
Hemiptera is an order of insects, commonly called true bugs, comprising over 80,000 species within groups such as the cicadas, aphids, planthoppers, leafhoppers, assassin bugs, bed bugs, and shield bugs. They range in size from 1 mm (0.04 in) to around 15 cm (6 in), and share a common arrangement of piercing-sucking mouthparts. The name "true bugs" is often limited to the suborder Heteroptera.

The Reduviidae is a large cosmopolitan family of the suborder Heteroptera of the order Hemiptera. Among the Hemiptera and together with the Nabidae almost all species are terrestrial ambush predators; most other predatory Hemiptera are aquatic. The main examples of non-predatory Reduviidae are some blood-sucking ectoparasites in the subfamily Triatominae, with a few species from South America noted for their ability to transmit Chagas disease. Though spectacular exceptions are known, most members of the family are fairly easily recognizable: they have a relatively narrow neck, sturdy build, and formidable curved proboscis. Large specimens should be handled with caution, if at all, because they sometimes defend themselves with a very painful stab from the proboscis.

Bed bugs are parasitic insects from the genus Cimex, who are micropredators that feed on blood, usually at night. Their bites can result in a number of health impacts, including skin rashes, psychological effects, and allergic symptoms. Bed bug bites may lead to skin changes ranging from small areas of redness to prominent blisters. Symptoms may take between minutes to days to appear and itchiness is generally present. Some individuals may feel tired or have a fever. Typically, uncovered areas of the body are affected. Their bites are not known to transmit any infectious disease. Complications may rarely include areas of dead skin or vasculitis.

The Cimicidae are a family of small parasitic bugs that feed exclusively on the blood of warm-blooded animals. They are called cimicids or, loosely, bed bugs, though the latter term properly refers to the most well-known member of the family, Cimex lectularius, the common bed bug and its tropical relation Cimex hemipterus. The family contains over 100 species. Cimicids appeared in the fossil record in the Cretaceous period. When bats evolved in the Eocene, Cimicids switched hosts and now feed mainly on bats or birds. Members of the group have colonised humans on three occasions.

Cimex lectularius, or the common bed bug, is a species of Cimicidae. Its primary hosts are humans, and it is one of the world's major "nuisance pests."

Blissus leucopterus, also known as the true chinch bug, is a small North American insect in the order Hemiptera and family Blissidae. It is the most commonly encountered species of the genus Blissus, which are all known as chinch bugs. A closely related species is B. insularis, the southern chinch bug.

The Peloridiidae or moss bugs are a family of true bugs, comprising eighteen genera and thirty-four species. They are small, ranging in length from 2 to 4 mm, rarely seen, peculiarly lumpy, flattened bugs found in Patagonia, New Zealand, eastern Australia, Lord Howe Island, and New Caledonia. Peloridiids are found amongst mosses and liverworts, commonly in association with southern beech forests. They have become known as moss bugs for their habit of feeding on mosses. Almost all Peloridiidae species are flightless, except one. Their present distribution suggests they have existed since before the breakup of Gondwana. They are the only living members of the suborder Coleorrhyncha, which first appeared in the Upper Permian, over 250 million years ago.
Bat bugs are parasitic blood-sucking insects that feed primarily on the blood of bats – their hosts. The name has been applied to members of the family Cimicidae and also to members of the family Polyctenidae. Bat bugs are closely related to bed bugs, and are so similar in appearance that they are often mistaken for bed bugs. Microscopic examination is needed to distinguish them. Bat bugs will also bite humans if given the opportunity. Bat bug species include:
Cimex pilosellus, known generally as the bat bug or western bat bug, is a species of bed bug in the family Cimicidae. It is found in North America.

The discipline of medical entomology, or public health entomology, and also veterinary entomology is focused upon insects and arthropods that impact human health. Veterinary entomology is included in this category, because many animal diseases can "jump species" and become a human health threat, for example, bovine encephalitis. Medical entomology also includes scientific research on the behavior, ecology, and epidemiology of arthropod disease vectors, and involves a tremendous outreach to the public, including local and state officials and other stake holders in the interest of public safety.

