
Telecine is the process of transferring film into video and is performed in a color suite. The term is also used to refer to the equipment used in the post-production process. Telecine enables a motion picture, captured originally on film stock, to be viewed with standard video equipment, such as television sets, video cassette recorders (VCR), DVD, Blu-ray Disc or computers. Initially, this allowed television broadcasters to produce programs using film, usually 16mm stock, but transmit them in the same format, and quality, as other forms of television production. Furthermore, telecine allows film producers, television producers and film distributors working in the film industry to release their productions on video and allows producers to use video production equipment to complete their filmmaking projects. Within the film industry, it is also referred to as a TK, because TC is already used to designate timecode. Motion picture film scanners are similar to telecines.

Color grading is a post-production process common to filmmaking and video editing of improving the appearance of an image for presentation in different environments on different devices. Various attributes of an image such as contrast, color, saturation, detail, black level, and white point may be enhanced whether for motion pictures, videos, or still images. Color grading and color correction are often used synonymously as terms for this process and can include the generation of artistic color effects through creative blending and compositing of different images. Color grading is generally now performed in a digital process either in a controlled environment such as a color suite, or in any location where a computer can be used in dim lighting.

A waveform monitor is a special type of oscilloscope used in television production applications. It is typically used to measure and display the level, or voltage, of a video signal with respect to time.
In filmmaking, dailies are the raw, unedited footage shot during the making of a motion picture. The term comes from when movies were all shot on film because usually at the end of each day, the footage was developed, synced to sound, and printed on film in a batch for viewing the next day by the director, selected actors, and film crew members. After the advent of digital filmmaking, "dailies" were available instantly after the take and the review process was no longer tied to the overnight processing of film and became more asynchronous. Now some reviewing may be done at the shoot, even on location, and raw footage may be immediately sent electronically to anyone in the world who needs to review the takes. For example, a director can review takes from a second unit while the crew is still on location or producers can get timely updates while travelling. Dailies serve as an indication of how the filming and the actors' performances are progressing. The term was also used to describe film dailies as "the first positive prints made by the laboratory from the negative photographed on the previous day".

1–inch type B VTR is a reel-to-reel analog recording video tape format developed by the Bosch Fernseh division of Bosch in Germany in 1976. The magnetic tape format became the broadcasting standard in continental Europe, but adoption was limited in the United States and United Kingdom, where the Type C videotape VTR met with greater success.

2-inch quadruplex videotape was the first practical and commercially successful analog recording video tape format. It was developed and released for the broadcast television industry in 1956 by Ampex, an American company based in Redwood City, California. The first videotape recorder using this format was built in the same year. This format revolutionized broadcast television operations and television production, since the only recording medium available to the TV industry until then was film used for kinescopes.

Sony HDVS is a range of high-definition video equipment developed in the 1980s to support an early analog high-definition television system thought to be the broadcast television systems that would be in use today. The line included professional video cameras, video monitors and linear video editing systems.
Time base correction (TBC) is a technique to reduce or eliminate errors caused by mechanical instability present in analog recordings on mechanical media.
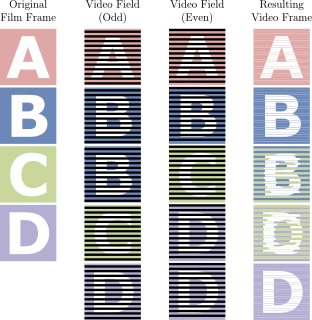
Three-two pull down is a term used in filmmaking and television production for the post-production process of transferring film to video.

Cintel was a British digital cinema company founded in 1927 by John Logie Baird and based in Ware, Hertfordshire. The early company was called Cinema Television Ltd. Cinema Television was sold to J Arthur Rank Organization renamed Rank Cintel in 1958. It specialized in the design and manufacture of professional post-production equipment, for transcribing film into video or data formats. It was formerly part of the Rank Organisation. Along with a line of telecines, Rank Cintel made 3 tube RGB color video projectors in the 1960s.
The Fernseh AG television company was registered in Berlin on July 3, 1929, by John Logie Baird, Robert Bosch, Zeiss Ikon and D.S. Loewe as partners. John Baird owned Baird Television Ltd. in London, Zeiss Ikon was a camera company in Dresden, D.S. Loewe owned a company in Berlin and Robert Bosch owned a company, Robert Bosch GmbH, in Stuttgart. with an initial capital of 100,000 Reichsmark. Fernseh AG did research and manufacturing of television equipment.
A virtual telecine is a piece of video equipment that can play back data files in real time. The colorist-video operator controls the virtual telecine like a normal telecine, although without controls like focus and framing. The data files can be from a Spirit DataCine, motion picture film scanner, CGI animation computer, or an Acquisition professional video camera. The normal input data file standard is DPX. The output of data files are often used in digital intermediate post-production using a film recorder for film-out. The control room for the virtual telecine is called the color suite.

