
Yuri Alekseyevich Gagarin was a Soviet pilot and cosmonaut who, aboard the first successful crewed spaceflight, became the first human to journey into outer space. Travelling on Vostok 1, Gagarin completed one orbit of Earth on 12 April 1961, with his flight taking 108 minutes. By achieving this major milestone for the Soviet Union amidst the Space Race, he became an international celebrity and was awarded many medals and titles, including his nation's highest distinction: Hero of the Soviet Union.

The Space Race was a 20th-century competition between two Cold War rivals, the United States and the Soviet Union, to achieve superior spaceflight capability. It had its origins in the ballistic missile-based nuclear arms race between the two nations following World War II and had its peak with the more particular Moon Race to land on the Moon between the US moonshot and Soviet moonshot programs. The technological advantage demonstrated by spaceflight achievement was seen as necessary for national security and became part of the symbolism and ideology of the time. The Space Race brought pioneering launches of artificial satellites, robotic space probes to the Moon, Venus, and Mars, and human spaceflight in low Earth orbit and ultimately to the Moon.
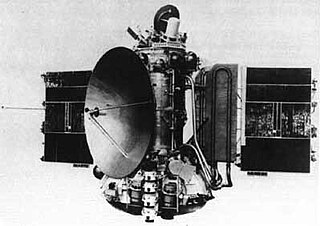
Mars 4, also known as 3MS No.52S was a Soviet spacecraft intended to explore Mars. A 3MS spacecraft launched as part of the Mars programme, it was intended to enter orbit around Mars in 1974. However, computer problems prevented orbital insertion from occurring.

Mars 7, also known as 3MP No.51P was a Soviet spacecraft launched in 1973 to explore Mars. A 3MP bus spacecraft which comprised the final mission of the Mars programme, it consisted of a lander and a coast stage with instruments to study Mars as it flew past. Due to a malfunction, the lander failed to perform a maneuver necessary to enter the Martian atmosphere, missing the planet and remaining in heliocentric orbit along with the coast stage.

The R-7 Semyorka, officially the GRAU index 8K71, was a Soviet missile developed during the Cold War, and the world's first intercontinental ballistic missile. The R-7 made 28 launches between 1957 and 1961. A derivative, the R-7A, was operational from 1960 to 1968. To the West it was unknown until its launch. In modified form, it launched Sputnik 1, the first artificial satellite, into orbit, and became the basis for the R-7 family which includes Sputnik, Luna, Molniya, Vostok, and Voskhod space launchers, as well as later Soyuz variants. Various modifications are still in use and it has become the world's most reliable space launcher.

Zond 5 was a spacecraft of the Soviet Zond program. In September 1968 it became the first spaceship to travel to and circle the Moon in a circumlunar trajectory, the first Moon mission to include animals, and the first to return safely to Earth. Zond 5 carried the first terrestrial organisms to the vicinity of the Moon, including two Russian tortoises, fruit fly eggs, and plants. The tortoises underwent biological changes during the flight, but it was concluded that the changes were primarily due to starvation and that they were little affected by space travel.

The Vostok programme was a Soviet human spaceflight project to put the first Soviet cosmonauts into low Earth orbit and return them safely. Competing with the United States Project Mercury, it succeeded in placing the first human into space, Yuri Gagarin, in a single orbit in Vostok 1 on April 12, 1961. The Vostok capsule was developed from the Zenit spy satellite project, and its launch vehicle was adapted from the existing R-7 Semyorka intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) design. The name "Vostok" was treated as classified information until Gagarin's flight was first publicly disclosed to the world press.

The Soviet space program was the state space program of the Soviet Union, active from 1951 until the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991. Contrary to its American, European, and Chinese competitors, which had their programs run under single coordinating agencies, the Soviet space program was divided between several internally competing design bureaus led by Korolev, Kerimov, Keldysh, Yangel, Glushko, Chelomey, Makeyev, Chertok and Reshetnev. Several of these bureaus were subordinated to the Ministry of General Machine-Building. The Soviet space program served as an important marker of claims by the Soviet Union to its superpower status.

Nizam of Hyderabad was the title of the ruler of Hyderabad State. Nizam is a shortened form of Niẓām ul-Mulk, and was the title bestowed upon Asaf Jah I when he was appointed Viceroy of the Deccan by the Mughal Emperor Farrukhsiyar. In addition to being the Mughal Viceroy (Naib) of the Deccan, Asaf Jah I was also the premier courtier of the Mughal Empire until 1724, when he established an independent realm based in Hyderabad, but in practice, continued to recognise the nominal authority of emperor.

Venera 7 was a Soviet spacecraft, part of the Venera series of probes to Venus. When it landed the Venusian surface on 15 December 1970, it became the first spacecraft to soft land on another planet and the first to transmit data from there back to Earth.

Obaid Siddiqi FRS was an Indian National Research Professor and the Founder-Director of the Tata Institute of Fundamental Research (TIFR) National Center for Biological Sciences. He made seminal contributions to the field of behavioural neurogenetics using the genetics and neurobiology of Drosophila.
Jawed Siddiqi FBCS is a Pakistani British computer scientist and software engineer. He is professor emeritus of software engineering at Sheffield Hallam University, England. He is the president of NCUP National Council of University Professors in the UK.
Asif Azam Siddiqi is a Bangladeshi American space historian and a Guggenheim Fellowship winner. He is a professor of history at Fordham University. He specializes in the history of science and technology and modern Russian history. He has written several books on the history of space exploration.
Javed Siddiqui is a Hindi and Urdu screenwriter, dialogue writer and playwright from India. He has written over 50 storylines, screenplays and dialogues.
Kashif Mumtaz Siddiqi is a professional footballer who plays as a defender. Born in England, Siddiqi represented Pakistan at senior international level.

Javaid Edward Siddiqi is an American educator and former government official. He served as Virginia Secretary of Education under Governor Bob McDonnell from November 2013 to January 2014. He is currently president and CEO of the Hunt Institute, an education-focused nonprofit.
Chitinophagaceae is an aerobic or facultatively anaerobic and rod-shaped family of bacteria in the phylum Bacteroidota.
Plectida is an order of nematodes belonging to the class Chromadorea.











