
The City of Idaho Springs is the Statutory City that is the most populous municipality in Clear Creek County, Colorado, United States. Idaho Springs is a part of the Denver–Aurora–Lakewood, CO Metropolitan Statistical Area. As of the 2010 census it had a population of 1,717. Idaho Springs is located in Clear Creek Canyon, in the mountains upstream from Golden, some 30 miles (50 km) west of Denver.

Black Canyon of the Gunnison National Park is an American national park located in western Colorado and managed by the National Park Service. There are two primary entrances to the park: the south rim entrance is located 15 miles (24 km) east of Montrose, while the north rim entrance is 11 miles (18 km) south of Crawford and is closed in the winter. The park contains 12 miles (19 km) of the 48-mile (77 km) long Black Canyon of the Gunnison River. The national park itself contains the deepest and most dramatic section of the canyon, but the canyon continues upstream into Curecanti National Recreation Area and downstream into Gunnison Gorge National Conservation Area. The canyon's name owes itself to the fact that parts of the gorge only receive 33 minutes of sunlight a day, according to Images of America: The Black Canyon of the Gunnison. In the book, author Duane Vandenbusche states, "Several canyons of the American West are longer and some are deeper, but none combines the depth, sheerness, narrowness, darkness, and dread of the Black Canyon."

Kootenay National Park is a national park of Canada located in southeastern British Columbia. The park consists of 1,406 km2 (543 sq mi) of the Canadian Rockies, including parts of the Kootenay and Park mountain ranges, the Kootenay River and the entirety of the Vermilion River. While the Vermilion River is completely contained within the park, the Kootenay River has its headwaters just outside the park boundary, flowing through the park into the Rocky Mountain Trench and eventually joining the Columbia River. The park ranges in elevation from 918 m (3,012 ft) at the southwestern park entrance to 3,424 m (11,234 ft) at Deltaform Mountain.

The Chilkoot Trail is a 33-mile (53 km) trail through the Coast Mountains that leads from Dyea, Alaska, in the United States, to Bennett, British Columbia, in Canada.

The Denver, South Park, and Pacific Railroad was a historic 3 ft narrow gauge railroad that operated in Colorado in the western United States in the late 19th century. The railroad opened up the first rail routes to a large section of the central Colorado mining district in the decades of the mineral boom. The railroad took its name from the fact that its main line from Denver ascended the Platte Canyon and traversed South Park, hence its popular name "The South Park Line." Founded in 1872 by Colorado Governor John Evans, the company was purchased by the Union Pacific Railway in 1880, though it continued to be operated independently. The line went bankrupt in 1889 and was reorganized under a new corporate name as the Denver, Leadville and Gunnison Railway. When the Union Pacific went bankrupt in 1893, the DL&G lines went into receivership and were eventually sold to the Colorado and Southern Railway. In the first half of the 20th century, nearly all the company's original lines were dismantled or converted into 4 ft 8+1⁄2 instandard gauge. The last train to run the old DSP&P tracks was from Como, Colorado on April 11, 1937. A section of the standard gauge line between Leadville and Climax is still operated as a passenger excursion railroad called the Leadville, Colorado and Southern Railroad. At its peak the Denver, South Park and Pacific Railroad had 335 miles (539 km) of narrow gauge line, making it the largest narrow gauge railroad in the state of Colorado.

The Poudre Canyon is a narrow verdant canyon, approximately 40 mi (64 km) long, on the upper Cache la Poudre River in Larimer County, Colorado in the United States. The canyon is a glacier-formed valley through the foothills of the Front Range of the Rocky Mountains northwest of Fort Collins.

Independence Pass, originally known as Hunter Pass, is a high mountain pass in central Colorado, United States. It is at elevation 12,095 ft (3,687 m) on the Continental Divide in the Sawatch Range of the Rocky Mountains. The pass is midway between Aspen and Twin Lakes, on the border between Pitkin and Lake counties.

The Fraser Canyon is a major landform of the Fraser River where it descends rapidly through narrow rock gorges in the Coast Mountains en route from the Interior Plateau of British Columbia to the Fraser Valley. Colloquially, the term "Fraser Canyon" is often used to include the Thompson Canyon from Lytton to Ashcroft, since they form the same highway route which most people are familiar with, although it is actually reckoned to begin above Williams Lake, British Columbia at Soda Creek Canyon near the town of the same name.

Curecanti National Recreation Area(Pronounced or .) is a National Park Service unit located on the Gunnison River in western Colorado. Established in 1965, Curecanti National Recreation Area is responsible for developing and managing recreational facilities on three reservoirs, Blue Mesa Reservoir, Morrow Point Reservoir and Crystal Reservoir, constructed on the upper Gunnison River in the 1960s by the U.S. Bureau of Reclamation to better utilize the vital waters of the Colorado River and its major tributaries. A popular destination for boating and fishing, Curecanti offers visitors two marinas, traditional and group campgrounds, hiking trails, boat launches, and boat-in campsites. The state's premiere lake trout and Kokanee salmon fisheries, Curecanti is a popular destination for boating and fishing, and is also a popular area for ice-fishing in the winter months.

