
The Neotropical realm is one of the eight biogeographic realms constituting Earth's land surface. Physically, it includes the tropical terrestrial ecoregions of the Americas and the entire South American temperate zone.

The white-nosed coati, also known as the coatimundi, is a species of coati and a member of the family Procyonidae. Local Spanish names for the species include antoon, gato solo, pizote, and tejón, depending upon the region. It weighs about 4–6 kg (8.8–13.2 lb), and the nose-to-tail length of the species is about 110 cm (3.6 ft) with about half of that being the tail length. However, small females can weigh as little as 3.1 kg (6.8 lb), while large males can weigh as much as 9 kg (20 lb).

Lagerstroemia, commonly known as crape myrtle, is a genus of around 50 species of deciduous and evergreen trees and shrubs native to the Indian subcontinent, southeast Asia, northern Australia, and other parts of Oceania, cultivated in warmer climates around the world. It is a member of the family Lythraceae, which is also known as the loosestrife family. These flowering trees are beautifully colored and are often planted both privately and commercially as ornamentals.

The subtropical zones or subtropics are geographical and climate zones to the north and south of the tropics. Geographically part of the temperate zones of both hemispheres, they cover the middle latitudes from 23°26′09.9″ (or 23.43609°) to approximately 35° north and south. The horse latitudes lie within this range.

Laurel forest, also called laurisilva or laurissilva, is a type of subtropical forest found in areas with high humidity and relatively stable, mild temperatures. The forest is characterized by broadleaf tree species with evergreen, glossy and elongated leaves, known as "laurophyll" or "lauroid". Plants from the laurel family (Lauraceae) may or may not be present, depending on the location.
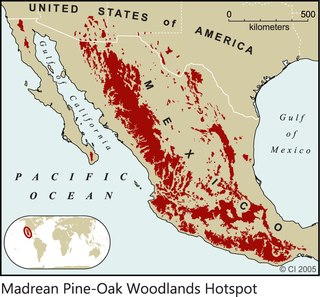
The Madrean pine–oak woodlands are subtropical woodlands found in the mountains of Mexico and the southwestern United States. They are a biogeographic region of the tropical and subtropical coniferous forests and temperate broadleaf and mixed forests biomes, located in North America.

Erinnyis obscura, the obscure sphinx, is a moth of the family Sphingidae. The species was first described by Johann Christian Fabricius in 1775.

The red pileated finch, also known as the red-crested finch, is a species of bird in the family Thraupidae. It is found in Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Ecuador, French Guiana, Guyana, Paraguay, Peru, on the eastern side of the Andes. Its natural habitats are subtropical or tropical dry forests, subtropical or tropical moist lowland forests, subtropical or tropical dry shrubland, and heavily degraded former forest. This is a common species, and the International Union for Conservation of Nature has rated its conservation status as "least concern".

The climate of the United States varies due to changes in latitude, and a range of geographic features, including mountains and deserts. Generally, on the mainland, the climate of the U.S. becomes warmer the farther south one travels, and drier the farther west, until one reaches the West Coast.
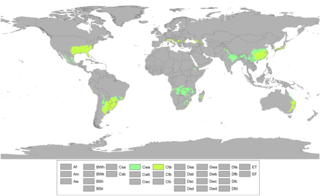
A humid subtropical climate is a temperate climate type characterized by hot and humid summers, and cool to mild winters. These climates normally lie on the southeast side of all continents, generally between latitudes 25° and 40° and are located poleward from adjacent tropical climates, and equatorward from either humid continental or oceanic climates. It is also known as warm temperate climate in some climate classifications.

Apantesis phalerata, commonly known as the harnessed tiger moth, is a species of moth within the Erebidae family, first described by Thaddeus William Harris in 1841.

Nigetia is a monotypic moth genus in the family Erebidae. Its only species, Nigetia formosalis, the thin-winged algibelle or thin-winged owlet moth, has a scattered distribution in eastern North America from Ontario to Connecticut, south to Florida and Texas. Both the genus and the species were first described by Francis Walker in 1866.

Catocala neogama, the bride, is a moth in the family Erebidae first described by James Edward Smith in 1797. It is found in North America east of the Rocky Mountains, from Maine and Quebec south to northern Florida and west to South Dakota, New Mexico, and into Arizona and Texas. Its westernmost population from the semiarid Colorado Plateau region is rather distinct and was once considered a separate species, but is now regarded as a well-marked subspecies C. n. euphemia.

Ecotourism in the United States is commonly practiced in protected areas such as national parks and nature reserves. The principles and behaviors of ecotourism are slowly becoming more widespread in the United States; for example, hotels in some regions strive to be more sustainable.

Eudryas unio, the pearly wood-nymph, is a species of moth of the family Noctuidae. It is found in most of the eastern United States from central New Hampshire and southern Ontario, south to southern Florida. In the west it ranges to the eastern Great Plains, south to southern Texas and Veracruz along the eastern coast of Mexico.

Dasychira basiflava, the yellow-based tussock, is a moth of the family Erebidae. The species was first described by Alpheus Spring Packard in 1865. It is found in North America from Massachusetts and southern Ontario west to Iowa, Texas, south to South Carolina and possibly Florida. It is also found in Southeastern Alaska.

Cisthene plumbea, the lead-colored lichen moth, is a moth of the family Erebidae. The species was first described by Richard Harper Stretch in 1885. It is found in eastern North America, from southern New Jersey south to northern Florida, west to Wisconsin and Texas.
Coenipeta medina is a species of moth in the family Erebidae first described by Achille Guenée in 1852. The species is found from Texas through Central America and Cuba to Brazil.

Cyanophrys herodotus, the tropical green hairstreak or tropical greenstreak, is a butterfly of the family Lycaenidae. It was described by Johan Christian Fabricius in 1793. It is found in Mexico, Guatemala, Panama, Nicaragua, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, Bolivia, Brazil, Paraguay and Argentina. Rare strays can be found as far north as southern Texas. The habitat consists of open disturbed areas in tropical and subtropical rainforests and cloudforests at altitudes ranging from 600 to about 2,000 meters.

Virbia laeta, the joyful holomelina, is a moth in the family Erebidae. It was described by Félix Édouard Guérin-Méneville in 1844. It is found in North America from New Brunswick south to Florida and west to Minnesota and south to Texas. The habitat consists of pine woodlands.



