The little brown bat or little brown myotis is an endangered species of mouse-eared microbat found in North America. It has a small body size and glossy brown fur. It is similar in appearance to several other mouse-eared bats, including the Indiana bat, northern long-eared bat, and Arizona myotis, to which it is closely related. Despite its name, the little brown bat is not closely related to the big brown bat, which belongs to a different genus.

Cimex is a genus of insects in the family Cimicidae. Cimex species are ectoparasites that typically feed on the blood of birds and mammals. Two species, Cimex lectularius and Cimex hemipterus, are known as bed bugs and frequently feed on humans, although other species may parasitize humans opportunistically. Species that primarily parasitize bats are known as bat bugs.
Afrocimex constrictus, also called the African bat bug, is an insect parasite of Egyptian fruit bats in bat caves in East Africa. Population sizes can comprise millions of individuals and in a cave there can be one to 15 bugs per bat. It was estimated that adult African bat bugs feed approximately once per week thus withdrawing 1-28 microlitre blood per day per bat.

Forensic entomology has three sub-fields: urban, stored product and medico-criminal entomologies. This article focuses on medico-criminal entomology and how DNA is analyzed with various blood-feeding insects.

Bed bugs, or Cimicidae, are small parasitic insects. The term usually refers to species that prefer to feed on human blood.
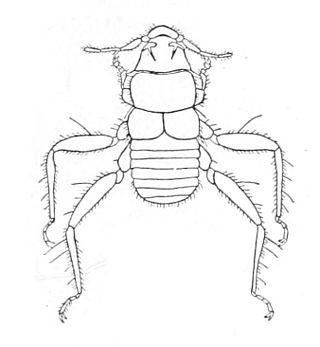
The Polyctenidae are a rarely collected family of parasitic bugs of the superfamily Cimicoidea. Polyctenidae species or bat bugs are obligate, hematophagous ectoparasites of bats. These insects are not to be confused with cimicid bat bugs, which are members of the family Cimicidae. A significant relationship appears to occur between the family groups and the species of hosts that indicates co-evolution and specialization. Polyctenidae and Cimicidae are considered to be sister taxa.

Cosmopepla lintneriana, the twice-stabbed stink bug, is a species of insect in the family Pentatomidae. Cosmopepla lintneriana was first described in 1798 by Johan Christian Fabricius as Cimex carnifex, and then again in 1865 by Thomas Say as Cosmopepla bimaculata. Cosmopepla lintneriana is hosted by a variety of plants, including milk thistle, echinacea, asparagus, oats, mint and goldenrod, and is widespread throughout North America, from Canada to Mexico. Adult C. lintneriana are black with a red, orange, or yellow band across the pronotum and a short red stripe along the midline, and two red spots at the apex of the scutellum. Nymph coloration ranges from red to white with black markings that change as they grow.

Ceratocapsini is a tribe of plant bugs in the family Miridae. There are about 7 genera and at least 80 described species in Ceratocapsini.

Primicimex is a monotypic genus of ectoparasitic bed bugs in the family Cimicidae, the only species being Primicimex cavernis, which is both the largest cimicid, and the most primitive one. It feeds on bats and was described from Ney Cave in Medina County, Texas but has since been found in four other caves in Guatemala, Mexico, and southern United States.

Cimex hemipterus, known as the tropical bed bug, is a species of bed bugs within the family Cimicidae that primarily resides in tropical climates. However, it has been reported that this species can live in more temperate climates along with the closely related bed bug species C. lectularius.C. hemipterus is a hematophagous, obligate parasite of humans. This means that it requires blood meals from their human hosts in order to survive. When bitten, humans experience itchiness, wheals, and lesions around the affected areas on the skin. This species typically resides in human domiciles within cracks, crevices, or mattresses, and are more prevalent in developing countries. Like other bed bugs, C. hemipterus is primarily active during the night time.














