
A neurotransmitter is a signaling molecule secreted by a neuron to affect another cell across a synapse. The cell receiving the signal, any main body part or target cell, may be another neuron, but could also be a gland or muscle cell.

The striatum, or corpus striatum, is a nucleus in the subcortical basal ganglia of the forebrain. The striatum is a critical component of the motor and reward systems; receives glutamatergic and dopaminergic inputs from different sources; and serves as the primary input to the rest of the basal ganglia.

Acetylcholine (ACh) is an organic chemical that functions in the brain and body of many types of animals as a neurotransmitter. Its name is derived from its chemical structure: it is an ester of acetic acid and choline. Parts in the body that use or are affected by acetylcholine are referred to as cholinergic. Substances that increase or decrease the overall activity of the cholinergic system are called cholinergics and anticholinergics, respectively.

The basal ganglia (BG), or basal nuclei, are a group of subcortical nuclei, of varied origin, in the brains of vertebrates. In humans, and some primates, there are some differences, mainly in the division of the globus pallidus into an external and internal region, and in the division of the striatum. The basal ganglia are situated at the base of the forebrain and top of the midbrain. Basal ganglia are strongly interconnected with the cerebral cortex, thalamus, and brainstem, as well as several other brain areas. The basal ganglia are associated with a variety of functions, including control of voluntary motor movements, procedural learning, habit learning, conditional learning, eye movements, cognition, and emotion.
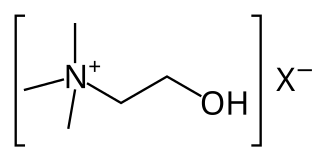
Cholinergic agents are compounds which mimic the action of acetylcholine and/or butyrylcholine. In general, the word "choline" describes the various quaternary ammonium salts containing the N,N,N-trimethylethanolammonium cation. Found in most animal tissues, choline is a primary component of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine and functions with inositol as a basic constituent of lecithin. Choline also prevents fat deposits in the liver and facilitates the movement of fats into cells.
The mesolimbic pathway, sometimes referred to as the reward pathway, is a dopaminergic pathway in the brain. The pathway connects the ventral tegmental area in the midbrain to the ventral striatum of the basal ganglia in the forebrain. The ventral striatum includes the nucleus accumbens and the olfactory tubercle.

Arousal is the physiological and psychological state of being awoken or of sense organs stimulated to a point of perception. It involves activation of the ascending reticular activating system (ARAS) in the brain, which mediates wakefulness, the autonomic nervous system, and the endocrine system, leading to increased heart rate and blood pressure and a condition of sensory alertness, desire, mobility, and readiness to respond.

The nucleus accumbens is a region in the basal forebrain rostral to the preoptic area of the hypothalamus. The nucleus accumbens and the olfactory tubercle collectively form the ventral striatum. The ventral striatum and dorsal striatum collectively form the striatum, which is the main component of the basal ganglia. The dopaminergic neurons of the mesolimbic pathway project onto the GABAergic medium spiny neurons of the nucleus accumbens and olfactory tubercle. Each cerebral hemisphere has its own nucleus accumbens, which can be divided into two structures: the nucleus accumbens core and the nucleus accumbens shell. These substructures have different morphology and functions.

The locus coeruleus (LC), also spelled locus caeruleus or locus ceruleus, is a nucleus in the pons of the brainstem involved with physiological responses to stress and panic. It is a part of the reticular activating system.

The reticular formation is a set of interconnected nuclei that are located throughout the brainstem. It is not anatomically well defined, because it includes neurons located in different parts of the brain. The neurons of the reticular formation make up a complex set of networks in the core of the brainstem that extend from the upper part of the midbrain to the lower part of the medulla oblongata. The reticular formation includes ascending pathways to the cortex in the ascending reticular activating system (ARAS) and descending pathways to the spinal cord via the reticulospinal tracts.

