
Indo-Colombian relations are the diplomatic relations between the Republic of Colombia and the Republic of India. Both countries established diplomatic ties on January 19, 1960. Colombia is currently the commercial point of entry into Latin America for Indian companies.

Diplomatic relations were established in the late 19th century, between Argentina and Japan.
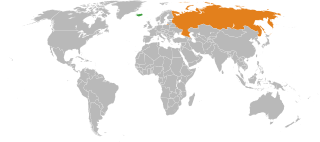
Iceland–Russia relations are the relations between the two countries, Iceland and Russia. Russia has an embassy in Reykjavík. Iceland has an embassy in Moscow, and two honorary consulates in Murmansk and Saint Petersburg. Relations between Iceland and Russia have floundered in recent years due to the Russian invasion of Ukraine and the poisoning of Sergei Skripal, and on June 9, 2023, Iceland announced it would be suspending operations at its embassy in Moscow.

The diplomatic relations between the Portuguese Republic and Romania date back to 1917, having been interrupted following World War II, before being re-established in June 1974, following the Carnation Revolution in Portugal. Since then, the relations between the two countries have been stable and friendly. Both nations are members of the Council of Europe, European Union, NATO and the United Nations.

Relations between the People's Republic of China and the Oriental Republic of Uruguay were first established in 1988. Relations were defined as “friendly and cooperative” by the Chinese government. The bilateral relation was promoted to a strategic partnership in 2016.

Egypt–Japan relations are foreign relations between Egypt and Japan. Such relations are described by the Egyptian ambassador to Japan as a "very strong friendship", with embassies mutually established. At present, the two nations maintain a cordial relationship with strong economic and trade relations. Since the formal diplomatic relations were established, both countries have kept embassies in each other's capitals, demonstrating a dedication to continued communication and cooperation. Bilateral connections have been strengthened via a history of friendly exchanges and frequent visits between the two countries at different governmental levels. Their interactions are mostly shaped by their economic and trade ties, which include major Japanese investment in Egypt and a thriving exchange of goods and services. This economic involvement is backed by a variety of agreements that ease trade, protect investments, and promote mutual growth. Currently, Egypt and Japan have a friendly and cooperative relationship based on common interests and a commitment to regional stability and prosperity. This connection has grown to include considerable cultural exchanges and educational collaborations, strengthening the two countries' already strong ties.

China–Mexico relations are the diplomatic relations between the People's Republic of China and the United Mexican States. Diplomatic relations were established in 1972. and both nations are members of the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation, Forum of East Asia–Latin America Cooperation, G-20 major economies and the United Nations.

Filipino–Thai relations refers to the bilateral relations between the Philippines and Thailand. The Philippines established formal diplomatic relations with Thailand on June 14, 1949. The relations between the two are described as warm and friendly. Thailand is one of the Philippines' major trade partners and one of the Philippines' sources of rice through Thai exports. Bilateral relations continues to be strengthened through talks and agreements on economic, security and cultural matters including concerns on rice trade, fight on drugs and human trafficking. Thailand has an embassy in Manila and an honorary consulate in Cebu, while the Philippines maintains an embassy in Bangkok. Both countries are members of ASEAN and the Non-Aligned Movement.

The nations of Ecuador and Mexico first established diplomatic relations in 1830. In April 2024, Mexico severed diplomatic relations due to a police raid on the Mexican Embassy in Quito. Since June 2024, Switzerland serves as the protecting power representing Ecuador's interests in Mexico and vice versa.

The nations of Algeria and Mexico established diplomatic relations in 1964. Both nations are members of the Group of 15, Group of 24 and the United Nations.
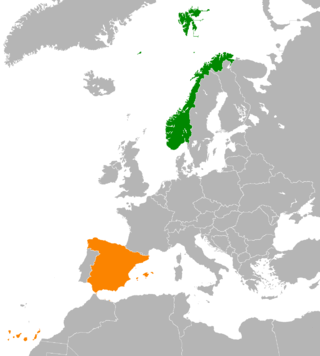
Norway–Spain relations are the bilateral and diplomatic relations between these two countries. Norway has an embassy in Madrid, and honorary consulates in Algeciras, Barcelona, Benidorm, Bilbao, Gijón, Gerona, La Coruña, Las Palmas de Gran Canaria, Málaga, Palma de Mallorca, Sevilla, Santa Cruz de Tenerife, Torrevieja, and Valencia. Spain has an embassy in Oslo, also accredited for Iceland. Relations between Spain and Norway are mainly defined by their membership in NATO and the Schengen Area.

Kuwait–Spain relations are the diplomatic relations between Kuwait and Spain. Kuwait has an embassy in Madrid. Spain has an embassy in Kuwait City.

Lebanon–Spain relations are the bilateral and diplomatic relations between these two countries. Lebanon has an embassy in Madrid, and Spain has an embassy in Beirut. Both countries are members of the Union for the Mediterranean.

Spain–Thailand relations are the bilateral and diplomatic relations between these two countries. Thailand has an embassy in Madrid and two honorary consulates in Barcelona and Santa Cruz de Tenerife. Spain has an embassy in Bangkok.

Cape Verde–Spain relations are the bilateral and diplomatic relations between these two countries. Cape Verde has an embassy in Madrid, a consulate-general in Las Palmas de Gran Canaria and two consulates in Alicante and La Coruña. Spain has an embassy in Praia.

Democratic Republic of the Congo–Spain relations are the bilateral relations between the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) and Spain. The Democratic Republic of the Congo has an embassy in Madrid. Spain has an embassy in Kinshasa.

Kenya–Spain relations are the bilateral and diplomatic relations between these two countries. Kenya has an embassy in Madrid. Spain has an embassy in Nairobi and an honorary consulate in Mombasa.

Nigeria–Spain relations are the bilateral and diplomatic relations between these two countries. Nigeria has an embassy in Madrid. Spain has an embassy in Abuja and a consulate-general in Lagos.

Spain–Tunisia relations are the bilateral relations between Spain and Tunisia. Tunisia has an embassy in Madrid and two consulates in Barcelona and Palma de Mallorca. Spain has an embassy in Tunisia. Both countries are members of the Union for the Mediterranean.
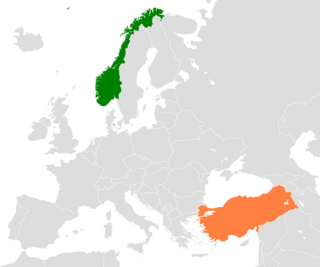
Norway–Turkey relations are foreign relations between Norway and Turkey. The bilateral relations were established in 1926.























