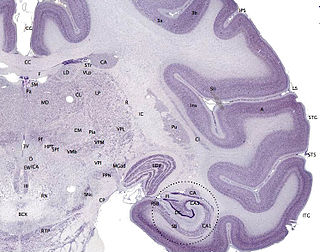
The cerebral cortex, also known as the cerebral mantle, is the outer layer of neural tissue of the cerebrum of the brain in humans and other mammals. The cerebral cortex mostly consists of the six-layered neocortex, with just 10% consisting of allocortex. It is separated into two cortices, by the longitudinal fissure that divides the cerebrum into the left and right cerebral hemispheres. The two hemispheres are joined beneath the cortex by the corpus callosum. The cerebral cortex is the largest site of neural integration in the central nervous system. It plays a key role in attention, perception, awareness, thought, memory, language, and consciousness. The cerebral cortex is part of the brain responsible for cognition.

The thalamus is a large mass of gray matter located in the dorsal part of the diencephalon. Nerve fibers project out of the thalamus to the cerebral cortex in all directions, allowing hub-like exchanges of information. It has several functions, such as the relaying of sensory signals, including motor signals to the cerebral cortex and the regulation of consciousness, sleep, and alertness.
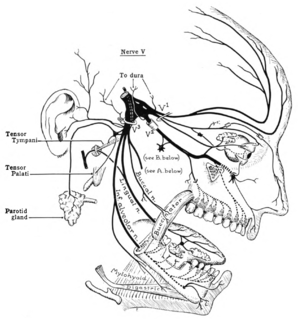
In neuroanatomy, the trigeminal nerve, also known as the fifth cranial nerve, cranial nerve V, or simply CN V, is a cranial nerve responsible for sensation in the face and motor functions such as biting and chewing; it is the most complex of the cranial nerves. Its name ("trigeminal", from Latin tri- 'three', and -geminus 'twin') derives from each of the two nerves (one on each side of the pons) having three major branches: the ophthalmic nerve (V1), the maxillary nerve (V2), and the mandibular nerve (V3). The ophthalmic and maxillary nerves are purely sensory, whereas the mandibular nerve supplies motor as well as sensory (or "cutaneous") functions. Adding to the complexity of this nerve is that autonomic nerve fibers as well as special sensory fibers (taste) are contained within it.

The vertebrate cerebrum (brain) is formed by two cerebral hemispheres that are separated by a groove, the longitudinal fissure. The brain can thus be described as being divided into left and right cerebral hemispheres. Each of these hemispheres has an outer layer of grey matter, the cerebral cortex, that is supported by an inner layer of white matter. In eutherian (placental) mammals, the hemispheres are linked by the corpus callosum, a very large bundle of nerve fibers. Smaller commissures, including the anterior commissure, the posterior commissure and the fornix, also join the hemispheres and these are also present in other vertebrates. These commissures transfer information between the two hemispheres to coordinate localized functions.

The internal capsule is a white matter structure situated in the inferomedial part of each cerebral hemisphere of the brain. It carries information past the basal ganglia, separating the caudate nucleus and the thalamus from the putamen and the globus pallidus. The internal capsule contains both ascending and descending axons, going to and coming from the cerebral cortex. It also separates the caudate nucleus and the putamen in the dorsal striatum, a brain region involved in motor and reward pathways.

The longitudinal fissure is the deep groove that separates the two cerebral hemispheres of the vertebrate brain. Lying within it is a continuation of the dura mater called the falx cerebri. The inner surfaces of the two hemispheres are convoluted by gyri and sulci just as is the outer surface of the brain.

In neuroanatomy, the corona radiata is a white matter sheet that continues inferiorly as the internal capsule and superiorly as the centrum semiovale. This sheet of both ascending and descending axons carries most of the neural traffic from and to the cerebral cortex. The corona radiata is associated with the corticopontine tract, the corticobulbar tract, and the corticospinal tract.

