
Chimaeras are cartilaginous fish in the order Chimaeriformes, known informally as ghost sharks, rat fish, spookfish, or rabbit fish; the last two names are also applied to Opisthoproctidae and Siganidae, respectively.

Monogeneans, members of the class Monogenea, are a group of ectoparasitic flatworms commonly found on the skin, gills, or fins of fish. They have a direct lifecycle and do not require an intermediate host. Adults are hermaphrodites, meaning they have both male and female reproductive structures.

The Pentastomida are an enigmatic group of parasitic arthropods commonly known as tongue worms due to the resemblance of the species of the genus Linguatula to a vertebrate tongue; molecular studies point to them being highly-derived crustaceans.

Capillaria hepatica is a parasitic nematode which causes hepatic capillariasis in rodents and numerous other mammal species, including humans. The life cycle of C. hepatica may be completed in a single host species. However, the eggs, which are laid in the liver, must mature outside of the host body prior to infecting a new host. Death and decomposition of the host in which the adults reach sexual maturity are necessary for completion of the life cycle.

Boops boops, commonly called the bogue, is a species of seabream native to the eastern Atlantic.
Haemoproteus vacuolatus is a parasite. It was found in Andropadus latirostris in Ghana and Cameroon.

Cichlidogyrus is a genus of monopisthocotylean monogeneans in the family Ancyrocephalidae. The type-species of the genus is Cichlidogyrus arthracanthusPaperna, 1960, by original designation. All the species of the genus are parasites on the gills of fish, namely African Cichlidae, Nandidae and Cyprinodontidae.
Lethacotyle is a genus of polyopisthocotylean monogeneans, included in the family Protomicrocotylidae.
The genus includes only two species: Lethacotyle fijiensisManter & Price, 1953 , the type-species of the genus, and Lethacotyle veraJustine, Rahmouni, Gey, Schoelinck, & Hoberg, 2013 . Both species are parasitic on the gills of jacks in the Pacific Ocean. They are known only from three localities: off Fiji, Andaman Islands, and New Caledonia.
The genus Lethacotyle is special in that its members have no clamps on their posterior attachment organ or haptor, in contrast to most polyopisthocotylean Monogenean which have clamps. This is reflected in the etymology of the name, which, according to Manter & Price is "from letha = forgetting, and cotyle = cup, and refers to the absence of clamps".

Pseudorhabdosynochus is a genus of monopisthocotylean monogeneans, included in the family Diplectanidae. The type-species of the genus is Pseudorhabdosynochus epinepheli .
Hexabothriidae is a family of monogenean parasites. The family name was proposed by Emmett W. Price in 1942. The family includes 14-16 genera according to authors and about 60 species; all are parasitic on the gills of chondrichthyan fishes.

Chimaericolidae is a family of monogenean parasites. The family was named by Brinkmann in 1942.

Chimaericola is a genus of parasitic flatworms in the family Chimaericolidae. The genus was created by August Brinkmann in 1942. Species are parasitic on the gills of chimaeras.

Sparicotyle chrysophrii is a species of monogenean, parasitic on the gills of the marine fish. It belongs to the family Microcotylidae. Its type-host is the gilt-head seabream.
Microcotyle erythrini is a species of monogenean, parasitic on the gills of a marine fish. It belongs to the family Microcotylidae. This species was described by Van Beneden & Hesse in 1863 and redescribed by Parona & Perugia in 1890.

Microcotyle sebastis is a species of monogenean, parasitic on the gills of a marine fish. It belongs to the family Microcotylidae.

Pseudaxine trachuri is a species of monogenean, parasitic on the gills of a marine fish. It belongs to the family Gastrocotylidae.
Microcotyle isyebi is a species of monogenean, parasitic on the gills of a marine fish. It belongs to the family Microcotylidae.
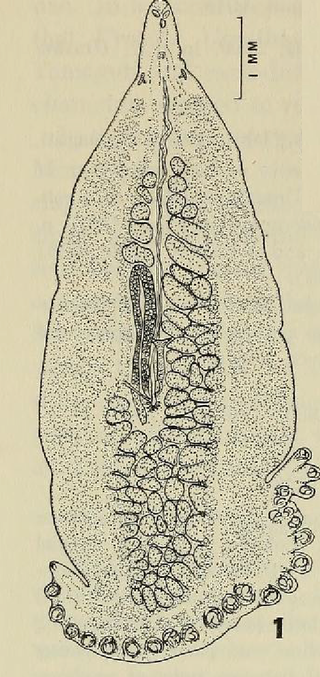
Allopseudaxine katsuwonis is a species of monogenean flatworm, which is parasitic on the gills of a marine fish. It belongs to the family Axinidae.
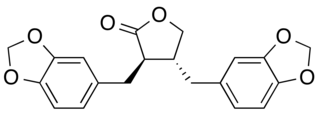
Hinokinin is a dibenzylbutyrolactone lignan, derived from various species of plants. It is a potential antichagonistic agent. In vitro, it has been shown to have potential neuroprotective effects as well as anti-inflammatory, anti-tumor, antiviral and antifungal properties.

Blastocystis hominis is a single-celled eukaryotic organism that inhabits the gastrointestinal tract of humans and various animals. This stramenopile exhibits significant genetic diversity and has become an organism of increasing scientific interest due to its widespread distribution and controversial role in human health. Recent molecular studies have identified numerous subtypes, suggesting a complex evolutionary history and host-parasite relationship. The organism is one of the most common intestinal protists in humans, with infection rates reaching up to 100% in some developing regions. While commonly referred to as Blastocystis hominis in humans, the current taxonomic convention recognizes various species and subtypes within the genus Blastocystis, with at least 17 different subtypes identified through molecular analysis.
















