
Serena Jameka Williams is an American former professional tennis player. Widely regarded as one of the greatest tennis players of all time, she was ranked world No. 1 in singles by the Women's Tennis Association (WTA) for 319 weeks, including a joint-record 186 consecutive weeks, and finished as the year-end No. 1 five times. She won 23 Grand Slam women's singles titles, the most in the Open Era, and the second-most of all time. She is the only player to accomplish a career Golden Slam in both singles and doubles.

Catocala is a generally Holarctic genus of moths in the family Erebidae. The genus was erected by Franz von Paula Schrank in 1802. The moths are commonly known as underwing moths or simply underwings. These terms are sometimes used for a few related moths, but usually – especially when used in plural, not as part of a species name – they are used to refer to Catocala only.

Catocala cerogama, the yellow-banded underwing, is a moth of the tribe Catocalini that occurs in North America. The species was first described by Achille Guenée in 1852.

Catocala adultera is a moth in the family Erebidae first described by Édouard Ménétries in 1856. It is found in northern Europe, from Siberia to the Russian Far East and Mongolia.

Catocala cara, the darling underwing, is an moth of the family Erebidae. The species was first described by Achille Guenée in 1852. It can be found in the United States east of the Rocky Mountains; it occurs west at least to Oklahoma and north at least to Illinois. It also ranges into southern Canada, but only barely so.

Catocala retecta, the yellow-gray underwing, is a moth of the family Erebidae. The species was first described by Augustus Radcliffe Grote in 1872. It can be found in North America from southern Ontario and Quebec south through Maine and New Jersey, south through Tennessee to Georgia and west to Arkansas and Kansas and north to Wisconsin. There is one recognised subspecies, Catocala retecta luctuosa, which is sometimes treated as a valid species with the common name yellow-fringed underwing.

Catocala meskei, or Meske's underwing, is a moth of the family Erebidae. The species was first described by Augustus Radcliffe Grote in 1873. It is found in North America from Maine and Quebec west to southern Alberta and Montana, south to South Carolina in the east and at least Montana in the west.

Catocala whitneyi, or Whitney's underwing, is a moth of the family Erebidae. The species was first described by G. M. Dodge in 1874. It is found in North America from North Dakota, Nebraska, and Kansas eastward through Wisconsin to Ohio and Tennessee. It has also been recorded as far west as Minnesota and Utah. In Canada, it has been found in Manitoba.

Catocala junctura, the joined underwing or Stretch's underwing, is a moth in the family Erebidae. The species was first described by Francis Walker in 1858. It is found throughout temperate North America, ranging from New York and Pennsylvania west to Montana, Colorado, Oklahoma, Arizona, and into Texas, and north to southern Illinois, extreme southern Alberta and Saskatchewan; it has also been recorded west of the Rocky Mountains from California and south-eastern British Columbia. It is typically found near water, where the food plants of its caterpillar larvae grow plentifully.

Catocala luciana, the shining underwing, is a moth of the family Erebidae. The species was first described by Herman Strecker in 1874. It is found in western North America, as far east as Minnesota and Illinois and northward into extreme southern Alberta and Saskatchewan. It occurs widely across the Great Plains, south to New Mexico, Arizona and California.
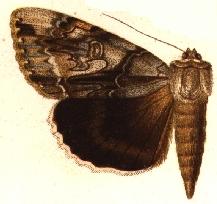
Catocala vidua, the widow underwing, is a moth of the family Erebidae. The species was first described by James Edward Smith in 1797. It is found in North America from southern Ontario, into Maine, New Hampshire and Connecticut, south at least to Tennessee, Georgia and Alabama, west to Texas and Oklahoma, and north to Wisconsin.

Catocala maestosa, commonly known as the sad underwing, is a species of moth in the family Erebidae. The species was first described by George Duryea Hulst in 1884. It is found in the United States from New York south to Florida and Alabama, west to Texas and eastern Oklahoma and north to Illinois, Indiana and Minnesota.

Catocala chelidonia is a moth of the family Erebidae. It is found from Arizona and Utah to California.

Catocala pretiosa, the precious underwing, is a moth of the family Erebidae. The species was first described by Joseph Albert Lintner in 1876. It was included in Catocala crataegi by many authors, but recently it has been revalidated as a distinct species. The subspecies of pretiosa is listed as a species of special concern and believed extirpated in the US state of Connecticut.

Catocala minuta, the little underwing, is a moth of the family Erebidae. The species was first described by William Henry Edwards in 1864. It is found in the US from New York to Florida and west to Texas and north to South Dakota, Indiana and Michigan.

Catocala louiseae, or Louise's underwing, is a moth of the family Erebidae. The species is endemic to the United States. The epithet, louiseae, is in honor of "the late Louise Mellon" who funded the Carnegie Museum of Natural History expedition on which the type specimen was collected. The species was first described by John Bauer in 1965.

Catocala orba, the Orba underwing, is a moth of the family Erebidae. The species was first described by Nikolai Yakovlevich Kuznetsov in 1903. It is found from Massachusetts south to Georgia and Florida, west to Texas, and as far north as Mississippi.

Catocala sordida, the sordid underwing, is a moth of the family Erebidae. The species was first described by Augustus Radcliffe Grote in 1877. It is found in North America from Saskatchewan east to New Brunswick and Prince Edward Island and south through Maine and Connecticut to Florida, west to Texas and north to Manitoba.

Ichiran Ramen is a Japanese ramen food-service business specializing in tonkotsu ramen. The chain restaurant began in Fukuoka in 1960 as a ramen stall named "Futaba Ramen" (屋台双葉ラーメン). It was later renamed "Ichiran" in 1966. After three decades of serving ramen from a single location, under the leadership of CEO Manabu Yoshitomi it opened its first concept store in 1993, which became the blueprint for all future Ichiran ramen shop locations.
















