
The red underwing is a moth of the family Erebidae. The species was first described by Carl Linnaeus in his 1767 12th edition of Systema Naturae.

Catocala is a generally Holarctic genus of moths in the family Erebidae. The genus was erected by Franz von Paula Schrank in 1802. The moths are commonly known as underwing moths or simply underwings. These terms are sometimes used for a few related moths, but usually – especially when used in plural, not as part of a species name – they are used to refer to Catocala only.

Catocala fulminea, the yellow bands underwing, is a moth of the family Erebidae. The species was first described by Giovanni Antonio Scopoli in his 1763 Entomologia Carniolica. It is found in central and southern Europe, east Asia and Siberia. The xarippe lineage has been proposed to be a distinct and valid species in its own right, instead of being only subspecifically distinct.

Catocala electa, the rosy underwing, is a moth of the family Erebidae. The species was first described by Karl Friedrich Vieweg in 1790. It can be found in Europe and Asia.

Catocala promissa, the light crimson underwing, is a moth of the family Erebidae. The species was first described by Michael Denis and Ignaz Schiffermüller in 1775. It can be found in Europe and Anatolia up to Armenia.

Catocala nymphaea is a species of moth of the family Erebidae. It was described by Eugenius Johann Christoph Esper in 1787. It is found in southern France, Austria, Albania, Portugal, Croatia, Italy, Greece, Corsica, Sicily, Crete, North Africa, Anatolia, Afghanistan and Kashmir.

Catocala nymphagoga, the oak yellow underwing, is a moth of the family Erebidae. It is found in Southern Europe, from Bulgaria up to the Iberian Peninsula and sometimes further north as a migrant. It is also found in North Africa and Asia Minor.

Catocala relicta, the white underwing or relict, is a moth of the family Erebidae. The species was first described by Francis Walker in 1858. It lives in southern Canada, from Newfoundland to Vancouver Island, south to Missouri, and Arizona.

Catocala obscura, the obscure underwing, is a moth of the family Erebidae. The species was first described by Ferdinand Heinrich Hermann Strecker in 1873. In Canada it is found in southern Quebec and Ontario and in the United States it is found from Massachusetts and Connecticut south to North Carolina, west to Mississippi and north to Iowa, Illinois, Ohio, and Michigan.
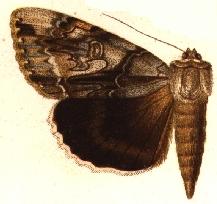
Catocala vidua, the widow underwing, is a moth of the family Erebidae. The species was first described by James Edward Smith in 1797. It is found in North America from southern Ontario, into Maine, New Hampshire and Connecticut, south at least to Tennessee, Georgia and Alabama, west to Texas and Oklahoma, and north to Wisconsin.

Catocala leechi is a moth of the family Erebidae first described by George Hampson in 1913. It is found in Kashmir.

Catocala szechuena is a moth of the family Erebidae first described by George Hampson in 1913. It is found in western China.

Catocala fuscinupta is a moth of the family Erebidae first described by George Hampson in 1913. It is found in Himachal Pradesh, India.

Catocala persimilis is a moth of the family Erebidae first described by Warren in 1888. It is found in western India.

Catocala musmi is a moth of the family Erebidae first described by George Hampson in 1913. It is found in China and Korea.

Catocala sordida, the sordid underwing, is a moth of the family Erebidae. The species was first described by Augustus Radcliffe Grote in 1877. It is found in North America from Saskatchewan east to New Brunswick and Prince Edward Island and south through Maine and Connecticut to Florida, west to Texas and north to Manitoba.

Ocneria detrita is a moth of the subfamily Lymantriinae. The species was first described by Eugenius Johann Christoph Esper in 1785. It is found in France, Italy and parts of central, south-east and eastern Europe.
Catocala fugitiva is a moth in the family Erebidae first described by Warren in 1914. It is found in Kazakhstan.

Catocala lupina is a moth in the family Erebidae first described by Gottlieb August Wilhelm Herrich-Schäffer in 1851. It is found from south-eastern Europe to south-western Siberia, Asia Minor and Transcaucasia.
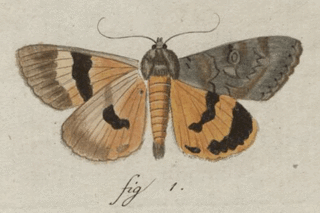
Catocala neonympha is a moth in the family Erebidae first described by Arthur Gardiner Butler in 1877. It is found in south-western Russia, Ukraine, Kazakhstan, eastern Turkey, Iraq, Armenia, Kurdistan, Afghanistan, the Altai Mountains and southern Siberia.












