The thalamus is a large mass of gray matter on the lateral walls of the third ventricle forming the dorsal part of the diencephalon. Nerve fibers project out of the thalamus to the cerebral cortex in all directions, known as the thalamocortical radiations, allowing hub-like exchanges of information. It has several functions, such as the relaying of sensory and motor signals to the cerebral cortex and the regulation of consciousness, sleep, and alertness.

The limbic system, also known as the paleomammalian cortex, is a set of brain structures located on both sides of the thalamus, immediately beneath the medial temporal lobe of the cerebrum primarily in the forebrain.

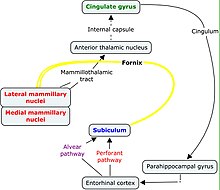
The mammillary bodies also mamillary bodies, are a pair of small round brainstem nuclei. They are located on the undersurface of the brain that, as part of the diencephalon, form part of the limbic system. They are located at the ends of the anterior arches of the fornix. They consist of two groups of nuclei, the medial mammillary nuclei and the lateral mammillary nuclei.

The fornix is a C-shaped bundle of nerve fibers in the brain that acts as the major output tract of the hippocampus. The fornix also carries some afferent fibers to the hippocampus from structures in the diencephalon and basal forebrain. The fornix is part of the limbic system. While its exact function and importance in the physiology of the brain are still not entirely clear, it has been demonstrated in humans that surgical transection—the cutting of the fornix along its body—can cause memory loss. There is some debate over what type of memory is affected by this damage, but it has been found to most closely correlate with recall memory rather than recognition memory. This means that damage to the fornix can cause difficulty in recalling long-term information such as details of past events, but it has little effect on the ability to recognize objects or familiar situations.
In neuroanatomy, a neural pathway is the connection formed by axons that project from neurons to make synapses onto neurons in another location, to enable neurotransmission. Neurons are connected by a single axon, or by a bundle of axons known as a nerve tract, or fasciculus. Shorter neural pathways are found within grey matter in the brain, whereas longer projections, made up of myelinated axons, constitute white matter.

The spinothalamic tract is a nerve tract in the anterolateral system in the spinal cord. This tract is an ascending sensory pathway to the thalamus. From the ventral posterolateral nucleus in the thalamus, sensory information is relayed upward to the somatosensory cortex of the postcentral gyrus.

The spinocerebellar tracts are nerve tracts originating in the spinal cord and terminating in the same side (ipsilateral) of the cerebellum. The two main tracts are the dorsal spinocerebellar tract, and the ventral spinocerebellar tract. Both of these tracts are located in the peripheral region of the lateral funiculi. Other tracts are the rostral spinocerebellar tract, and the cuneocerebellar tract.

The Papez circuit, or medial limbic circuit, is a neural circuit for the control of emotional expression. In 1937, James Papez proposed that the circuit connecting the hypothalamus to the limbic lobe was the basis for emotional experiences. Paul D. MacLean reconceptualized Papez's proposal and coined the term limbic system. MacLean redefined the circuit as the "visceral brain" which consisted of the limbic lobe and its major connections in the forebrain – hypothalamus, amygdala, and septum. Over time, the concept of a forebrain circuit for the control of emotional expression has been modified to include the prefrontal cortex.

The septal area, consisting of the lateral septum and medial septum, is an area in the lower, posterior part of the medial surface of the frontal lobe, and refers to the nearby septum pellucidum.

The medial dorsal nucleus is a large nucleus in the thalamus. It is separated from the other thalamic nuclei by the internal medullary lamina.
The isothalamus is a division used by some researchers in describing the thalamus.

The anterior nuclei of thalamus are a collection of nuclei at the rostral end of the dorsal thalamus. They comprise the anteromedial, anterodorsal, and anteroventral nuclei.

The thalamic fasciculus is a component of the subthalamus (ventral thalamus). It is synonymous with field H1 of Forel. Fibers from the lenticular fasciculus (field H2 of Forel), are joined by fibers from the ansa lenticularis – different parts of the internal globus pallidus, before they enter the ventral anterior nucleus of the thalamus to form the thalamic fasciculus. The fasciculus also contains fibers from the cerebellothalamic tract, and the pallidothalamic tract.
The spinoreticular tract is a partially decussating (crossed-over) four-neuron sensory pathway of the central nervous system. The tract transmits slow nociceptive/pain information from the spinal cord to reticular formation which in turn relays the information to the thalamus via reticulothalamic fibers as well as to other parts of the brain. Most (85%) second-order axons arising from sensory C first-order fibers ascend in the spinoreticular tract - it is consequently responsible for transmitting "slow", dull, poorly-localised pain. By projecting to the reticular activating system (RAS), the tract also mediates arousal/alertness in response to noxious (harmful) stimuli. The tract is phylogenetically older than the spinothalamic ("neospinothalamic") tract.
The trisynaptic circuit or trisynaptic loop is a relay of synaptic transmission in the hippocampus. The trisynaptic circuit is a neural circuit in the hippocampus, which is made up of three major cell groups: granule cells in the dentate gyrus, pyramidal neurons in CA3, and pyramidal neurons in CA1. The hippocampal relay involves 3 main regions within the hippocampus which are classified according to their cell type and projection fibers. The first projection of the hippocampus occurs between the entorhinal cortex (EC) and the dentate gyrus (DG). The entorhinal cortex transmits its signals from the parahippocampal gyrus to the dentate gyrus via granule cell fibers known collectively as the perforant path. The dentate gyrus then synapses on pyramidal cells in CA3 via mossy cell fibers. CA3 then fires to CA1 via Schaffer collaterals which synapse in the subiculum and are carried out through the fornix. Collectively the dentate gyrus, CA1 and CA3 of the hippocampus compose the trisynaptic loop.

The pallidothalamic tracts are a part of the basal ganglia. They provide connectivity between the internal globus pallidus (GPi) and the thalamus, primarily the ventral anterior nucleus and the ventral lateral nucleus.
The mammillotegmental fasciculus is a small bundle of efferent fibers from the hypothalamus running from the mammillary body to the tegmentum. Its functions are not well defined for humans, but based on animal studies it seems to be related to regulating visceral function and processing spatial information. The mammillotegmental fasciculus was first described by the German neuroanatomist, Bernhard von Gudden, from which it takes its alternate name, mammillo-tegmental bundle of Gudden.
The dorsal tegmental nucleus (DTN), also known as dorsal tegmental nucleus of Gudden (DTg), is a group of neurons located in the brain stem, which are involved in spatial navigation and orientation.
Patient N.A. was an American man who developed anterograde amnesia as a result of a fencing accident. He was a patient studied by Larry Squire, a professor of psychiatry, neuroscience and psychology at the University of California. The cause of his amnesia was found to be a thalamic lesion extending to the hypothalamus. Damage to the temporal cortex was also found and thought to be a result of an exploratory surgery.