urban areas of Orange County and Los Angeles County, California. The stretches of I-15 in Idaho, Utah, and Arizona have been designated as the "Veterans Memorial Highway". The southern end is at a junction with I-8 and State Route 15 in San Diego, and the northern end is at a connection with Alberta Highway 4 at the Sweetgrass–Coutts Border Crossing.

The southwestern United States, also known as the American Southwest or simply the Southwest, is a geographic and cultural region of the United States that generally includes Arizona, New Mexico, and adjacent portions of California, Colorado, Nevada, Oklahoma, Texas, and Utah. The largest cities by metropolitan area are Phoenix, Las Vegas, El Paso, Albuquerque, and Tucson. Prior to 1848, in the historical region of Santa Fe de Nuevo México as well as parts of Alta California and Coahuila y Tejas, settlement was almost non-existent outside of Nuevo México's Pueblos and Spanish or Mexican municipalities. Much of area had been a part of New Spain and Mexico until the United States acquired the area through the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo in 1848 and the smaller Gadsden Purchase in 1854.

The Western United States is the region comprising the westernmost states of the United States. As American settlement in the U.S. expanded westward, the meaning of the term the West changed. Before about 1800, the crest of the Appalachian Mountains was seen as the western frontier. The frontier moved westward and eventually the lands west of the Mississippi River were considered the West.

The Mohave Valley is a valley located mostly on the east shore of the south-flowing Colorado River in northwest Arizona. The valley extends into California's San Bernardino County; the northern side of the valley extends into extreme southeast Clark County, Nevada. The main part of the valley lies in southwest Mohave County, Arizona and is at the intersection of the southeast Mojave and northwest Sonoran deserts.
The Pacific Coast Theater of the American Civil War consists of major military operations in the United States on the Pacific Ocean and in the states and Territories west of the Continental Divide. The theater was encompassed by the Department of the Pacific that included the states of California, Oregon, and Nevada, the territories of Washington, Utah, and later Idaho.

Muhlenbergia is a genus of plants in the grass family.

The Lower Colorado River Valley (LCRV) is the river region of the lower Colorado River of the southwestern United States in North America that rises in the Rocky Mountains and has its outlet at the Colorado River Delta in the northern Gulf of California in northwestern Mexico, between the states of Baja California and Sonora. This north–south stretch of the Colorado River forms the border between the U.S. states of California/Arizona and Nevada/Arizona, and between the Mexican states of Baja California/Sonora.

The Deserts of California have unique ecosystems and habitats, a sociocultural and historical "Old West" collection of legends, districts, and communities, and they also form a popular tourism region of dramatic natural features and recreational development. All of the deserts are located in eastern Southern California, in the Western United States.

Catocala chelidonia is a moth of the family Erebidae. It is found from Arizona and Utah to California.

Catocala andromache, the Andromache underwing, is a moth of the family Erebidae. The species was first described by Henry Edwards in 1885. It is found in the United States from southern California to Arizona.
Monardella linoides is a species of flowering plant in the mint family known by the common name flaxleaf monardella.

Nemacladus is a genus of flowering plants in the bellflower family known generally as threadplants. There are 18 accepted species native to the southwestern United States and northern Mexico. These are annual herbs with very slender, sometimes threadlike, branching stems bearing small five-lobed flowers.

The Arizona transition zone is a diagonal northwest-by-southeast region across central Arizona. The region is a transition from the higher elevation Colorado Plateau to the northeast in Northeast Arizona and the Basin and Range region of southwest and south regions of lower elevation deserts.

The Piute Wash of extreme southeastern Nevada and northeast San Bernardino County California is the south-flowing drainage of the Piute Valley. The wash and valley are located northwest of Needles, California.

The Mountain States form one of the nine geographic divisions of the United States that are officially recognized by the United States Census Bureau. It is a subregion of the Western United States.
Mormon Road, also known to the 49ers as the Southern Route, of the California Trail, was a seasonal wagon road first pioneered by a Mormon party from Salt Lake City, Utah led by Jefferson Hunt, that followed the route of Spanish explorers and the Old Spanish Trail across southwestern Utah, northwestern Arizona, southern Nevada and the Mojave Desert of California to Los Angeles in 1847. From 1855, it became a military and commercial wagon route between California and Utah, called the Los Angeles - Salt Lake Road. In later decades this route was variously called the "Old Mormon Road", the "Old Southern Road", or the "Immigrant Road" in California. In Utah, Arizona and Nevada it was known as the "California Road".
















