
Chalcid wasps are insects within the superfamily Chalcidoidea, part of the order Hymenoptera. The superfamily contains some 22,500 known species, and an estimated total diversity of more than 500,000 species, meaning the vast majority have yet to be discovered and described. The name "chalcid" is often confused with the name "chalcidid", though the latter refers strictly to one constituent family, the Chalcididae, rather than the superfamily as a whole; accordingly, most recent publications (e.g.,) use the name "chalcidoid" when referring to members of the superfamily.
The individual member states of the African Union (AU) coordinate foreign policy through this agency, in addition to conducting their own international relations on a state-by-state basis. The AU represents the interests of African peoples at large in intergovernmental organizations (IGO's); for instance, it is a permanent observer at the United Nations' General Assembly.

The Leucospidae are a specialized group of wasps within the superfamily Chalcidoidea, that are ectoparasitoids of aculeate wasps or bees. They are typically mimics of bees or stinging wasps, often black with yellow, red, or white markings, sometimes metallic, with a robust mesosoma and very strong sculpturing. The hind femora are often greatly enlarged, with a row of teeth or serrations along the lower margin as in Chalcididae. The wing has a longitudinal fold. The female ovipositor is sometimes short, but if not, it is recurved and lies along the dorsal side of the metasoma, a unique feature. The males are also unusual, in the fusion of many of the metasomal segments to form a capsule-like "carapace".
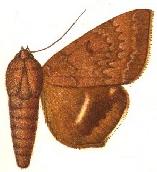
Achaea albicilia is a species of moth of the family Erebidae first described by Francis Walker in 1858. It is found in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, the Gambia, Ivory Coast, Malawi, Nigeria, Sierra Leone, South Africa, Tanzania and Uganda.
Diadegma mollipla is a wasp which parasitises the larvae of the diamondback moth and the potato tuber moth. Its range includes the Canary Islands, Britain and parts of Africa.
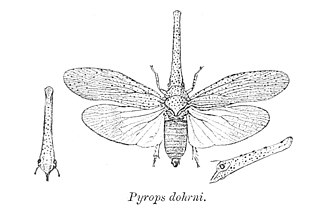
Zanna is a genus of tropical lantern bugs found in Asia and Africa. They are mostly grey with black speckling with a long snout with some folds on the surface. Although usually placed in the family Fulgoridae, molecular studies question this placement.
Emeryrhynchium is a monotypical afrotropical genus of potter wasps known from Equatorial Africa. Its only known species is Emeryrhynchium emeryanus.
Ghesquierellana hirtusalis is a moth in the family Crambidae. It was described by Francis Walker in 1859. It is found on the Comoros (Mohéli) and in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Ethiopia, Réunion, Madagascar, Sierra Leone, South Africa, Zimbabwe, and Mali.

Xylocopa olivacea is a species of carpenter bee. It has a completely yellow thorax and a yellow band on the first tergite. This species is very similar to X. calens, endemic to Madagascar. X. calens just differs in the length of the hair on the metasoma.
Paracyphononyx is a genus of spider wasps distributed in the tropics and warmer temperate regions; they differ from other pompilids in that they do not permanently disable the host spider but allow the spider to resume activity after the wasp has laid its egg on the spider while the wasp larva exists as koinobiont ectoparasitoid of the spider.
Cratocentrus is a genus of wasps in the family Chalcididae. Species are found in Asia and Africa.
Cratocentrus ruficornis is a species of wasp in the family Chalcididae. It is found in Namibia, South Africa and Zimbabwe.

Leucospis is a genus of wasps belonging to the family Leucospidae. Most species are brightly coloured with yellow and black patterning and about 2 cm long. They have characteristically enlarged femurs on the hind leg with the lower margin toothed. The wings have a longitudinal fold and the long ovipositor is bent over their backs above the abdomen or metasoma. They are parasitic on wasps and solitary bees that construct cells and provision food for their offspring. The Leucospis larvae live and grow as ectoparasites of the host larvae. Usually, only, one parasite emerges from a single cell. The genus Micrapion from South Africa is very closely related and phylogenetic studies suggest merging of the two genera. The genus Leucospis is found across the world in the tropical regions.
Teleasinae is a subfamily of wasps in the family Platygastridae. There are about 14 genera and more than 250 species in Teleasinae.

Haltichella is a genus of chalcidid wasps in the family Chalcididae. There are at least 20 described species in Haltichella.

Psilochalcis is a genus of chalcidid wasps in the family Chalcididae. There are at least 20 described species in Psilochalcis.

Trissolcus is a genus of parasitoid wasps in the family Platygastridae. There are at least 70 described species in Trissolcus.

Haltichellinae is a subfamily of chalcidid wasps in the family Chalcididae.

Dirhinus is a genus of parasitic wasps in the family Chalcididae. The genus has a worldwide distribution.









