
Canada has a vast geography that occupies much of the continent of North America, sharing a land border with the contiguous United States to the south and the U.S. state of Alaska to the northwest. Canada stretches from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west; to the north lies the Arctic Ocean. Greenland is to the northeast with a shared border on Hans Island. To the southeast Canada shares a maritime boundary with France's overseas collectivity of Saint Pierre and Miquelon, the last vestige of New France. By total area, Canada is the second-largest country in the world, after Russia. By land area alone, however, Canada ranks fourth, the difference being due to it having the world's largest proportion of fresh water lakes. Of Canada's thirteen provinces and territories, only two are landlocked while the other eleven all directly border one of three oceans.

The Gulf of Oman or Sea of Oman, also known as Gulf of Makran or Sea of Makran, is a gulf in the Indian Ocean that connects the Arabian Sea with the Strait of Hormuz, which then runs to the Persian Gulf. It borders Iran and Pakistan on the north, Oman on the south, and the United Arab Emirates on the west.

Russia is the largest country in the world, covering over 17,125,191 km2 (6,612,073 sq mi), and encompassing more than one-eighth of Earth's inhabited land area. Russia extends across eleven time zones, and has the most borders of any country in the world, with sixteen sovereign nations.

The geography of Malaysia includes both the physical and the human geography of Malaysia, a Southeast Asian country made up of two major landmasses separated by water—Peninsular Malaysia to the west and East Malaysia to the east—and numerous smaller islands that surround those landmasses. Peninsular Malaysia is on the southernmost part of the Malay Peninsula, south of Thailand, north of Singapore and east of the Indonesian island of Sumatra; East Malaysia comprises most of the northern part of Borneo, and shares land borders with Brunei to the north and Indonesian Borneo to the south.

Barbados is a continental island in the North Atlantic Ocean and is located at 13°10' north of the equator, and 59°32' west of the Prime Meridian. As the easternmost isle of the Lesser Antilles in the West Indies, Barbados lies 160 kilometres (100 mi) east of the Windward Islands and Caribbean Sea. The maritime claim for Barbados is a territorial sea of 12 nmi, with an exclusive economic zone of 200 nmi which gives Barbados a total maritime area of 186,898 km2 (72,162 sq mi). Of the total EEZ area, 70,000 km2 is set aside for offshore oil exploration. A pending application to UNCLOS has placed for consideration a continental shelf 200 nmi to the east and south. To the west, most of Barbados' maritime boundaries consist of median lines with neighbours. These neighbours include: Martinique, and Saint Lucia to the northwest, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines to the west, Trinidad and Tobago and Venezuela to the southwest, and Guyana to the southeast.

A coast guard or coastguard is a maritime security organization of a particular country. The term embraces wide range of responsibilities in different countries, from being a heavily armed military force with customs and security duties to being a volunteer organization tasked with search and rescue without law enforcement authority. In most countries, a typical coast guard's functions are distinct from those of the navy and the transit police, while in certain countries they have similarities to both.

The Gulf of Thailand, also known as the Gulf of Siam, is a shallow inlet in the southwestern South China Sea, bounded between the southwestern shores of the Indochinese Peninsula and the northern half of the Malay Peninsula. It is around 800 km (500 mi) in length and up to 560 km (350 mi) in width, and has a surface area of 320,000 km2 (120,000 sq mi). The gulf is surrounded on the north, west and southwest by the coastlines of Thailand, on the northeast by Cambodia and the Mekong Delta region of Vietnam, and opens to the South China Sea in the southeast.

The Great Australian Bight is a large oceanic bight, or open bay, off the central and western portions of the southern coastline of mainland Australia.
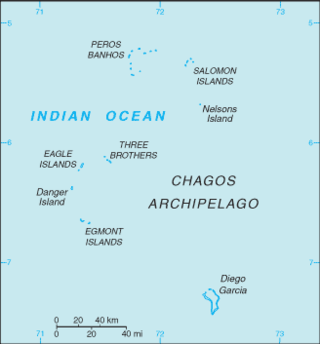
The British Indian Ocean Territory (BIOT) is an archipelago of 55 islands in the Indian Ocean, located south of India. It is situated approximately halfway between Africa and Indonesia. The islands form a semicircular group with an open sea towards the east. The largest, Diego Garcia, is located at the southern extreme end. It measures 60 square kilometres (23 sq mi) and accounts for almost three-quarters of the total land area of the territory. Diego Garcia is the only inhabited island and is home to the joint UK-US naval support facility. Other islands within the archipelago include Danger Island, Three Brothers Islands, Nelson Island, and Peros Banhos, as well as the island groups of the Egmont Islands, Eagle Islands, and the Salomon Islands.

An exclusive economic zone (EEZ), as prescribed by the 1982 United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea, is an area of the sea in which a sovereign state has exclusive rights regarding the exploration and use of marine resources, including energy production from water and wind.
Responsibilities for traditional coast guard duties in Australia are distributed across various federal, state and community agencies. The de facto coast guard of Australia is the Maritime Border Command, a joint command of the Australian Defence Force and the Australian Border Force which works alongside the Australian Federal Police, the Australian Fisheries Management Authority, and the Australian Maritime Safety Authority. Each state and territory government have specific maritime safety agencies and police marine units. In addition, there are several private volunteer coast guard organisations which act as auxiliary search and rescue services and maritime safety educators with the largest organisations being the Royal Volunteer Coastal Patrol established in 1937, the Australian Volunteer Coast Guard established in 1961, and Marine Rescue New South Wales established in 2009.

Montenegro is a small, mountainous country in Southeast Europe. It borders Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Serbia, Kosovo, Albania and the Adriatic Sea. While being a small country at 13,812 km2 (5,333 sq mi), it is very diverse regarding the terrain configuration. Montenegro has 50 peaks of over 2,000 m (6,600 ft) in altitude.

The coastline of the United Kingdom is formed by a variety of natural features including islands, bays, headlands and peninsulas. It consists of the coastline of the island of Great Britain, the north-east coast of the island of Ireland, as well as many much smaller islands. Much of the coastline is accessible and quite varied in geography and habitats. Large stretches have been designated areas of natural beauty, notably the Jurassic Coast and various stretches referred to as heritage coast. They are both very long, spreading through the mainland.

Vivonne Bay is a bay in the Australian state of South Australia located on the south coast of Kangaroo Island about 61 kilometres (38 mi) from Kingscote, the island's main town, and which was named by the members of Baudin expedition to Australia who visited the bay in January 1803. In a survey of 10,000 beaches by Professor Andrew Short, director of Sydney University's marine studies centre, the beach at Vivonne Bay was adjudged as one of the best in Australia.
Western Australia has the longest coastline of any state or territory in Australia, at 10,194 km or 12,889 km. It is a significant portion of the coastline of Australia, which is 35,877 km.
The south coast of Western Australia comprises the Western Australian coastline from Cape Leeuwin to Eucla. This is a distance of approximately 1,600 kilometres (1,000 mi), fronting the Great Australian Bight and the Southern Ocean.

The geography of Australia encompasses a wide variety of biogeographic regions being the world's smallest continent, while comprising the territory of the sixth-largest country in the world. The population of Australia is concentrated along the eastern and south-eastern coasts. The geography of the continent is extremely diverse, ranging from the snow-capped mountains of the Australian Alps and Tasmania to large deserts, tropical and temperate forests, grasslands, heathlands and woodlands.

The geography of Queensland in the north-east of Australia, is varied. It includes tropical islands, sandy beaches, flat river plains that flood after monsoon rains, tracts of rough, elevated terrain, dry deserts, rich agricultural belts and densely populated urban areas.
















