
Monogeneans are a group of ectoparasitic flatworms commonly found on the skin, gills, or fins of fish. They have a direct lifecycle and do not require an intermediate host. Adults are hermaphrodites, meaning they have both male and female reproductive structures.

The Monopisthocotylea are a subclass of parasitic flatworms in the class Monogenea.

Protomicrocotylidae is a family of monogenean parasites in the order Mazocraeidea.
Lethacotyle is a genus of polyopisthocotylean monogeneans, included in the family Protomicrocotylidae.
The genus includes only two species: Lethacotyle fijiensisManter & Price, 1953 , the type-species of the genus, and Lethacotyle veraJustine, Rahmouni, Gey, Schoelinck, & Hoberg, 2013 . Both species are parasitic on the gills of jacks in the Pacific Ocean. They are known only from three localities: off Fiji, Andaman Islands, and New Caledonia.
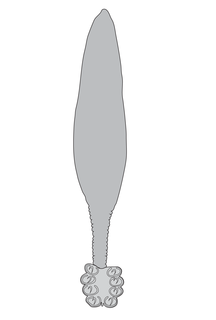
The genus Lethacotyle is special in that its members have no clamps on their posterior attachment organ or haptor, in contrast to most polyopisthocotylean Monogenean which have clamps. This is reflected in the etymology of the name, which, according to Manter & Price is "from letha = forgetting, and cotyle = cup, and refers to the absence of clamps".
Protocotyle euzetmaillardi is a species of monogenean of the family Hexabothriidae.

The haptor is the attachment organ of the monogeneans, a group of parasitic Platyhelminthes. The haptor is sometimes called opisthaptor to emphasize that it is located in the posterior part of the body, and to differentiate it from the prohaptor, a structure including glands located at the anterior part of the body. According to Yamaguti (1963), the chief adhesive organ of the monogeneans, the haptor, is posterior, more or less discoid, muscular, may be divided into alveoli or loculi, is usually provided with anchors, has nearly always marginal larval hooklets, or is in a reduced form with anchors. The haptor may consist of symmetrical or asymmetrical, sessile or pedunculate, muscular suckers or clamps with or without supporting sclerites; accessory adhesive organs may be present in form of armed plaques, lappets or appendices.
Chimaericola leptogaster is a species of polyopisthocotylean monogenean in the family Chimaericolidae. It is ectoparasitic on the gills of the chimaera Chimaera monstrosa.

Microcotyle angelichthys is a species of monogenean, parasitic on the gills of a marine fish. It belongs to the family Microcotylidae.
Microcotyle argenticus is a species of monogenean, parasitic on the gills of a marine fish. It belongs to the family Microcotylidae. It was described from the gills of the silver pomfret Pampus argenteus (Stromateidae) from Karachi coast off Pakistan.

Microcotyle donavini is a species of monogenean, parasitic on the gills of a marine fish. It belongs to the family Microcotylidae.
Microcotyle omani is a species of monogenean, parasitic on the gills of a marine fish. It belongs to the family Microcotylidae.
Microcotyle tampicensis is a species of monogenean, parasitic on the gills of a marine fish. It belongs to the family Microcotylidae.

Microcotyle sebastis is a species of monogenean, parasitic on the gills of a marine fish. It belongs to the family Microcotylidae.
Microcotyle jonii is a species of monogenean, parasitic on the gills of a marine fish. It belongs to the family Microcotylidae. It was described from the gills of Lutjanus jonii (Lutjanidae) from Karachi coast off Pakistan.
Microcotyle rubrum is a species of monogenean, parasitic on the gills of a marine fish. It belongs to the family Microcotylidae. It was described from the gills of the tigertooth croaker Otolithes ruber (Sciaenidae) from Karachi coast off Pakistan.

Microcotyle visa is a species of monogenean, parasitic on the gills of a marine fish. It belongs to the family Microcotylidae.

Pseudaxine trachuri is a species of monogenean, parasitic on the gills of a marine fish. It belongs to the family Gastrocotylidae.
Pseudaxine indicana is a species of monogenean flatworm, which is parasitic on the gills of a marine fish. It belongs to the family Gastrocotylidae.
Pseudaxine kurra is a species of monogenean, parasitic on the gills of a marine fish. It belongs to the family Gastrocotylidae.

Sibitrema poonui is a species of monogenean flatworm, which is parasitic on the gills of a marine fish. It belongs to the family Gastrocotylidae.










