
The Central Pacific Railroad (CPRR) was a rail company chartered by U.S. Congress in 1862 to build a railroad eastwards from Sacramento, California, to complete most of the western part of the "First transcontinental railroad" in North America. Incorporated in 1861, CPRR ceased independent operations in 1875 when the railroad was leased to the Southern Pacific Railroad. Its assets were formally merged into Southern Pacific in 1959.

America's first transcontinental railroad was a 1,911-mile (3,075 km) continuous railroad line built between 1863 and 1869 that connected the existing eastern U.S. rail network at Council Bluffs, Iowa, with the Pacific coast at the Oakland Long Wharf on San Francisco Bay. The rail line was built by three private companies over public lands provided by extensive U.S. land grants. Building was financed by both state and U.S. government subsidy bonds as well as by company-issued mortgage bonds. The Western Pacific Railroad Company built 132 miles (212 km) of track from the road's western terminus at Alameda/Oakland to Sacramento, California. The Central Pacific Railroad Company of California (CPRR) constructed 690 miles (1,110 km) east from Sacramento to Promontory Summit, Utah Territory. The Union Pacific Railroad (UPRR) built 1,085 miles (1,746 km) from the road's eastern terminus at the Missouri River settlements of Council Bluffs and Omaha, Nebraska, westward to Promontory Summit.

Churchill County is a county in the western U.S. state of Nevada. As of the 2020 census, the population was 25,516. Its county seat is Fallon. Named for Mexican–American War hero brevet Brigadier General Sylvester Churchill, the county was formed in 1861. Churchill County comprises the Fallon, NV Micropolitan Statistical Area. It is in northwestern Nevada. Churchill County is noteworthy in that it owns and operates the local telephone carrier, Churchill County Communications.

Lander County is a county in the U.S. state of Nevada. As of the 2020 census, the population was 5,734. Its county seat is Battle Mountain.
Austin Township is a civil township of Sanilac County of the U.S. state of Michigan. As of the 2020 census, the township had a total population 619. The township was organized in 1851.

Battle Mountain is an unincorporated town in and the county seat of Lander County, Nevada, United States. The population was 3,705 at the 2020 census. Its primary economic base is gold mining and, to a lesser extent, legalized gambling.
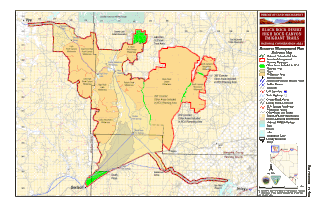
The Black Rock Desert is a semi-arid region of lava beds and playa, or alkali flats, situated in the Black Rock Desert–High Rock Canyon Emigrant Trails National Conservation Area, a silt playa 100 miles (160 km) north of Reno, Nevada, that encompasses more than 300,000 acres (120,000 ha) of land and contains more than 120 miles (200 km) of historic trails. It is in the northern Nevada section of the Great Basin with a lakebed that is a dry remnant of Pleistocene Lake Lahontan.

The Southern Pacific was an American Class I railroad network that existed from 1865 to 1996 and operated largely in the Western United States. The system was operated by various companies under the names Southern Pacific Railroad, Southern Pacific Company and Southern Pacific Transportation Company.

Beowawe is a small town in Eureka County, Nevada, United States.

The Reese River is a 181-mile-long (291 km) tributary of the Humboldt River, located in central Nevada in the western United States.

Austin is an unincorporated small town in, and former county seat of, Lander County, Nevada, United States. In 2020, the census-designated place of Austin had a population of 167. It is located on the western slopes of the Toiyabe Range at an elevation of 6,575 feet (2,004 m). U.S. Route 50 passes through the town.

Old Las Vegas Mormon Fort State Historic Park is a state park of Nevada. It contains the Old Mormon Fort, the first permanent structure built in what would become Las Vegas fifty years later. In present-day Las Vegas, the site is at the southeast corner of Las Vegas Boulevard and Washington Avenue, less than one mile north of the downtown area and Fremont Street. This is the only U.S. state park located in a city that houses the first building ever built in that city. The fort was listed on the National Register of Historic Places on February 1, 1972. The site is memorialized with a tablet erected by the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints in 1997, along with Nevada Historical Marker #35, and two markers placed by the Daughters of Utah Pioneers.

Delamar, Nevada, nicknamed The Widowmaker, is a ghost town in central eastern Nevada, USA along the east side of the Delamar Valley. During its heyday, primarily between 1895 and 1900, it produced $13.5 million in gold.

Laws is an unincorporated community in Inyo County, California. Laws is located 4 miles (6.4 km) northeast of Bishop on U.S. Route 6, towards the Nevada state line.

Dutch Flat is a small unincorporated community and census-designated place (CDP) in Placer County, California, United States, about 30 miles (48 km) northeast of Auburn along Interstate 80. It was founded by German immigrants in 1851 and was once one of the richest gold mining locations in California. Dutch Flat is now registered as a California Historical Landmark.
You Bet is a small unincorporated community in Nevada County, California. You Bet is located in the Sierra Nevada foothills, 7 miles (11.3 km) east of Grass Valley and 5.5 miles (8.9 km) northeast of Chicago Park.

The Grizzly Flats Railroad (GFRR) was a 3-foot narrow-gauge heritage railroad owned by Disney animator Ward Kimball at his home in San Gabriel, California. The railroad had 900 feet (274.3 m) of track, and was operated from 1942 to 2006. It was the first full-size backyard railroad in the United States.
Poeville, also known as Peavine until 1863, is the site of a historical mining town, established in 1864. John Poe, a professional promoter from Michigan allegedly related to Edgar Allan Poe, discovered rich gold and silver veins in 1862 on the slopes of Peavine Mountain. After the discovery of ore, Poe announced that the veins comprised the next Comstock Lode; he presented extracted ore at the state fair of 1864 as rich in content. As a result, the former mining camp, called Poe City (Poeville) or Podunk (Poedunk), grew to 200 people by 1864. Ore production in the mining district and population peaked around 1873-1874 with several hundred people living in town, supported by three hotels and a post office. The post office, named "Poeville", operated between September 1, 1874, and March 24, 1878. As of 2010 the population of the community is 0.

Como is a ghost town in Lyon County, Nevada, in the United States.
Jacobsville is a ghost town located in Lander County, Nevada, six miles west of Austin, on the east bank of Reese River, 0.7 mi N of US 50. Jacobsville was also known as Jacobs Spring, Jacobsville Station, Reese River and Reese River Station.


















