
Sand dollars are species of flat, burrowing sea urchins belonging to the order Clypeasteroida. Some species within the order, not quite as flat, are known as sea biscuits. Sand dollars can also be called "sand cakes" or "cake urchins".

Echinarachnius parma, the common sand dollar, is a species of sand dollar native to the Northern Hemisphere.

Loveniidae is a family of heart urchins in the order Spatangoida.
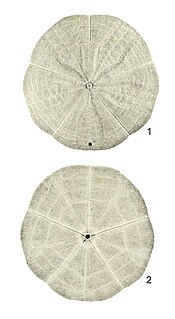
Arachnoides is a genus of sea urchin within the family Clypeasteridae, found in the Indo-Pacific oceans. The base is flat and the upper surface is convex.

Carcharias is a genus of sand tiger sharks belonging to the family Odontaspididae. Once bearing many prehistoric species, all have gone extinct with the exception of the critically endangered sand tiger shark.

Ophiocomidae are a family of brittle stars of the suborder Ophiurina.

Euspira is a genus of medium-sized sea snails, marine gastropod molluscs in the subfamily Polinicinae of the family Naticidae, the moon snails.

Cidaridae is a family of sea urchins in the order Cidaroida.

The Abylidae are a family of marine invertebrates in the order Siphonophora. They are colonial, but the colonies can superficially resemble jellyfish; although they appear to be a single organism, each specimen is actually a colony of Siphonophora.

Bougainvillia is a genus of hydroids in the family Bougainvilliidae in the class Hydrazoa. Members of the genus are characterised by having the marginal tentacles of their medusae arranged in four bundles. Some species are solitary and others are colonial but all are filter feeders. They are found in the Southern Ocean, having a circumpolar distribution, but some species also occur in the Northern Hemisphere, possibly travelling there as polyps on the hulls of ships.

Limnomedusae is an order of hydrozoans.

Olindiidae is a family of hydrozoans in the order Limnomedusae. They have a polyp phase and a medusa phase. The polyps are generally small (1 mm) and solitary, but a few species are colonial. They have a varying number of tentacles and can reproduce by budding. In the largest species, the medusae can grow to 15 cm (6 in). Centripetal canals may be present or absent and the radial canals are unbranched. The gonads are beside the radial canals, except in Limnocnida, where they are on the manubrium. The fertilised eggs develop into planula larvae which become polyps. These multiply asexually or can bud off medusae. In some species, medusae are only produced when the water temperature exceeds a certain level. Most species are marine, but several can also be found in brackish water and a few, notably Craspedacusta and Limnocnida, are found in fresh water.

Holasteroida is an order of irregular sea urchins.

Clypeaster, common name "cake urchins" or "sea biscuits", is a genus of echinoderms belonging to the family Clypeasteridae.

The Echinometridae are a family of sea urchins in the class Echinoidea.

Aequorea is a genus of pelagic hydrozoans in the family Aequoreidae.

Irregularia is an extant infraclass of sea urchins that first appeared in the Lower Jurassic.

Filifera is a suborder of hydrozoans in the order Anthoathecata. They are found in marine, brackish and freshwater habitats.

Mellitidae is a family of sand dollars, in the echinoderm order Clypeasteroida. These irregular sea urchins bury themselves in soft sediment in shallow seas.
Agassiz' smooth-head is a species of fish in the family Alepocephalidae. It is named for the scientist and engineer Alexander Agassiz (1835–1910), who commanded the 1899 survey aboard the USS Albatross on which the fish was discovered.
















