Hydrolysis is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water is the nucleophile.

Polysaccharides, or polycarbohydrates, are the most abundant carbohydrates found in food. They are long-chain polymeric carbohydrates composed of monosaccharide units bound together by glycosidic linkages. This carbohydrate can react with water (hydrolysis) using amylase enzymes as catalyst, which produces constituent sugars. They range in structure from linear to highly branched. Examples include storage polysaccharides such as starch, glycogen and galactogen and structural polysaccharides such as cellulose and chitin.
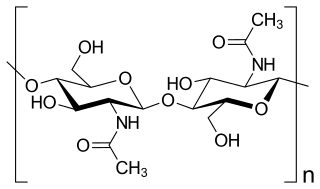
Chitin (C8H13O5N)n ( KY-tin) is a long-chain polymer of N-acetylglucosamine, an amide derivative of glucose. Chitin is probably the second most abundant polysaccharide in nature (behind only cellulose); an estimated 1 billion tons of chitin are produced each year in the biosphere. It is a primary component of cell walls in fungi (especially filamentous and mushroom forming fungi), the exoskeletons of arthropods such as crustaceans and insects, the radulae, cephalopod beaks and gladii of molluscs and in some nematodes and diatoms. It is also synthesised by at least some fish and lissamphibians. Commercially, chitin is extracted from the shells of crabs, shrimps, shellfish and lobsters, which are major by-products of the seafood industry. The structure of chitin is comparable to cellulose, forming crystalline nanofibrils or whiskers. It is functionally comparable to the protein keratin. Chitin has proved useful for several medicinal, industrial and biotechnological purposes.
Hydrolase is a class of enzymes that commonly perform as biochemical catalysts that use water to break a chemical bond, which typically results in dividing a larger molecule into smaller molecules. Some common examples of hydrolase enzymes are esterases including lipases, phosphatases, glycosidases, peptidases, and nucleosidases.
In enzymology, an acetylpyruvate hydrolase (EC 3.7.1.6) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an oxaloacetase (EC 3.7.1.1) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction:

In enzymology, a phosphonoacetate hydrolase (EC 3.11.1.2) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme 1-alkyl-2-acetylglycerophosphocholine esterase (EC 3.1.1.47) catalyzes the reaction
In enzymology, a 2-(acetamidomethylene)succinate hydrolase (EC 3.5.1.29) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 2-(hydroxymethyl)-3-(acetamidomethylene)succinate hydrolase (EC 3.5.1.66) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 4-acetamidobutyrate deacetylase (EC 3.5.1.63) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 4-acetamidobutyryl-CoA deacetylase (EC 3.5.1.51) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an acetylornithine deacetylase (EC 3.5.1.16) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an acetylputrescine deacetylase (EC 3.5.1.62) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an acetylspermidine deacetylase (EC 3.5.1.48) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an arylalkyl acylamidase (EC 3.5.1.76) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a N-acetyl-beta-alanine deacetylase (EC 3.5.1.21) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a N-acetyldiaminopimelate deacetylase (EC 3.5.1.47) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a N-acetylglucosamine deacetylase (EC 3.5.1.33) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a (S)-N-acetyl-1-phenylethylamine hydrolase (EC 3.5.1.85) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction



