The Triassic is a geologic period and system which spans 50.6 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.36 Mya. The Triassic is the first and shortest period of the Mesozoic Era. Both the start and end of the period are marked by major extinction events. The Triassic Period is subdivided into three epochs: Early Triassic, Middle Triassic and Late Triassic.

The Early Triassic is the first of three epochs of the Triassic Period of the geologic timescale. It spans the time between 251.902 Ma and 247.2 Ma. Rocks from this epoch are collectively known as the Lower Triassic series, which is a unit in chronostratigraphy.

In the geologic timescale, the Olenekian is an age in the Early Triassic epoch; in chronostratigraphy, it is a stage in the Lower Triassic series. It spans the time between 251.2 Ma and 247.2 Ma. The Olenekian is sometimes divided into the Smithian and the Spathian subages or substages. The Olenekian follows the Induan and is followed by the Anisian.

In the geologic timescale, the Middle Triassic is the second of three epochs of the Triassic period or the middle of three series in which the Triassic system is divided in chronostratigraphy. The Middle Triassic spans the time between 247.2 Ma and 237 Ma. It is preceded by the Early Triassic Epoch and followed by the Late Triassic Epoch. The Middle Triassic is divided into the Anisian and Ladinian ages or stages.

Shonisaurus is a genus of ichthyosaur. At least 37 incomplete fossil specimens of the marine reptile have been found in the Luning Formation of Nevada, USA. This formation dates to the late Carnian age of the late Triassic period, about 237–227 million years ago.

The Moenkopi Formation is a geological formation that is spread across the U.S. states of New Mexico, northern Arizona, Nevada, southeastern California, eastern Utah and western Colorado. This unit is considered to be a group in Arizona. Part of the Colorado Plateau and Basin and Range, this red sandstone was laid down in the Lower Triassic and possibly part of the Middle Triassic, around 240 million years ago.

Cymbospondylus was a basal early ichthyosaur that lived between the early and middle Triassic period. Previously, the genus was classified as a shastasaurid, however, more recent work finds it to be more basal. Cymbospondylus was a cosmopolitan genus found in Nevada, Europe and Spitsbergen. The largest species of Cymbospondylus may have reached lengths of 17 m (56 ft).

Pistosaurus is an extinct genus of aquatic sauropterygian reptile closely related to plesiosaurs. Fossils have been found in France and Germany, and date to the Middle Triassic. It contains a single species, Pistosaurus longaevus. Pistosaurus is known as the oldest "subaquatic flying" reptile on earth.

Mixosaurus is an extinct genus of Middle Triassic ichthyosaur. Its fossils have been found near the Italy–Switzerland border and in South China.

Omphalosaurus is an extinct genus of marine reptile from the Early Triassic to Middle Triassic, thought to be in the order of Ichthyosauria. Most of what is known about Omphalosaurus is based on multiple jaw fragments, ribs, and vertebrae. Specimens of Omphalosaurus have been described from the western United States, Germany, Austria and the island of Spitsbergen off the northern coast of Norway.

Birgeria is a genus of carnivorous marine ray-finned fish from the Triassic period. Birgeria had a global distribution. Fossils were found in Madagascar, Spitsbergen, Germany, Switzerland, Italy, Slovenia, China, Russia, Canada and Nevada, United States. The oldest fossils are from Griesbachian aged beds of the Wordie Creek Formation of East Greenland.

Augustasaurus is a genus of aquatic sauropterygian reptile belonging to the Pistosauria, a clade containing plesiosaurs and their close relatives. Pistosaurus and Augustasaurus were thought to be the only known members of the family Pistosauridae. However, some recent cladistic analyses found Augustasaurus to be a more advanced pistosaur, as a sister group of the order Plesiosauria. The only known species of Augustasaurus is Augustasaurus hagdorni, which was first described in 1997.

Pteronisculus is an extinct genus of prehistoric bony fish that lived during the Early Triassic and Middle Triassic epochs of the Triassic period. The preoccupied genus name "Glaucolepis" Stensiö, 1921 is a synonym of Pteronisculus White, 1933.

Boreosomus is an extinct genus of Triassic ray-finned fish. It was first described from the Arctic island of Spitsbergen, but was later also discovered in other parts of the world. Boreosomus had a worldwide distribution during the Early Triassic. Fossils of Boreosomus were found, apart from Spitsbergen, in Greenland, Madagascar and Canada. The type species is Boreosomus arcticus.

Toretocnemus is an extinct genus of ichthyosaur. Its remains have been found in California, United States, in Triassic layers of the Carnian Hosselkus Limestone.
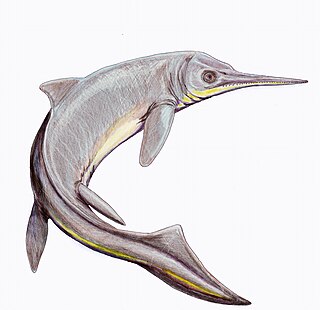
The Mixosauria were an early group of ichthyosaurs, living between 247.2 and 235 million years ago, during the Triassic period. Fossils of mixosaurs have been found all over the world: China, Timor, Indonesia, Italy, Germany, Spitsbergen, Switzerland, Svalbard, Canada, Alaska, and Nevada.

Pistosauroidea is a group of marine reptiles within the superorder Sauropterygia that first appeared in the latter part of the Early Triassic and were the ancestors of plesiosaurs. Pistosauroids are rare in Triassic marine assemblages, and are represented by only a few fossils from central Europe, the United States, and China. Recent phylogenetic analyses consider the Triassic pistosauroids to be a paraphyletic grouping, meaning that they do not form a true clade. Plesiosauria is now placed within Pistosauroidea, while the traditional pistosauroids are successively more basal, or primitive, sauropterygians.
Paleontology in Nevada refers to paleontological research occurring within or conducted by people from the U.S. state of Nevada. Nevada has a rich fossil record of plants and animal life spanning the past 650 million years of time. The earliest fossils from the state are from Esmeralda County, and are Late Proterozoic in age and represent reefs of photosynthesizing blue-green algae, amongst these reefs were some of the oldest known shells in the fossil record, the Cloudina-fauna. Much of the Proterozoic and Paleozoic fossil story of Nevada is that of a warm, shallow, tropical sea, with a few exceptions towards the Late Paleozoic. As such many fossils across the state are those of marine animals, such as trilobites, brachiopods, bryozoans, honeycomb corals, archaeocyaths, and horn corals.

Thalattoarchon is an extinct genus of ichthyosaur from the Middle Triassic of the western United States. The type species Thalattoarchon saurophagis was discovered in Nevada, USA, in 2010 and formally described in 2013. It is known from a single skeleton, holotype FMNH PR 3032, consisting of a partial skull, vertebral column, hip bones, and parts of the hind fins. The total length of Thalattoarchon is estimated to have been at least 8.6 metres (28 ft). Thalattoarchon is thought to have been one of the first marine macropredators capable of eating prey that was similar in size to itself, an ecological role that can be compared to that of modern orcas. Thalattoarchon lived four million years after the first appearance of ichthyosaurs in the Early Triassic and is therefore the oldest known marine reptile to have been an apex predator. It lived eight million years after the Permian-Triassic extinction event, indicating a fast recovery of marine ecosystems after the mass extinction.

Ardoreosomus is an extinct genus of ray-finned fish. It was described from the Induan aged Candelaria Formation of Nevada, United States, which was located near the equator during the Early Triassic epoch. It contains only one species, A. occidentalis (monotypy).


















