
Charles-Philippe Robin (4 June 1821 – 6 October 1885) was a French anatomist, biologist, and histologist born in Jasseron, département Ain.

A biologist is a scientist who has specialized knowledge in the field of biology, the scientific study of life. Biologists involved in fundamental research attempt to explore and further explain the underlying mechanisms that govern the functioning of living matter. Biologists involved in applied research attempt to develop or improve more specific processes and understanding, in fields such as medicine and industry.

Jasseron is a commune in the Ain department in eastern France.

Ain is a department named after the Ain River on the eastern edge of France. It is part of the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes region and bordered by the rivers Saône and Rhône.
He studied medicine in Paris, and while still a student took a scientific journey with Hermann Lebert to Normandy and the Channel Islands, where they collected specimens for the Musée Orfila. In 1846 he received his medical doctorate, and at different stages of his career he was a professor of natural history, anatomy, and histology. He was a member of the Académie Nationale de Médecine (1858) and Academy of Science (1866). In 1873 he was appointed director of the marine zoology laboratory at Concarneau.

Paris is the capital and most populous city of France, with an area of 105 square kilometres and an official estimated population of 2,140,526 residents as of 1 January 2019. Since the 17th century, Paris has been one of Europe's major centres of finance, commerce, fashion, science, and the arts.

Hermann Lebert was a German physician and naturalist.

Normandy is one of the 18 regions of France, roughly referring to the historical Duchy of Normandy.
Robin's contributions to medical science were many and varied. He was among the first scientists in France to use the microscope in normal and pathological anatomy. He was the first to describe the species Candida albicans (a diploid fungus), and he contributed new information on the micro-structure of ganglia and of neuroglia. He also described the role of osteoclasts in bone formation, and he conducted original studies on the electrical organs of Rajidae (electric skates).

A microscope is an instrument used to see objects that are too small to be seen by the naked eye. Microscopy is the science of investigating small objects and structures using such an instrument. Microscopic means invisible to the eye unless aided by a microscope.
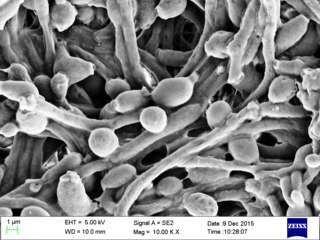
Candida albicans is an opportunistic pathogenic yeast that is a common member of the human gut flora. It does not proliferate outside the human body. It is detected in the gastrointestinal tract and mouth in 40–60% of healthy adults. It is usually a commensal organism, but it can become pathogenic in immunocompromised individuals under a variety of conditions. It is one of the few species of the genus Candida that causes the human infection candidiasis, which results from an overgrowth of the fungus. Candidiasis is for example often observed in HIV-infected patients. C. albicans is the most common fungal species isolated from biofilms either formed on (permanent) implanted medical devices or on human tissue. C. albicans, C. tropicalis, C. parapsilosis, and C. glabrata are together responsible for 50–90% of all cases of candidiasis in humans. A mortality rate of 40% has been reported for patients with systemic candidiasis due to C. albicans. By one estimate, invasive candidiasis contracted in a hospital causes 2,800 to 11,200 deaths yearly in the US. Nevertheless, these numbers may not truly reflect the true extent of damage this organism causes, given new studies indicating that C. albicans can cross the blood brain barrier.
With Pierre François Olive Rayer, Claude Bernard, and Charles-Édouard Brown-Séquard, he established the Société de biologie (1848).

Pierre François Olive Rayer was a French physician who was a native of Saint Sylvain. He made important contributions in the fields of pathological anatomy, physiology, comparative pathology and parasitology.

Claude Bernard was a French physiologist. Historian I. Bernard Cohen of Harvard University called Bernard "one of the greatest of all men of science". Among many other accomplishments, he was one of the first to suggest the use of blind experiments to ensure the objectivity of scientific observations. He originated the term milieu intérieur, and the associated concept of homeostasis.

Charles-Édouard Brown-Séquard FRS was a Mauritian physiologist and neurologist who, in 1850, became the first to describe what is now called Brown-Séquard syndrome.
Robin was a prolific writer, being the author of over 300 written articles during his lifetime. With Émile Littré he published a revision of Pierre-Hubert Nysten’s Dictionnaire de médecine, de chirurgie, etc. The eponymous Virchow-Robin spaces are named after him and pathologist Rudolf Virchow. Virchow-Robin spaces are lymphatic spaces between the vessels of the central nervous system.

Émile Maximilien Paul Littré was a French lexicographer, freemason and philosopher, best known for his Dictionnaire de la langue française, commonly called "The Littré".
Pierre-Hubert Nysten was a French physiologist and pediatrician who was a native of Liège.

Rudolf Ludwig Carl Virchow was a German physician, anthropologist, pathologist, prehistorian, biologist, writer, editor, and politician. He is known as "the father of modern pathology" and as the founder of social medicine, and to his colleagues, the "Pope of medicine". He received the Copley Medal in 1892. He was a foreign member of the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences and was elected to the Prussian Academy of Sciences, but he declined to be ennobled as "von Virchow".


















