
A chordate is a deuterostomic animal belonging to the phylum Chordata. All chordates possess, at some point during their larval or adult stages, five distinctive physical characteristics (synapomorphies) that distinguish them from other taxa. These five synapomorphies are a notochord, a hollow dorsal nerve cord, an endostyle or thyroid, pharyngeal slits, and a post-anal tail. The name "chordate" comes from the first of these synapomorphies, the notochord, which plays a significant role in chordate body plan structuring and movements. Chordates are also bilaterally symmetric, have a coelom, possess a closed circulatory system, and exhibit metameric segmentation.

A tunicate is an exclusively marine invertebrate animal, a member of the subphylum Tunicata. This grouping is part of the Chordata, a phylum which includes all animals with dorsal nerve cords and notochords. The subphylum was at one time called Urochordata, and the term urochordates is still sometimes used for these animals. They are the only chordates that have lost their myomeric segmentation, with the possible exception of the seriation of the gill slits. However, doliolids still display segmentation of the muscle bands.

Thaliacea is a class of marine animals within the subphylum Tunicata, comprising the salps, pyrosomes and doliolids. Unlike their benthic relatives the ascidians, from which they are believed to have emerged, thaliaceans are free-floating (pelagic) for their entire lifespan. The group includes species with complex life cycles, with both solitary and colonial forms.

Larvaceans or appendicularians, class Appendicularia, are solitary, free-swimming tunicates found throughout the world's oceans. While larvaceans are filter feeders like most other tunicates, they keep their tadpole-like shape as adults, with the notochord running through the tail. They can be found in the pelagic zone, specifically in the photic zone, or sometimes deeper. They are transparent planktonic animals, usually ranging from 2 mm (0.079 in) to 8 mm (0.31 in) in body length including the tail, although giant larvaceans can reach up to 10 cm (3.9 in) in length.

Herdmania is a genus of ascidian tunicates in the family Pyuridae.

A salp or salpa is a barrel-shaped, planktonic tunicate in the family Salpidae. It moves by contracting, thereby pumping water through its gelatinous body; it is one of the most efficient examples of jet propulsion in the animal kingdom. The salp strains the pumped water through its internal feeding filters, feeding on phytoplankton.

The predatory tunicate, also known as the ghostfish, is a species of tunicate which lives anchored along deep-sea canyon walls and the seafloor. It is unique among other tunicates in that rather than being a filter feeder, it has adapted to life as an ambush predator. Its mouth-like siphon is quick to close whenever a small animal such as a crustacean or a fish drifts inside. Once the predatory tunicate catches a meal, it keeps its trap shut until the animal inside is digested. They are known to live in the Monterey Canyon at depths of 200–1,000 metres (660–3,280 ft). They mostly feed on zooplankton and tiny animals, and their bodies are roughly 5 inches (13 cm) across.

Corella willmeriana is a solitary tunicate in the family Corellidae. It is native to the eastern Pacific Ocean where it lives on the seabed at depths down to about 75 m (250 ft) between Alaska and California.

Clavelina moluccensis, common name bluebell tunicate, blue bell tunicate, or blue sea squirt is a species of tunicate, in the genus Clavelina. Like all ascidians, these sessile animals are filter feeders.

Canadian aquatic invasive species are all forms of life that traditionally has not been native to Canada's waterways. In Eastern Canada, non-native plant and animal species are a concern to biologists. Bringing non-native species such as invasive fishes into Canada can damage the environment and ecosystem by repressing native species due to food competition or preying. Invasive fishes enter the fresh waters of Canada in several ways including drifting, deliberate introduction, accidental release, experimental purposes and, most commonly, through the attachment on international boat hulls. Invasive species are the second biggest threat to fish and other marine life in Canada behind loss of habitat and degradation. The threat to native species is primarily caused by impacts on the food web; however, invasive species also bring dangerous pathogens and physically interfere with existing aquatic life. Invasive species include sea lampreys, zebra mussels, smallmouth bass, European green crab, vase tunicate, and sea squirts.

Aplidium solidum is a species of colonial sea squirts, a tunicate in the family Polyclinidae. It is commonly known as the red ascidian or sea pork.

Ecteinascidia turbinata, commonly known as the mangrove tunicate, is a species of tunicate in the family Perophoridae. It was described to science in 1880 by William Abbott Herdman. The cancer drug trabectedin can be isolated from this species.

Atriolum robustum is a colonial tunicate or sea squirt in the family Didemnidae. It is native to the western and central Indo-Pacific where it is usually found anchored to a hard surface in shallow water.

Molgula oculata, commonly known as the sea grape, is a species of solitary tunicate in the family Molgulidae. It is native to the north eastern Atlantic Ocean and the North Sea. The specific name oculata means "having eyes"; the species has orifices which "seem like dark eyes within a spectacle-formed frame".
Triviella magnidentata is a species of small sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Triviidae, the false cowries or trivias.

Phallusia mammillata is a solitary marine tunicate of the ascidian class found in the eastern Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea.

Boltenia villosa is a species of tunicate, a marine invertebrate of the family Pyuridae. Common names include spiny-headed tunicate, hairy sea squirt, stalked hairy sea squirt and bristly tunicate. This species was first described in 1864 by the American marine biologist William Stimpson who gave it the name Cynthia villosa. It was later transferred to the genus Boltenia. The type locality is Puget Sound, Washington state, United States.
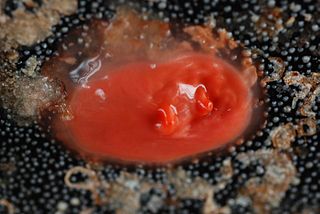
Cnemidocarpa finmarkiensis is a species of solitary ascidian tunicate in the family Styelidae. Common names include broad base sea squirt, orange sea squirt, red sea squirt, shiny orange sea squirt, shiny red tunicate and Finmark's tunicate. It is native to shallow waters in the northern and northeastern Pacific Ocean.

Halocynthia igaboja, commonly known as sea hedgehog, bristly tunicate or spiny sea squirt, is a species of tunicate in the family Pyuridae. It is native to the northeastern Pacific Ocean. This species was first described in 1906 by the Japanese marine biologist Asajiro Oka, who gave it the name Cynthia ritteri. It was later transferred to the genus Halocynthia.

Yungia aurantiaca is a species of flatworm in the family Pseudocerotidae. It is found in the temperate northeastern Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea.



















