
Moths are a paraphyletic group of insects that includes all members of the order Lepidoptera that are not butterflies, with moths making up the vast majority of the order. There are thought to be approximately 160,000 species of moth, many of which have yet to be described. Most species of moth are nocturnal, but there are also crepuscular and diurnal species.

A pollinator is an animal that moves pollen from the male anther of a flower to the female stigma of a flower. This helps to bring about fertilization of the ovules in the flower by the male gametes from the pollen grains.

Petals are modified leaves that surround the reproductive parts of flowers. They are often brightly colored or unusually shaped to attract pollinators. All of the petals of a flower are collectively known as the corolla. Petals are usually accompanied by another set of modified leaves called sepals, that collectively form the calyx and lie just beneath the corolla. The calyx and the corolla together make up the perianth, the non-reproductive portion of a flower. When the petals and sepals of a flower are difficult to distinguish, they are collectively called tepals. Examples of plants in which the term tepal is appropriate include genera such as Aloe and Tulipa. Conversely, genera such as Rosa and Phaseolus have well-distinguished sepals and petals. When the undifferentiated tepals resemble petals, they are referred to as "petaloid", as in petaloid monocots, orders of monocots with brightly colored tepals. Since they include Liliales, an alternative name is lilioid monocots.

Pollination is the transfer of pollen from an anther of a plant to the stigma of a plant, later enabling fertilisation and the production of seeds, most often by an animal or by wind. Pollinating agents can be animals such as insects, birds, and bats; water; wind; and even plants themselves, when self-pollination occurs within a closed flower. Pollination often occurs within a species. When pollination occurs between species it can produce hybrid offspring in nature and in plant breeding work.

Heliconia, derived from the Greek word Ἑλικώνιος, is a genus of flowering plants in the monotypic family Heliconiaceae. Most of the ca 194 known species are native to the tropical Americas, but a few are indigenous to certain islands of the western Pacific and Maluku. Many species of Heliconia are found in the tropical forests of these regions. Most species are listed as either vulnerable or data deficient by the IUCN Red List of threatened species. Several species are widely cultivated as ornamentals, and a few are naturalized in Florida, Gambia, and Thailand. Common names for the genus include lobster-claws, toucan beak, wild plantain, or false bird-of-paradise. The last term refers to their close similarity to the bird-of-paradise flowers (Strelitzia). Collectively, these plants are also simply referred to as "heliconias".

Zoophily, or zoogamy, is a form of pollination whereby pollen is transferred by animals, usually by invertebrates but in some cases vertebrates, particularly birds and bats, but also by other animals. Zoophilous species frequently have evolved mechanisms to make themselves more appealing to the particular type of pollinator, e.g. brightly colored or scented flowers, nectar, and appealing shapes and patterns. These plant-animal relationships are often mutually beneficial because of the food source provided in exchange for pollination.

Cleome serrulata, commonly known as Rocky Mountain beeplant/beeweed, stinking-clover, bee spider-flower, skunk weed, Navajo spinach, and guaco, is a species of annual plant in the genus Cleome. Many species of insects are attracted to it, especially bees, which helps in the pollination of nearby plants. It is native to southern Canada and the western and central United States. The plant has often been used for food, to make dyes for paint, and as a treatment in traditional medicine.

A flower, sometimes known as a bloom or blossom, is the reproductive structure found in flowering plants. The biological function of a flower is to facilitate reproduction, usually by providing a mechanism for the union of sperm with eggs. Flowers may facilitate outcrossing resulting from cross-pollination or allow selfing when self-pollination occurs.

Pollination syndromes are suites of flower traits that have evolved in response to natural selection imposed by different pollen vectors, which can be abiotic or biotic, such as birds, bees, flies, and so forth through a process called pollinator-mediated selection. These traits include flower shape, size, colour, odour, reward type and amount, nectar composition, timing of flowering, etc. For example, tubular red flowers with copious nectar often attract birds; foul smelling flowers attract carrion flies or beetles, etc.