A film chain or film island is a television – professional video camera with one or more projectors aligned into the photographic lens of the camera. With two or more projectors a system of front-surface mirrors that can pop-up are used in a multiplexer. These mirrors switch different projectors into the camera lens. The camera could be fed live to air for broadcasting through a vision mixer or recorded to a VTR for post-production or later broadcast. In most TV use this has been replaced by a telecine.
da Vinci Systems was an American digital cinema company founded in 1984 in Coral Springs, Florida as a spinoff of Video Tape Associates. It was known for its hardware-based color correction products, GPU-based color grading, digital mastering systems, and film restoration and remastering systems. It was one of the earliest pioneers in post-production products. The company was owned by Dynatech Corporation for the majority of its lifespan until being bought by JDS Uniphase in 2005 and by Blackmagic Design in 2009.

D6 HDTV VTR is SMPTE videocassette standard. A D6 VTR can record and playback HDTV video uncompressed. The only D6 VTR product is the Philips, now Thomson's Grass Valley's Media Recorder, model DCR 6024, also called the D6 Voodoo VTR. The VTR was a joint project between Philips Digital Video Systems of Germany and Toshiba in Japan. The tape deck module was designed and made by Philips in Weiterstadt, Germany, and the digital processor module designed and made by Toshiba. Since there is no data compression, after 20 tape copies of multi generations there is no noticeable loss of quality. As a very high-end, costly system about 70 were sold to high-end post houses from about 2000 to 2005. The VTR had a data record option. The data module could record and play back 2k DPX files at 6 frames per second over a HIPPI connection. The VTR came in a data only model, or with a switch module, so the record deck could be used for both video and data recording. The tape deck was also sold stand alone as a giga bit recorder to record and playback raw data. Toshiba made the video tape for the VTR. The high price of the video tape limited the use of the VTR.

IVC 2 inch Helical scan was a high-end broadcast quality helical scan analog recording VTR format developed by International Video Corporation (IVC), and introduced in 1975. Previously, IVC had made a number of 1 inch Helical VTRs. IVC saw a chance to make a VTR that would have the quality of the then-standard 2 inch Quadruplex videotape format but with the advantages of helical scan. They then developed a VTR using this technology, the IVC Model 9000.

Spirit DataCine is a telecine and a motion picture film scanner. This device is able to transfer 16mm and 35mm motion picture film to NTSC or PAL television standards or one of many High-definition television standards. With the data transfer option a Spirit DataCine can output DPX data files. The image pick up device is a solid state charge-coupled device. This eliminated the need for glass vacuum tube CRTs used on older telecines. The units can transfer negative film, primetime, intermediate film and print film, stock. One option is a Super 8 gate for the transfer of Super 8 mm film. With a sound pick up option, optical 16mm and 35mm sound can be reproduced, also 16mm magnetic strip sound. The unit can operate stand alone or be controlled by a scene by scene color corrector. Ken Burns created The Civil War, a short documentary film included in the DVD release, on how he used the Spirit DataCine to transfer and remaster this film. The operator of the unit is called a Colorist or Colorist Assistant. The Spirit DataCine has become the standard for high-end real-time film transfer and scanning. Over 370 units are used in post-production facilities around the world. Most current film productions are transferred on Spirit DataCines for Television, Digital television, Cable television, Satellite television, Direct-to-video, DVD, Blu-ray Disc, pay-per-view, In-flight entertainment, Stock footage, Dailies, Film preservation, digital intermediate and digital cinema. The Spirit DataCine is made by DFT Digital Film Technology GmbH in Darmstadt, Germany.
Sondor is a manufacturer of Audio Video equipment located in Zollikon, Switzerland until 2017. Sondor was founded in 1952 by Willy Hungerbuehler. Sondor started as a manufacturer of 16 mm film and 35mm film magnetic film equipment. They are noted as inventing the standard for bi-phase interlocking pulse signals to sync sound to film. Sondor added a film transport telecine to it line of film sound equipment. Sondor products are found in many in post-production studios for record and playback and in movie theater for sound playback. playback.
Pandora International is a maker of hardware and software systems for video editing, Telecine Control and Colour Correction. Pandora was founded in 1985 By Steve Brett and Martin Greenwood, later Aine Marsland joined the team and took over the administration of the company. Pandora International devices are able to colour-correct video and 16 mm and 35 mm motion picture film in real time. Pandora International is based in Greenhithe, Kent, England.
The Primetime Engineering Emmy Awards, or Engineering Emmys, are one of two sets of Emmy Awards that are presented for outstanding achievement in engineering development in the television industry. The Primetime Engineering Emmys are presented by the Academy of Television Arts & Sciences (ATAS), while the separate Technology and Engineering Emmy Awards are given by its sister organization, the National Academy of Television Arts and Sciences (NATAS).
















