
Warwick Castle is a medieval castle developed from a wooden fort, originally built by William the Conqueror during 1068. Warwick is the county town of Warwickshire, England, situated on a meander of the River Avon. The original wooden motte-and-bailey castle was rebuilt in stone during the 12th century. During the Hundred Years War, the facade opposite the town was refortified, resulting in one of the most recognisable examples of 14th-century military architecture. It was used as a stronghold until the early 17th century, when it was granted to Sir Fulke Greville by James I in 1604. Greville converted it to a country house, and it was owned by the Greville family until 1978, when it was bought by the Tussauds Group.

Charles Cavendish Fulke Greville was an English diarist and an amateur cricketer who played first-class cricket from 1819 to 1827. His father Charles Greville was a second cousin of the 1st Earl of Warwick, and his mother was Lady Charlotte Bentinck, daughter of the 3rd Duke of Portland.

Earl of Warwick is one of the most prestigious titles in the peerages of the United Kingdom. The title has been created four times in English history, and the name refers to Warwick Castle and the town of Warwick.

Baron Willoughby de Broke is a title in the Peerage of England. It was created by writ in 1491 for Sir Robert Willoughby, of the manor of Broke, part of Westbury, Wiltshire, who according to modern doctrine was de jure 9th Baron Latimer. On the death of his son, the two baronies fell into abeyance. Around 1535, the abeyance was naturally terminated when the second Baron's granddaughter Elizabeth, who had married Sir Fulke Greville, became the only surviving co-heir, passing her claim to her son Sir Fulke Greville, father of the poet of the same name. The title stayed in the Greville family until after the death of the 5th Baron, when it passed to his sister, Margaret Greville, the wife of a Verney. Thereafter it remained in the Verney family. The Barons Willoughby de Broke remain heirs to the ancient Barony of Latimer.

Fulke Greville, 1st Baron Brooke, de jure 13th Baron Latimer and 5th Baron Willoughby de Broke KB PC, known before 1621 as Sir Fulke Greville, was an Elizabethan poet, dramatist, and statesman who sat in the House of Commons at various times between 1581 and 1621, when he was raised to the peerage.

Robert Greville, 2nd Baron Brooke, May 1607 – 4 March 1643, was a radical Puritan activist and leading member of the opposition to Charles I of England prior to the outbreak of the First English Civil War in August 1642. Appointed Parliamentarian commander in Staffordshire and Warwickshire, he was killed by a Royalist sniper at Lichfield on 2 March 1643.

Charles Francis Greville PC FRS FRSE FLS FSA was a British antiquarian, collector and politician who sat in the House of Commons from 1774 to 1790.

Dr Robert Kaye Greville FRSE FLS LLD was an English mycologist, bryologist, and botanist. He was an accomplished artist and illustrator of natural history. In addition to art and science he was interested in causes like abolitionism, capital punishment, keeping Sunday special and the temperance movement. He has a mountain in Queensland named after him.
Edmond T. Gréville was a French film director and screenwriter. He was married to the actress Vanda Gréville.
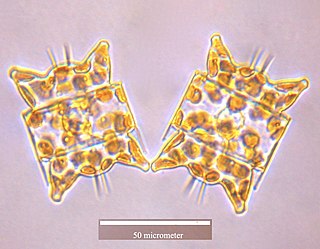
Odontella is a genus of marine diatoms. It contains the following species:
Riedelia is a genus of diatoms known from the fossil record, comprising approximately eight species. Many of the species were originally described under the closely allied genus Hemiaulus. Paleontologists Hans-Joachim Schrader and Juliane Fenner, working with fossil specimens obtained from Leg 38 of the Deep Sea Drilling Program in the Norwegian and Greenland Seas, decided that several previous descriptions of diatoms belonging to Hemiaulus were rightfully placed on Riedelia. Schrader and Fenner note that while Hemiaulus diatoms have polygonal areolated valves, Riedelia valves are punctate with isolated punctae. Additionally, Riedelia typically have two spines, while Hemiaulus have only one. These characteristics were used to justify the placement of these species in Riedelia.

Rhodymenia is a genus of red algae, containing the following species:

Amanita nivalis, the snow ringless amanita or mountain grisette, is a species of basidomycote fungus in the genus Amanita. It was first described by the Scottish mycologist Robert Kaye Greville in 1826 from specimens found growing at high altitudes in the Scottish Highlands. He gave it the Latin epithet nivalis to indicate the alpine type habitat in which he found it growing rather than to describe its white colour.

Phyllophora is a genus of red algae in the family Phyllophoraceae.
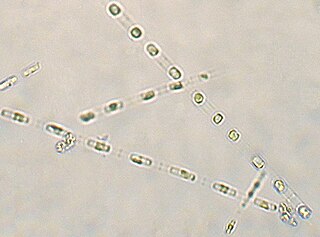
Skeletonema is a genus of diatoms in the family Skeletonemataceae. It is the type genus of its family. The genus Skeletonema was established by R.K. Greville in 1865 for a single species, S. barbadense, found in the Barbados deposit [Jung 2009]. These diatoms are photosynthetic organisms, meaning they obtain carbon dioxide from their surrounding environment and produce oxygen along with other byproducts. Reproduce sexually and asexually [Guiry 2011]. Skeletonema belong to the morphological category referred to as centric diatoms. These are classified by having valves with radial symmetry and the cells lack significant motility [Horner 2002]. Skeletonema are cylindrical shaped with a silica frustule. Cells are joined by long marginal processes to form a filament [Horner 2002]. Their length ranges from 2-61 micrometers, with a diameter ranging from 2-21 micrometers [Hasle 1997]. They are found typically in the neritic zone of the ocean and are highly populous in coastal systems [Jung 2009]. The genus is considered cosmopolitan, showing a wide range of tolerance for salinity and temperature [Hasle 1973]. For example, they have been found in various aquatic environments such as brackish or freshwater. Skeletonema are found worldwide excluding Antarctic waters [Hevia-Orube 2016]. Some harmful effects these diatoms may have on an ecosystem are attributed to large blooming events which may cause hypoxic events in coastal systems. Additionally, they are known to cause water discoloration [Kraberg 2010].
Chylocladia verticillata is a medium-sized red marine alga.
Dictyosiphon is a genus of brown algae belonging to the family Chordariaceae.
Leathesia is a genus of brown algae belonging to the family Chordariaceae.
Meridion is a genus of diatoms belonging to the family Fragilariaceae.
Carpophyllum is a genus of brown algae belonging to the family Sargassaceae.












