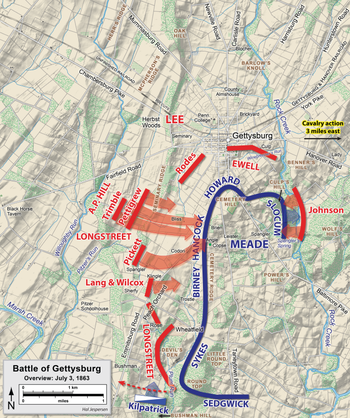
The Battle of Gettysburg was a three-day battle in the American Civil War fought between Union and Confederate forces between July 1 and July 3, 1863, in and around Gettysburg, Pennsylvania. The battle, which was won by the Union, is widely considered the Civil War's turning point, ending the Confederacy's aspirations to establish an independent nation. It was the Civil War's bloodiest battle, claiming over 50,000 combined casualties over three days.

The Gettysburg Battlefield is the area of the July 1–3, 1863, military engagements of the Battle of Gettysburg in and around Gettysburg, Pennsylvania. Locations of military engagements extend from the 4-acre (1.6 ha) site of the first shot at Knoxlyn Ridge on the west of the borough, to East Cavalry Field on the east. A military engagement prior to the battle was conducted at the Gettysburg Railroad trestle over Rock Creek, which was burned on June 27.
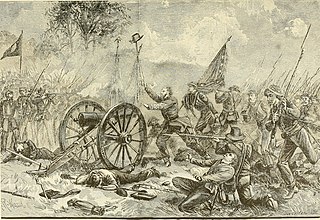
Pickett's Charge, was an infantry assault on the last day of the Battle of Gettysburg in Pennsylvania during the Civil War. Ordered by Confederate General Robert E. Lee against Major General George G. Meade's Union positions on Cemetery Hill, the attack was a costly mistake that decisively ended Lee's invasion of the north and forced a retreat back to Virginia.

Cemetery Hill is a landform on the Gettysburg Battlefield that was the scene of fighting each day of the Battle of Gettysburg. The northernmost part of the Army of the Potomac defensive "fish-hook" line, the hill is gently sloped and provided a site for American Civil War artillery.

Little Round Top is the smaller of two rocky hills south of Gettysburg, Pennsylvania—the companion to the adjacent, taller hill named Big Round Top. It was the site of an unsuccessful assault by Confederate troops against the Union left flank on July 2, 1863, the second day of the Battle of Gettysburg, during the American Civil War.

Gettysburg is a 1993 American epic war film about the Battle of Gettysburg in the American Civil War. Written and directed by Ronald F. Maxwell, the film was adapted from the 1974 historical novel The Killer Angels by Michael Shaara. It features an ensemble cast, including Tom Berenger as James Longstreet, Jeff Daniels as Joshua Chamberlain, Martin Sheen as Robert E. Lee, Stephen Lang as George Pickett, and Sam Elliott as John Buford.

Culp's Hill, which is about 3⁄4 mi (1,200 m) south of the center of Gettysburg, Pennsylvania, played a prominent role in the Battle of Gettysburg. It consists of two rounded peaks, separated by a narrow saddle. Its heavily wooded higher peak is 630 ft (190 m) above sea level. The lower peak is about 100 feet shorter than its companion. The eastern slope descends to Rock Creek, about 160 feet lower in elevation, and the western slope is to a saddle with Stevens Knoll with a summit 100 ft (30 m) lower than the main Culp's Hill summit. The hill was owned in 1863 by farmer Henry Culp and was publicized as "Culp's Hill" by October 31, 1865.
Richard Brooke Garnett was a career United States Army officer and a Confederate general in the American Civil War. He was court-martialed by Stonewall Jackson for his actions in command of the Stonewall Brigade at the First Battle of Kernstown, and killed during Pickett's Charge at the Battle of Gettysburg.

George Jerrison Stannard was a Vermont farmer, teacher, government official and Union general in the American Civil War.

The first day of the Battle of Gettysburg during the American Civil War took place on July 1, 1863, and began as an engagement between isolated units of the Army of Northern Virginia under Confederate General Robert E. Lee and the Army of the Potomac under Union Maj. Gen. George G. Meade. It soon escalated into a major battle which culminated in the outnumbered and defeated Union forces retreating to the high ground south of Gettysburg, Pennsylvania.

During the second day of the Battle of Gettysburg Confederate Gen. Robert E. Lee attempted to capitalize on his first day's accomplishments. His Army of Northern Virginia launched multiple attacks on the flanks of the Union Army of the Potomac, commanded by Maj. Gen. George G. Meade. The assaults were unsuccessful, and resulted in heavy casualties for both sides.

On the third day of the Battle of Gettysburg during the disastrous infantry assault nicknamed Pickett's Charge, there were two cavalry battles: one approximately three miles (5 km) to the east, in the area known today as East Cavalry Field, the other southwest of the [Big] Round Top mountain.

The high-water mark of the Confederacy or high tide of the Confederacy refers to an area on Cemetery Ridge near Gettysburg, Pennsylvania, marking the farthest point reached by Confederate forces during Pickett's Charge on July 3, 1863. Similar to a high water mark of water, the term is a reference to arguably the Confederate Army's best chance of achieving victory in the war. The line of advance was east of "The Angle" stone wall.
The Philadelphia Brigade was a Union Army brigade that served in the American Civil War. It was raised primarily in the city of Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, with the exception of the 106th regiment which contained men from Lycoming and Bradford counties.

Chapman Biddle was a member of the prominent Biddle family of Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, who served as an officer in the Union Army in the American Civil War. He commanded a brigade of infantry at the Battle of Gettysburg.

George Lamb Willard was an officer in the United States Army who served in the Mexican-American War and the American Civil War. He lost his life leading a brigade in the II Corps at the Battle of Gettysburg. Colonel Willard was the namesake of Fort Willard.
Sylvanus Tunning Rugg was an officer in the Union Army who commanded an artillery battery at the Battle of Gettysburg during the American Civil War, as well as in other leading battles of the Army of the Potomac. He also served in the Western Theater late in his career.

The 151st Pennsylvania Infantry was a Union Army regiment serving for a term of nine months during the American Civil War. The regiment sustained seventy-six percent casualties in the Battle of Gettysburg, its only major engagement.

The Confederate Army of Northern Virginia began its Retreat from Gettysburg on July 4, 1863. Following General Robert E. Lee's failure to defeat the Union Army at the Battle of Gettysburg, he ordered a retreat through Maryland and over the Potomac River to relative safety in Virginia.
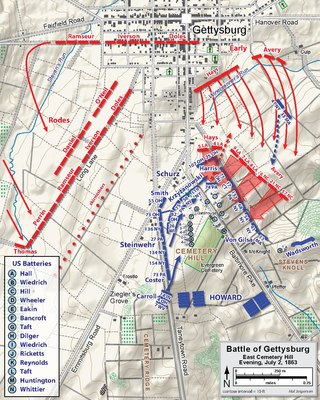
The battle of East Cemetery Hill during the American Civil War was a military engagement on the second day of the Battle of Gettysburg, in which an attack of the Confederacy's Louisiana Tigers Brigade and a brigade led by Colonel Robert Hoke was repelled by the forces of Colonel Andrew L. Harris and Colonel Leopold von Gilsa of the XI Corps, plus reinforcements. The site is on Cemetery Hill's east-northeast slope, east of the summit of the Baltimore Pike.