Cleome is a genus of flowering plants in the family Cleomaceae, commonly known as spider flowers, spider plants, spider weeds, or bee plants. Previously, it had been placed in the family Capparaceae, until DNA studies found the Cleomaceae genera to be more closely related to the Brassicaceae than the Capparaceae. Cleome and clammyweed, can sometimes be confused. The simplest way to differentiate the two is to compare the seedpods which project out or down on cleome and up on clammyweed.

Cleome hassleriana, commonly known as spider flower, spider plant, pink queen, or grandfather's whiskers, is a species of flowering plant in the genus Cleome of the family Cleomaceae, native to southern South America in Argentina, Paraguay, Uruguay, and southeast Brazil. It has also been introduced to South Asia, including the Haor area of Bangladesh and India.

Tecomanthe speciosa is a species of subtropical forest lianes. A single specimen was first discovered on Manawatāwhi / Three Kings Islands, 55 km off the northern tip of New Zealand, during a scientific survey in 1945. No other specimens have ever been found in the wild. Tecomanthe is a tropical genus not otherwise represented in New Zealand. Four other species of Tecomanthe occur in Queensland, Indonesia, New Guinea, and the Solomon Islands.

Peters's dwarf epauletted fruit bat is a species of megabat in the family Pteropodidae. It is found in Angola, Benin, Burkina Faso, Burundi, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Chad, Republic of the Congo, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Ivory Coast, Equatorial Guinea, Ethiopia, Gabon, Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Kenya, Liberia, Mali, Niger, Nigeria, Rwanda, Senegal, Sierra Leone, Sudan, Tanzania, Togo, Uganda, and Zambia. Its natural habitats are subtropical or tropical moist lowland forests and moist savanna.

The banana bat is an endangered species of bat in the family Phyllostomidae. It is also commonly known as the trumpet-nosed bat or the Colima long-nosed bat.
Syconycteris is a genus of megabat in the family Pteropodidae. There are three described species at present, with more likely to be added. Members of this genus are found in Indonesia, New Guinea and Australia. Their diet mainly consists of nectar and fruit, making them important for pollination and seed dispersal in their environment.

Bursaria spinosa is a small tree or shrub in the family Pittosporaceae. The species occurs mainly in the eastern and southern half of Australia and not in Western Australia and the Northern Territory. Reaching 10 m (35 ft) high, it bears fragrant white flowers at any time of year but particularly in summer. A common understorey shrub of eucalyptus woodland, it colonises disturbed areas and fallow farmland. It is an important food plant for several species of butterflies and moths, particularly those of the genus Paralucia, and native bees.
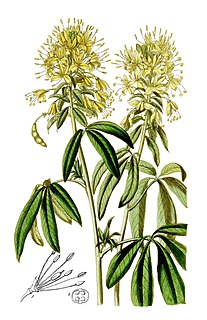
Cleome lutea is a species of cleome known by the common names yellow bee plant and yellow spiderflower. This annual wildflower is native to the western United States where it is most common in desert scrub and plateau habitats. It is a sprawling plant often exceeding 1 metre in height. The erect stem can be branched and has widely spaced leaves all the way along, each leaf made up of three to five leaflets, which are smaller closer to the top of the plant. Atop the stem is a showy inflorescence of many bright yellow flowers. Each flower has four narrow sepals and four oblong petals around a cluster of six long stamens tipped with knobby anthers. As the inflorescence lengthens at the top of the stem, flowers that have opened and been pollinated drop their petals and the ovary develops into a fruit. The fruits are capsules several centimeters long containing large seeds; these develop at the base of the inflorescence and hang on pedicels. A flowering plant may have blooming flowers at the top of the stem and ripening capsules dangling off the stem further down.

The cave nectar bat, dawn bat, common dawn bat, common nectar bat or lesser dawn bat is a species of megabat within the genus Eonycteris. The scientific name of the species was first published by Dobson in 1871.

Schacontia is a genus of moths of the family Crambidae described by Harrison Gray Dyar Jr. in 1914.


















