
Peritonitis is inflammation of the localized or generalized peritoneum, the lining of the inner wall of the abdomen and cover of the abdominal organs. Symptoms may include severe pain, swelling of the abdomen, fever, or weight loss. One part or the entire abdomen may be tender. Complications may include shock and acute respiratory distress syndrome.

Enterococcus is a large genus of lactic acid bacteria of the phylum Bacillota. Enterococci are gram-positive cocci that often occur in pairs (diplococci) or short chains, and are difficult to distinguish from streptococci on physical characteristics alone. Two species are common commensal organisms in the intestines of humans: E. faecalis (90–95%) and E. faecium (5–10%). Rare clusters of infections occur with other species, including E. casseliflavus, E. gallinarum, and E. raffinosus.
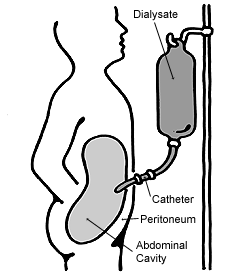
Peritoneal dialysis (PD) is a type of dialysis that uses the peritoneum in a person's abdomen as the membrane through which fluid and dissolved substances are exchanged with the blood. It is used to remove excess fluid, correct electrolyte problems, and remove toxins in those with kidney failure. Peritoneal dialysis has better outcomes than hemodialysis during the first couple of years. Other benefits include greater flexibility and better tolerability in those with significant heart disease.

Caulobacter crescentus is a Gram-negative, oligotrophic bacterium widely distributed in fresh water lakes and streams. The taxon is more properly known as Caulobacter vibrioides.
Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (SBP) is the development of a bacterial infection in the peritoneum, despite the absence of an obvious source for the infection. It is specifically an infection of the ascitic fluid – an increased volume of peritoneal fluid. Ascites is most commonly a complication of cirrhosis of the liver. It can also occur in patients with nephrotic syndrome. SBP has a high mortality rate.

Waxworms are the caterpillar larvae of wax moths, which belong to the family Pyralidae. Two closely related species are commercially bred – the lesser wax moth and the greater wax moth. They belong to the tribe Galleriini in the snout moth subfamily Galleriinae. Another species whose larvae share that name is the Indian mealmoth, though this species is not available commercially.

Alcaligenes is a genus of Gram-negative, aerobic, rod-shaped bacteria in the order of Burkholderiales.
Pseudomonas oryzihabitans is a nonfermenting yellow-pigmented, gram-negative, rod-shaped bacterium that can cause sepsis, peritonitis, endophthalmitis, and bacteremia. It is an opportunistic pathogen of humans and warm-blooded animals that is commonly found in several environmental sources, from soil to rice paddies. They can be distinguished from other nonfermenters by their negative oxidase reaction and aerobic character. This organism can infect individuals that have major illnesses, including those undergoing surgery or with catheters in their body. Based on the 16S RNA analysis, these bacteria have been placed in the Pseudomonas putida group.
Pseudomonas infection refers to a disease caused by one of the species of the genus Pseudomonas.
Streptococcus equinus is a Gram-positive, nonhemolytic, nonpathogenic, lactic acid bacterium of the genus Streptococcus. It is the principal Streptococcus found in the alimentary canal of a horse, and makes up the majority of the bacterial flora in horse feces. Equivalence with Streptococcus bovis has been contested.
Rothia dentocariosa is a species of Gram-positive, round- to rod-shaped bacteria that is part of the normal community of microbes residing in the mouth and respiratory tract.
Pasteurella canis is a Gram-negative, nonmotile, penicillin-sensitive coccobacillus of the family Pasteurellaceae. Bacteria from this family cause zoonotic infections in humans, which manifest themselves as skin or soft-tissue infections after an animal bite. It has been known to cause serious disease in immunocompromised patients.

Achromobacter xylosoxidans is a Gram-negative, aerobic, oxidase and catalase-positive, motile bacterium with peritrichous flagella, from the genus Achromobacter. It is generally found in wet environments. Achromobacter xylosoxidans can cause infections such as bacteremia, especially in patients with cystic fibrosis. In 2013, the complete genome of an A. xylosoxidans strain from a patient with cystic fibrosis was sequenced.
Paecilomyces variotii, also known by the name Byssochlamys spectabilis for the sexual state, is a common environmental mold from the Phylum Ascomycota. It is widespread in the environment and can be found in composts, soils and wood, as well es a common environmental contaminant in indoor air and carpet dust. Ascospores of the sexual state of P. variotii are strongly heat-resistant. As such the fungus is a common contaminant of heat-treated foods and juices. Paecilomyces variotii has been associated with a number of infective diseases of humans and animals.
Phialemonium curvatum is a pathogenic fungus in the phylum Ascomycota. The genus was created to accommodate taxa intermediate to Acremonium and Phialophora. This genus is characterized by its abundance of adelophialides and few discrete phialides with no signs of collarettes. Specifically, P. curvatum is characterized by its grayish white colonies and its allantoid conidia. Phialemonium curvatum is typically found in a variety of environments including air, soil, industrial water and sewage. Furthermore, P. curvatum affects mainly immunocompromised and is rarely seen in immunocompetent people. The species has been known to cause peritonitis, endocarditis, endovascular infections, osteomyelitis as well as cutaneous infections of wounds and burns.
Citrobacter youngae is a Gram-negative species of bacteria.
Citrobacter braakii is a Gram-negative species of bacteria. It has been reported to cause sepsis in an immunocompromised person.
Neisseria weaveri is a gram-negative bacterium associated with dog bite wounds. It is rod-shaped and non-motile with type strain M-5.
Curvularia inaequalis is a plant saprobe that resides in temperate and subtropical environments. It is commonly found in the soils of forage grasses and grains. The species has been observed in a broad distribution of countries including Turkey, France, Canada, The United States, Japan and India. This species is dematiaceous and a hyphomycete.
Encapsulating peritoneal sclerosis(EPS) is a chronic clinical syndrome with an insidious onset that manifests as chronic undernourishment accompanied by sporadic, acute, or subacute gastrointestinal obstruction symptoms. Peritoneal dialysis is most commonly linked to encapsulating peritoneal sclerosis, especially when peritoneal dialysis is stopped. The diagnosis is verified by macroscopic and/or radiological observations of intestinal encapsulation, calcification, thickening of the peritoneum, or sclerosis.









