
Acanthaceae is a family of dicotyledonous flowering plants containing almost 250 genera and about 2500 species. Most are tropical herbs, shrubs, or twining vines; some are epiphytes. Only a few species are distributed in temperate regions. The four main centres of distribution are Indonesia and Malaysia, Africa, Brazil, and Central America. Representatives of the family can be found in nearly every habitat, including dense or open forests, scrublands, wet fields and valleys, sea coast and marine areas, swamps, and mangrove forests.

Thomas Nuttall was an English botanist and zoologist who lived and worked in America from 1808 until 1841.

Sir William Jackson Hooker was an English systematic botanist and organiser, and botanical illustrator. He held the post of Regius Professor of Botany at Glasgow University, and was Director of the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. He enjoyed the friendship and support of Sir Joseph Banks for his exploring, collecting and organising work. His son, Joseph Dalton Hooker, succeeded him to the Directorship of Kew Gardens.

Augustin Pyramus de Candolle also spelled Augustin Pyrame de Candolle was a Swiss botanist. René Louiche Desfontaines launched de Candolle's botanical career by recommending him at an herbarium. Within a couple of years de Candolle had established a new genus, and he went on to document hundreds of plant families and create a new natural plant classification system. Although de Candolle's main focus was botany, he also contributed to related fields such as phytogeography, agronomy, paleontology, medical botany, and economic botany.

The genus Carthamus, the distaff thistles, includes plants in the thistle family. The group is native to Europe, North Africa, and parts of Asia. The flower has been used since ancient times in the Philippines, which it has been called kasubha by the Tagalog people.

Tetracoccus is a plant genus under the family Picrodendraceae. Shrubby-spurge is a common name for plants in this genus.

Acanthus is a genus of about 30 species of flowering plants in the family Acanthaceae, native to tropical and warm temperate regions, with the highest species diversity in the Mediterranean Basin and Asia. This flowering plant is nectar producing and is susceptible to predation by butterflies, such as Anartia fatima, and other nectar feeding organisms. Common names include Acanthus and Bear's breeches. The generic name derives from the Greek term ἄκανθος (akanthos) for Acanthus mollis, a plant that was commonly imitated in Corinthian capitals.

Glebionis coronaria, formerly called Chrysanthemum coronarium, is a species of flowering plant in the daisy family. It is native to the Mediterranean region. It is cultivated and naturalized in East Asia and in scattered locations in North America.

Mangalavanam is an ecologically sensitive area situated at the centre of the Indian city of Kochi, covering about 2.74 hectares. It also houses a shallow tidal lake connected with Kochi backwaters by a canal. It is situated behind the Kerala High Court building. It is a nesting ground for a large variety of migratory birds and supports many types of mangroves. The Managalavanam is often regarded as the "green lung of Kochi", considering its role in keeping the city's air pollution under check. The area is a roosting place for many kinds of resident and migratory birds.
Phototoxins are toxins that can cause allergic reactions in particularly susceptible individuals and which can cause dangerous photosensitivity in a much broader range of subjects.

Streblus is a genus of flowering plant in the mulberry family, Moraceae. The genus is found in the Pacific across Southeast Asia, Eastern Australia, New Zealand and the Pacific Islands. Species include:
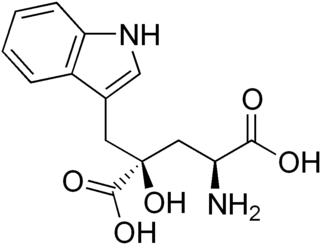
Monatin, commonly known as arruva, is a naturally occurring, high intensity sweetener isolated from the plant Sclerochiton ilicifolius, found in the Transvaal region of South Africa. Monatin contains no carbohydrate or sugar, and nearly no food energy, unlike sucrose or other nutritive sweeteners.

The Indus River Delta-Arabian Sea mangroves are a large mangrove ecoregion on the Arabian Sea coast of Sindh Province, Pakistan. The Indus River Delta forms a vast alluvial fan composed of mud flats interspersed with channels and fringed with mangrove forests. Much of the forested area has been destroyed and the remaining parts are threatened.
Lagarosiphon is a genus of aquatic plants described as a genus in 1841. It is native to Africa and Madagascar.
- Lagarosiphon cordofanus(Hochst.) Casp. - Cameroon + Ethiopia to Namibia + Mpumalanga
- Lagarosiphon hydrilloidesRendle - Ghana, Kenya, Uganda
- Lagarosiphon ilicifoliusOberm. - Uganda to Namibia
- Lagarosiphon madagascariensisCasp. - Madagascar
- Lagarosiphon major(Ridl.) Moss - Zimbabwe, Botswana, Lesotho, South Africa
- Lagarosiphon muscoidesHarv. - Mali to Sudan to KwaZulu-Natal
- Lagarosiphon rubellusRidl. - Angola
- Lagarosiphon steudneriCasp. - Ethiopia
- Lagarosiphon verticillifoliusOberm. - Mozambique, Zimibabwe, KwaZulu-Natal, Swaziland, Mpumalanga, Limpopo
Tetracoccus ilicifolius is a rare species of flowering shrub in the family Picrodendraceae known by the common names hollybush and holly-leaved tetracoccus.

Acanthus ilicifolius, commonly known as holly-leaved acanthus, sea holly, and holy mangrove is a species of shrubs or herbs, of the plant family Acanthaceae, native to Australia, Australasia, and Southeast Asia. It is used as medicine in asthma and rheumatism.

Senecio ilicifolius is a plant endemic to South Africa and belonging to the family Asteraceae.
Jishengella is a genus of bacteria from the family of Micromonosporaceae with one known species. Jishengella endophytica has been isolated from the roots of the plant Acanthus ilicifolius from Wenchang in China.
















