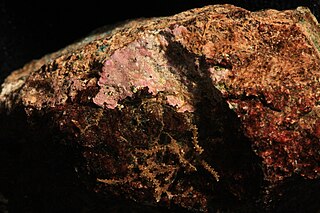The glaucophytes, also known as glaucocystophytes or glaucocystids, are a small group of freshwater unicellular algae, less common today than they were during the Proterozoic. Only 15 species have been described, but more species are likely to exist. Together with the red algae (Rhodophyta) and the green algae plus land plants, they form the Archaeplastida. However, the relationships among the red algae, green algae and glaucophytes are unclear, in large part due to limited study of the glaucophytes.
Gymnodinium is a genus of dinoflagellates, a type of marine and freshwater plankton. It is one of the few naked dinoflagellates, or species lacking armor. Since 2000, the species which had been considered to be part of Gymnodinium have been divided into several genera, based on the nature of the apical groove and partial LSU rDNA sequence data. Amphidinium was redefined later. Gymnodinium belong to red dinoflagellates that, in concentration, can cause red tides.

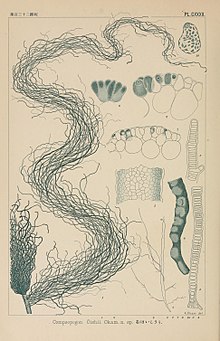
Lemanea is a genus of freshwater red algae, in the order Batrachospermales. Both species are considered to be widespread in the northern hemisphere. Although placed in the Rhodophyta it in fact is green in colour.

AlgaeBase is a global species database of information on all groups of algae, as well as one group of flowering plants, the sea-grasses.
Schmitzia hiscockiana is a small, rare, red seaweed or marine alga of the phylum Rhodophyta or red algae. It was discovered and named in 1985.

Gastroclonium reflexum is a small red alga (Rhodophyta) reported from Ireland and Britain.
Picocystis is a monotypic genus of green algae, the sole species is Picocystis salinarum. It is placed within its own class, Picocystophyceae in the division Chlorophyta.
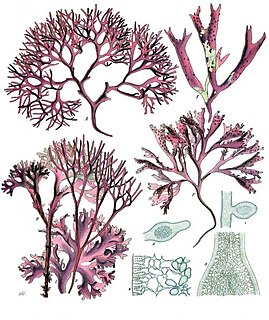
Red algae, or Rhodophyta, are one of the oldest groups of eukaryotic algae. The Rhodophyta also comprises one of the largest phyla of algae, containing over 7,000 currently recognized species with taxonomic revisions ongoing. The majority of species (6,793) are found in the Florideophyceae (class), and mostly consist of multicellular, marine algae, including many notable seaweeds. Red algae are abundant in marine habitats but are relatively rare in freshwaters. Approximately 5% of the red algae occur in freshwater environments with greater concentrations found in warmer areas. Except for two coastal cave dwelling species in the asexual class Cyanidiophyceae, there are no terrestrial species, which may be due to an evolutionary bottleneck where the last common ancestor lost about 25% of its core genes and much of its evolutionary plasticity.

Ralfsiales is an order of crustose brown algae containing two families.
Bangia is an extant genus of division Rhodophyta that grows in marine or freshwater habitats. Bangia has small thalli with rapid growth and high reproductive output, and exhibits behavior characteristic of r-selected species. The plants are attached by down-growing rhizoids, usually in dense purple-black to rust-colored clumps. The chloroplasts of Bangia, like others in the division Rhodophyta, contain chlorophyll a and sometimes chlorophyll d, as well as accessory pigments such as phycobilin pigments and xanthophylls. Depending on the relative proportions of these pigments and the light conditions, the overall color of the plant can range from green to red to purple to grey; however, the red pigment, phycoerythrin, is usually dominant.
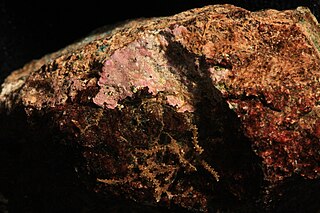
Hildenbrandia is a genus of thalloid red alga comprising 26 species. The slow-growing, non-mineralized thalli take a crustose form. Hildenbrandia reproduces by means of conceptacles and produces tetraspores.

Galaxaura is a genus of thalloid red algae. Dichotomous branches are formed; the medulla has a filamentous construction. It may be related to the fossil Gymnocodiaceae.
Sirodotia Kylin (1912) is a genus of freshwater red alga which was described by Kylin in 1912. The family Batrachospermaceae belongs to the order Batrachospermales and has six well known genera namely Batrachospermum, Kumanoa, Sirodotia, Nothocladus, Tuomeya, and Sheathia. The morphology of the gametophyte of Batrachospermum, Sirodotia, Tuomeya, and Nothocladus are more are less similar to each other. Necchi and Entwisle (1990) proposed to delimit them from generic level to section level of genus Batrachospermum. Sheathia was the member of genus Batrachospermum and has risen to generic level. phylogenetic studies revealed a distinctive genus level of the above with full support in bootstrap analysis and Sirodotia has been raised to generic level.

Christine Adair Maggs is a British phycologist. Formerly Executive Dean of the Faculty of Science & Technology at Bournemouth University, she is now the Chief Scientist of the Joint Nature Conservation Committee.

Choreocolax polysiphoniae is a minute marine parasitic alga in the division Rhodophyta.

Batrachospermaceae is a family of fresh water red algae (Rhodophyta). Genera within the Batrachospermaceae generally have a "Lemanea-type" life history with carpospores germinating to produce chantransia. Sporophyte phase with meiosis occurs in an apical cell to produce the gametophyte stage. Pit connections have two pit plug cap layers with the other layer enlarged. This family of freshwater red algae is uniaxial, meaning each filament with a single apical cell. The genera included within Batrachospermaceae are listed in the table below.

Michael Dominic Richard Guiry, is an Irish botanist, who specialises in phycology (algae). See for example the articles. He is the founder and director of the algal database, AlgaeBase.

Timothy John Entwisle, is an Australian botanist, much of whose research work is in phycology (algae). See for example the articles. He was awarded a Ph.D. from La Trobe University in 1986 for work on the taxonomy of Vaucheria.

Callithamniaceae is a family of red algae (Rhodophyta) in the order Ceramiales. The family was first described by Friedrich Traugott Kützing in 1843.

Hildenbrandia rubra is a marine species of thalloid red alga. It forms thin reddish crusts on rocks and pebbles in the intertidal zone and the shallow subtidal zone. It is a common species with a cosmopolitan distribution, and is able to tolerate a wide range of conditions.