The parahippocampal gyrus is a grey matter cortical region of the brain that surrounds the hippocampus and is part of the limbic system. The region plays an important role in memory encoding and retrieval. It has been involved in some cases of hippocampal sclerosis. Asymmetry has been observed in schizophrenia.

The cerebellum has four deep cerebellar nuclei embedded in the white matter in its center.4 pairs of nuclei are embedded deep i the medullary centre, in the medial to lateral direction. They are fastigial nuclei, globose nuclei, emboliform nuclei, dented nuclei.

The dentate nucleus is a cluster of neurons, or nerve cells, in the central nervous system that has a dentate – tooth-like or serrated – edge. It is located within the deep white matter of each cerebellar hemisphere, and it is the largest single structure linking the cerebellum to the rest of the brain. It is the largest and most lateral, or farthest from the midline, of the four pairs of deep cerebellar nuclei, the others being the globose and emboliform nuclei, which together are referred to as the interposed nucleus, and the fastigial nucleus. The dentate nucleus is responsible for the planning, initiation and control of voluntary movements. The dorsal region of the dentate nucleus contains output channels involved in motor function, which is the movement of skeletal muscle, while the ventral region contains output channels involved in nonmotor function, such as conscious thought and visuospatial function.
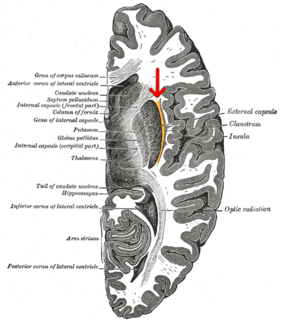
The external capsule is a series of white matter fiber tracts in the brain. These fibers run between the most lateral segment of the lentiform nucleus and the claustrum.

The calcarine sulcus is an anatomical landmark located at the caudal end of the medial surface of the brain of humans and other primates. Its name comes from the Latin "calcar" meaning "spur". It is very deep, and known as a complete sulcus.
The projection fibers consist of efferent and afferent fibers uniting the cortex with the lower parts of the brain and with the spinal cord. In human neuroanatomy, bundles of axons called tracts, within the brain, can be categorized by their function into association fibers, projection fibers, and commissural fibers.

The commissural fibers or transverse fibers are axons that connect the two hemispheres of the brain. In contrast to commissural fibers, association fibers connect regions within the same hemisphere of the brain, and projection fibers connect each region to other parts of the brain or to the spinal cord.

Association fibers are axons that connect cortical areas within the same cerebral hemisphere.

The basilar part of pons, also known as basis pontis, is the ventral part of the pons; the dorsal part is known as the pontine tegmentum.

A nerve tract is a bundle of nerve fibers (axons) connecting nuclei of the central nervous system. In the peripheral nervous system this is known as a nerve, and has associated connective tissue. The main nerve tracts in the central nervous system are of three types: association fibers, commissural fibers, and projection fibers. A tract may also be referred to as a commissure, decussation, pathway or fasciculus. A commissure connects the two cerebral hemispheres at the same levels, while a decussation connects at different levels.

The anatomy of the cerebellum can be viewed at three levels. At the level of gross anatomy, the cerebellum consists of a tightly folded and crumpled layer of cortex, with white matter underneath, several deep nuclei embedded in the white matter, and a fluid-filled ventricle in the middle. At the intermediate level, the cerebellum and its auxiliary structures can be broken down into several hundred or thousand independently functioning modules or compartments known as microzones. At the microscopic level, each module consists of the same small set of neuronal elements, laid out with a highly stereotyped geometry.
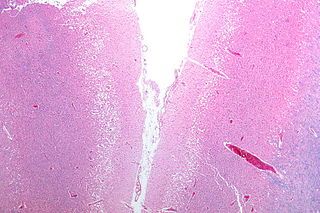
Cortical pseudolaminar necrosis, also known as cortical laminar necrosis and simply laminar necrosis, is the (uncontrolled) death of cells in the (cerebral) cortex of the brain in a band-like pattern, with a relative preservation of cells immediately adjacent to the meninges.

















