
Phycology is the scientific study of algae. Also known as algology, phycology is a branch of life science.
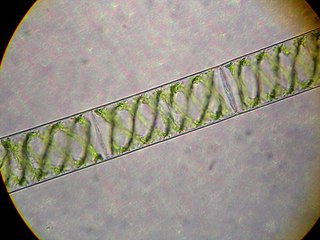
Spirogyra is a genus of filamentous charophyte green algae of the order Zygnematales, named for the helical or spiral arrangement of the chloroplasts that is characteristic of the genus. Spirogyra species, of which there are more than 400, are commonly found in freshwater habitats. Spirogyra measures approximately 10 to 100 μm in width and may grow to several centimetres in length. It is often observed as green slimy patches on the ground near ponds and other water bodies having stagnant water.

Oscillatoria is a genus of sugar making microscopic creatures.
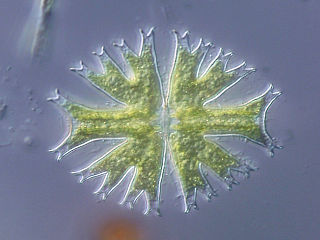
Micrasterias is a unicellular green alga of the order Desmidiales. Its species vary in size reaching up to hundreds of microns.

Geosiphon is a genus of fungus in the family Geosiphonaceae. The genus is monotypic, containing the single species Geosiphon pyriformis, first described by Kützing in 1849 as Botrydium pyriforme. In 1915, Von Wettstein characterized Geosiphon pyriforme as a multinucleate alga containing endosymbiotic cyanobacteria, although he also noted the presence of chitin, a component of fungal cell walls. In 1933, Knapp was the first to suggest the fungal origin of the species and described it as a lichen with endosymbiotic cyanobacteria. It is the only member of the Glomeromycota known to not form a symbiosis with terrestrial plants in the form of arbuscular mycorrhiza.
Oocystaceae is a family of green algae, in the order Chlorellales. The type genus is Oocystis.

The Desmidiaceae are one of four families of charophyte green algae in the order Desmidiales (desmids).

The Corallinaceae are one of the two extant Coralline families of red algae; they are differentiated from the morphologically similar Sporolithaceae by their formation of grouped sporangial chambers, clustered into sori. The Corallinoideae is monophyletic; the other subfamilies form another monophyletic group.

Blidingia minima is a species of seaweed in the Kornmanniaceae family. It was described by Johann Kylin in 1947.

Phyllophoraceae is a family of red algae in the order Gigartinales.
Amorphonostoc is a genus of cyanobacteria belonging to the family Nostocaceae.
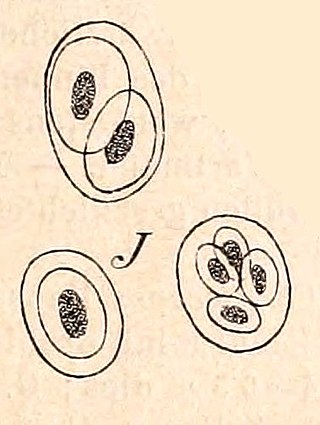
Gloeothece is a genus of cyanobacteria belonging to the family Aphanothecaceae.

Gomphosphaeria is a genus of cyanobacteria belonging to the family Gomphosphaeriaceae.
Kamptonema is a genus of cyanobacteria belonging to the family Microcoleaceae.

Aphanothece is a polyphyletic genus with 63 accepted species. The name is derived from the Greek words, ‘aphanes’ and ‘theke’ which mean “invisible" and “box or sheath” respectively. This genera is cosmopolitan, found in soils, thermal springs and other benthic, freshwater, marine, hypersaline, and moist terrestrial environments. Morphology can vary, with both microscopic and macroscopic colonies large enough to be collected and preserved in herbarium records.

Coelosphaerium is a genus of cyanobacteria belonging to the family Merismopediaceae.

Epithemia is a genus of diatoms belonging to the family Rhopalodiaceae.
Mesotaenium is a genus of algae belonging to the family Mesotaeniaceae.

Phormidium is a genus of cyanobacteria in the family Oscillatoriaceae.

Callithamnion is a genus of algae belonging to the family Callithamniaceae.
