The ventrolateral preoptic nucleus (VLPO), also known as the intermediate nucleus of the preoptic area (IPA), is a small cluster of neurons situated in the anterior hypothalamus, sitting just above and to the side of the optic chiasm in the brain of humans and other animals. The brain's sleep-promoting nuclei, together with the ascending arousal system which includes components in the brainstem, hypothalamus and basal forebrain, are the interconnected neural systems which control states of arousal, sleep, and transitions between these two states. The VLPO is active during sleep, particularly during non-rapid eye movement sleep, and releases inhibitory neurotransmitters, mainly GABA and galanin, which inhibit neurons of the ascending arousal system that are involved in wakefulness and arousal. The VLPO is in turn innervated by neurons from several components of the ascending arousal system. The VLPO is activated by the endogenous sleep-promoting substances adenosine and prostaglandin D2. The VLPO is inhibited during wakefulness by the arousal-inducing neurotransmitters norepinephrine and acetylcholine. The role of the VLPO in sleep and wakefulness, and its association with sleep disorders – particularly insomnia and narcolepsy – is a growing area of neuroscience research.
The zona incerta (ZI) is a horizontally elongated region of gray matter in the subthalamus below the thalamus. Its connections project extensively over the brain from the cerebral cortex down into the spinal cord.

The olfactory tubercle (OT), also known as the tuberculum olfactorium, is a multi-sensory processing center that is contained within the olfactory cortex and ventral striatum and plays a role in reward cognition. The OT has also been shown to play a role in locomotor and attentional behaviors, particularly in relation to social and sensory responsiveness, and it may be necessary for behavioral flexibility. The OT is interconnected with numerous brain regions, especially the sensory, arousal, and reward centers, thus making it a potentially critical interface between processing of sensory information and the subsequent behavioral responses.
Neuromodulation is the physiological process by which a given neuron uses one or more chemicals to regulate diverse populations of neurons. Neuromodulators typically bind to metabotropic, G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) to initiate a second messenger signaling cascade that induces a broad, long-lasting signal. This modulation can last for hundreds of milliseconds to several minutes. Some of the effects of neuromodulators include: alter intrinsic firing activity, increase or decrease voltage-dependent currents, alter synaptic efficacy, increase bursting activity and reconfiguration of synaptic connectivity.
The amygdalofugal pathway is one of the three major efferent pathways of the amygdala, meaning that it is one of the three principal pathways by which fibers leave the amygdala. It leads from the basolateral nucleus and central nucleus of the amygdala. The amygdala is a limbic structure in the medial temporal lobe of the brain. The other main efferent pathways from the amygdala are the stria terminalis and anterior commissure.
Sleep onset is the transition from wakefulness into sleep. Sleep onset usually transmits into non-rapid eye movement sleep but under certain circumstances it is possible to transit from wakefulness directly into rapid eye movement sleep.

The relationship between sleep and memory has been studied since at least the early 19th century. Memory, the cognitive process of storing and retrieving past experiences, learning and recognition, is a product of brain plasticity, the structural changes within synapses that create associations between stimuli. Stimuli are encoded within milliseconds; however, the long-term maintenance of memories can take additional minutes, days, or even years to fully consolidate and become a stable memory that is accessible. Therefore, the formation of a specific memory occurs rapidly, but the evolution of a memory is often an ongoing process.

The nucleus basalis, also known as the nucleus basalis of Meynert or nucleus basalis magnocellularis, is a group of neurons located mainly in the substantia innominata of the basal forebrain. Most neurons of the nucleus basalis are rich in the neurotransmitter acetylcholine, and they have widespread projections to the neocortex and other brain structures.

A cholinergic neuron is a nerve cell which mainly uses the neurotransmitter acetylcholine (ACh) to send its messages. Many neurological systems are cholinergic. Cholinergic neurons provide the primary source of acetylcholine to the cerebral cortex, and promote cortical activation during both wakefulness and rapid eye movement sleep. The cholinergic system of neurons has been a main focus of research in aging and neural degradation, specifically as it relates to Alzheimer's disease. The dysfunction and loss of basal forebrain cholinergic neurons and their cortical projections are among the earliest pathological events in Alzheimer's disease.
The parafacial zone (PZ) is a brain structure located in the brainstem within the medulla oblongata believed to be heavily responsible for non-rapid eye movement (non-REM) sleep regulation, specifically for inducing slow-wave sleep.














