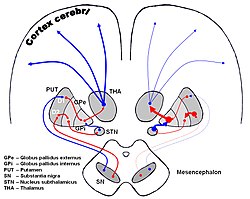
The basal ganglia (BG) or basal nuclei are a group of subcortical nuclei found in the brains of vertebrates. In humans and other primates, differences exist, primarily in the division of the globus pallidus into external and internal regions, and in the division of the striatum. Positioned at the base of the forebrain and the top of the midbrain, they have strong connections with the cerebral cortex, thalamus, brainstem and other brain areas. The basal ganglia are associated with a variety of functions, including regulating voluntary motor movements, procedural learning, habit formation, conditional learning, eye movements, cognition, and emotion.
Articles related to anatomy include:

The internal capsule is a paired white matter structure, as a two-way tract, carrying ascending and descending fibers, to and from the cerebral cortex. The internal capsule is situated in the inferomedial part of each cerebral hemisphere of the brain. It carries information past the subcortical basal ganglia. As it courses it separates the caudate nucleus and the thalamus from the putamen and the globus pallidus. It also separates the caudate nucleus and the putamen in the dorsal striatum, a brain region involved in motor and reward pathways.

The spinothalamic tract is a nerve tract in the anterolateral system in the spinal cord. This tract is an ascending sensory pathway to the thalamus. From the ventral posterolateral nucleus in the thalamus, sensory information is relayed upward to the somatosensory cortex of the postcentral gyrus.

The dorsal column–medial lemniscus pathway (DCML) (also known as the posterior column-medial lemniscus pathway is the major sensory pathway of the central nervous system that conveys sensations of fine touch, vibration, two-point discrimination, and proprioception from the skin and joints. It transmits this information to the somatosensory cortex of the postcentral gyrus in the parietal lobe of the brain. The pathway receives information from sensory receptors throughout the body, and carries this in the gracile fasciculus and the cuneate fasciculus, tracts that make up the white matter dorsal columns of the spinal cord. At the level of the medulla oblongata, the fibers of the tracts decussate and are continued in the medial lemniscus, on to the thalamus and relayed from there through the internal capsule and transmitted to the somatosensory cortex. The name dorsal-column medial lemniscus comes from the two structures that carry the sensory information: the dorsal columns of the spinal cord, and the medial lemniscus in the brainstem.

The lentiform nucleus are the putamen (laterally) and the globus pallidus (medially), collectively. Due to their proximity, these two structures were formerly considered one, however, the two are separated by a thin layer of white matter - the external medullary lamina - and are functionally and connectionally distinct.

The spinocerebellar tracts are nerve tracts originating in the spinal cord and terminating in the same side (ipsilateral) of the cerebellum. The two main tracts are the dorsal spinocerebellar tract, and the ventral spinocerebellar tract. Both of these tracts are located in the peripheral region of the lateral funiculi. Other tracts are the rostral spinocerebellar tract, and the cuneocerebellar tract.

The subthalamus or ventral thalamus is a part of the diencephalon. Its most prominent structure is the subthalamic nucleus. The subthalamus connects to the globus pallidus, a subcortical nucleus of the basal ganglia.
The zona incerta (ZI) is a horizontally elongated small nucleus that separates the larger subthalamic nucleus from the thalamus. Its connections project extensively over the brain from the cerebral cortex down into the spinal cord.

The substantia innominata, also innominate substance or substantia innominata of Meynert, is a series of layers in the human brain consisting partly of gray and partly of white matter, which lies below the anterior part of the thalamus and lentiform nucleus. It is included as part of the anterior perforated substance. It is part of the basal forebrain structures and includes the nucleus basalis. A portion of the substantia innominata, below the globus pallidus is considered as part of the extended amygdala.

The basal ganglia form a major brain system in all vertebrates, but in primates there are special differentiating features. The basal ganglia include the striatum, pallidus, substantia nigra and subthalamic nucleus. In primates the pallidus is divided into an external and internal globus pallidus, the external globus pallidus is present in other mammals but not the internal globus pallidus. Also in primates, the dorsal striatum is divided by a large nerve tract called the internal capsule into two masses named the caudate nucleus and the putamen. These differences contribute to a complex circuitry of connections between the striatum and cortex that is specific to primates, reflecting different functions in primate cortical areas.
The isothalamus is a division used by some researchers in describing the thalamus.

The ventral anterior nucleus (VA) is a nucleus in the ventral nuclear group of the thalamus. It acts with the anterior part of the ventral lateral nucleus to modify signals from the basal ganglia.

The ventral lateral nucleus (VL) is a nucleus in the ventral nuclear group of the thalamus.

The thalamic fasciculus is a component of the subthalamus (ventral thalamus). It is synonymous with field H1 of Forel. Fibers from the lenticular fasciculus (field H2 of Forel), are joined by fibers from the ansa lenticularis – different parts of the internal globus pallidus, before they enter the ventral anterior nucleus of the thalamus to form the thalamic fasciculus. The fasciculus also contains fibers from the cerebellothalamic tract, and the pallidothalamic tract.

The lenticular fasciculus is a tract connecting the globus pallidus (internus) to the thalamus and is a part of the thalamic fasciculus. It is synonymous with field H2 of Forel. The thalamic fasciculus (composed of both the lenticular fasciculus and ansa lenticularis) runs to the thalamus. It is part of a pathway connecting the globus pallidus and the thalamus.

The internal globus pallidus, and the external globus pallidus (GPe) make up the globus pallidus. In rodents its homologue is known as the entopeduncular nucleus. The GPi is one of the output nuclei of the basal ganglia. The GABAergic neurons of the GPi send their axons to the ventral anterior nucleus (VA) and the ventral lateral nucleus (VL) in the dorsal thalamus, to the centromedian complex, and to the pedunculopontine complex.
The ventral pallidum (VP) is a structure within the basal ganglia of the brain. It is an output nucleus whose fibres project to thalamic nuclei, such as the ventral anterior nucleus, the ventral lateral nucleus, and the medial dorsal nucleus. The VP is a core component of the reward system which forms part of the limbic loop of the basal ganglia, a pathway involved in the regulation of motivational salience, behavior, and emotions. It is involved in addiction.
The fields of Forel is a complex region in the posterior subthalamus, consisting of a concentrated collection of bundles of fibers. The tracts formed include the thalamic fasciculus that includes the ansa lenticularis and lenticular fasciculus, cerebellothalamic tracts, and pallidothalamic tracts. Other included fibers connect to other brain regions. These tracts are described in regions known as H fields.