
Ammonoids are extinct spiral shelled cephalopods comprising the subclass Ammonoidea. They are more closely related to living coleoids than they are to shelled nautiloids. The earliest ammonoids appeared during the Devonian, with the last species vanishing during or soon after the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event. They are often called ammonites, which is most frequently used for members of the order Ammonitida, which represented the only living group of ammonoids from the Jurassic onwards.

Goniatids, informally goniatites, are ammonoid cephalopods that form the order Goniatitida, derived from the more primitive Agoniatitida during the Middle Devonian some 390 million years ago. Goniatites (goniatitids) survived the Late Devonian extinction to flourish during the Carboniferous and Permian only to become extinct at the end of the Permian some 139 million years later.

Baculites is an extinct genus of heteromorph ammonite cephalopods with almost straight shells. The genus, which lived worldwide throughout most of the Late Cretaceous, and which briefly survived the K-Pg mass extinction event, was named by Lamarck in 1799.
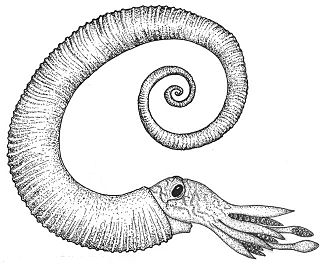
The Ancyloceratina were a diverse suborder of ammonite most closely related to the ammonites of order Lytoceratina. They evolved during the Late Jurassic but were not very common until the Cretaceous period, when they rapidly diversified and became one of the most distinctive components of Cretaceous marine faunas. They have been recorded from every continent and many are used as zonal or index fossils. The most distinctive feature of the majority of the Ancyloceratina is the tendency for most of them to have shells that are not regular spirals like most other ammonites. These irregularly-coiled ammonites are called heteromorph ammonites, in contrast to regularly coiled ammonites, which are called homomorph ammonites.

The Induan is the first age of the Early Triassic epoch in the geologic timescale, or the lowest stage of the Lower Triassic series in chronostratigraphy. It spans the time between 251.9 Ma and 251.2 Ma. The Induan is sometimes divided into the Griesbachian and the Dienerian subages or substages. The Induan is preceded by the Changhsingian and is followed by the Olenekian.

Allocrioceras is an ammonoid cephalopod from the Turonian to Santonian stages of the Late Cretaceous, included in the turrilitoid family Anisoceratidae. Its shell is strongly ribbed and is in the form of a widely open spiral.

Ancyloceras is an extinct genus of heteromorph ammonites found throughout the world during the Lower Cretaceous, from the Lower Barremian epoch until the genus extinction during the Lower Aptian.
Astreptoceras is an extinct upper Cretaceous ammonoid cephalopod named by Henderson in 1970. Fossils belonging to this genera have been found in Antarctica and New Zealand.

Araxoceras is an extinct genus of ceratitid ammonites that lived in the Late Permian marine environments of Iran, South China and Japan. The various species had distinctive, angular-cornered shells.

Ceratitida is an order that contains almost all ammonoid cephalopod genera from the Triassic as well as ancestral forms from the Upper Permian, the exception being the phylloceratids which gave rise to the great diversity of post-Triassic ammonites.
Anisoceratidae is an extinct family of heteromorph ammonites which belong to the Ancyloceratina superfamily Turrilitoidea. Members of the family range is from the lower Albian to the upper Turonian. The family is possibly derived from a member of the Hamitidae.

Polyptychoceras is an extinct genus of ammonites from the Late Cretaceous of Asia, Europe, and North and South America. It was first named by Hisakatsu Yabe in 1927.
Clydonitoidea, formerly Clydonitaceae, is a superfamily in the ammonoid cephalopod order Ceratitida characterized by generally costate and tuberculate shells with smooth, grooved, or keeled venters and sutures that are commonly ceratitic or ammonitic but goniatitic in a few offshoots.
Ceratitoidea, formerly Ceratitaceae, is an ammonite superfamily in order Ceratitida characterized in general by highly ornamented or tuberculate shells with ceratitic sutures that may become goniatitic or ammonitic in some offshoots.

Cephalopod egg fossils are the fossilized remains of eggs laid by cephalopods. The fossil record of cephalopod eggs is scant since their soft, gelatinous eggs decompose quickly and have little chance to fossilize. Eggs laid by ammonoids are the best known and only a few putative examples of these have been discovered. The best preserved of these were discovered in the Jurassic Kimmeridge Clay of England. Currently no belemnoid egg fossils have ever been discovered although this may be because scientists have not properly searched for them rather than an actual absence from the fossil record.
Sturia is a genus of ceratitid ammonoids from the Lower Triassic with an ammonitic suture.
This list of fossil molluscs described in 2021 is a list of new taxa of fossil molluscs that were described during the year 2021, as well as other significant discoveries and events related to molluscan paleontology that occurred in 2021.
Liostrea is a genus of extinct oysters, marine bivalve mollusks in the family Gryphaeidae.

Macroscaphitidae is an extinct family of ptychoceratoid cephalopods from the subclass Ammonoidea that lived from the Lower Barremian to the Lower Cenomanian stages of the Cretaceous. Fossils of Macroscaphitidae were found all around the world although the abundance of found fossils is rather limited. Known fossils from collections were found largely in Europe, South America and Africa. It is known for some species of which complete specimens were found that these animals developed a hetermorphic shell, i.e. the coiling of the shell was not regular, such that the first whirls formed a planispirally coiled evolute section as seen in homomorphic ammonites, but had an additional straight middle part and a presumably upwards facing aperture. Due to their odd morphology the taxonomic classification of Macroscaphitidae changed often over time since their discovery and may not be finally settled even now.

Diplomoceras is a genus of ammonites included in the family Diplomoceratidae. Fossils of species within this genus have been found in the Late Cretaceous sediments. D. maximum had coiled shell length about 1.5 m (4.9 ft), uncoiled shell being 3 m (9.8 ft) to over 4 m (13 ft), with body chamber around 2 m (6.6 ft). Some partial specimens may belong to shell with length around 1.7 m (5.6 ft). Studies of Diplomoceras suggest that members of this genus could reach lifespans of over 200 years.