The Gila National Forest is a protected national forest in New Mexico in the southwestern part of the United States established in 1905. It covers approximately 2,710,659 acres (10,969.65 km2) of public land, making it the sixth largest National Forest in the continental United States. The Forest also manages that part of the Apache National Forest that is in New Mexico which totals an additional 614,202 acres for a total of 3.3 million acres managed by the Gila National Forest. Part of the forest, the Gila Wilderness, was established in 1924 as the first designated wilderness reservation by the U.S. federal government. Aldo Leopold Wilderness and the Blue Range Wilderness are also found within its borders.

Likely is a unincorporated community in British Columbia, Canada. It is located in the Cariboo region of the province, and is situated where the west arm of Quesnel Lake empties into the Quesnel River. Roads from Likely lead southwest to Williams Lake, northwest to Quesnel, south to Horsefly, and north to Barkerville. Likely is in the Quesnel Highland, a transition zone between the Cariboo Plateau and the Cariboo Mountains.

Blue Mesa Reservoir is an artificial reservoir located on the upper reaches of the Gunnison River in Gunnison County, Colorado. The largest lake located entirely within the state, Blue Mesa Reservoir was created by the construction of Blue Mesa Dam, a 390-foot tall earthen fill dam constructed on the Gunnison by the U.S. Bureau of Reclamation in 1966 for the generation of hydroelectric power. Managed as part of the Curecanti National Recreation Area, a unit of the National Park Service, Blue Mesa Reservoir is the largest lake trout and Kokanee salmon fishery in Colorado.

Oak Creek Canyon is a river gorge located in northern Arizona between the cities of Flagstaff and Sedona. The canyon is often described as a smaller cousin of the Grand Canyon because of its scenic beauty. State Route 89A enters the canyon on its north end via a series of hairpin turns before traversing the bottom of the canyon for about 13 miles (21 km) until the highway enters the town of Sedona.

The Rio Chama, a major tributary river of the Rio Grande, is located in the U.S. states of Colorado and New Mexico. The river is about 130 miles (210 km) long altogether. From its source to El Vado Dam its length is about 50 miles (80 km), from El Vado Dam to Abiquiu Dam is about 51 miles (82 km), and from Abiquiu Dam to its confluence with the Rio Grande is about 34 miles (55 km).

Granite is an unincorporated community with a U.S. Post Office in Chaffee County, Colorado, United States. The zip code of Granite is 81228. According to the 2010 census, the population is 116.

Nathrop is an unincorporated town, a post office, and a census-designated place (CDP) located in and governed by Chaffee County, Colorado, United States. The Nathrop post office has the ZIP code 81236. At the United States Census 2010, the population of the 81236 ZIP Code Tabulation Area was 1,017 including adjacent areas.
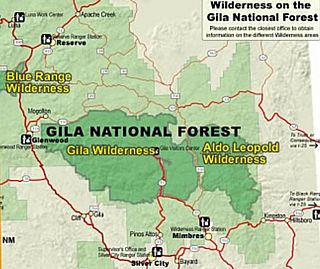
Gila Wilderness was designated the world's first wilderness area on June 3, 1924. Along with Aldo Leopold Wilderness and Blue Range Wilderness, the 558,014 acre wilderness is part of New Mexico's Gila National Forest. The wilderness is approximately 27 miles (43 km) from north to south and 39 miles (63 km) east to west. U.S. Wilderness Areas do not allow motorized or mechanized vehicles, including bicycles. Camping, hunting, and fishing are allowed with proper permit, but no roads, buildings, logging, or mining are permitted. Wilderness areas within National Forests and Bureau of Land Management areas allow hunting in season.

State Highway 67 (SH 67) is a 71-mile-long (114 km) state highway encompassing five distinct segments in south-central Colorado. SH 67's southern terminus is at SH 96 in Wetmore, and the northern terminus is at U.S. Route 85 in Sedalia. It traverses the former route of the Florence and Cripple Creek Railroad through Phantom Canyon as a county road and carrying part of the Gold Belt Byway.
Alpine, elevation 9,269 feet (2,825 m), is a small community, sometimes considered a ghost town, in Chaffee County, Colorado, United States. It was founded in the 1860s as a mining town.

Sugarite Canyon State Park is a state park of New Mexico, United States, featuring a historic early-20th century coal-mining camp and natural scenery at the border of the Rocky Mountains and the Great Plains. The park is located on the Colorado–New Mexico state line 6 miles (9.7 km) northeast of Raton, New Mexico.




















