
Concorde is a retired Anglo-French supersonic airliner jointly developed and manufactured by Sud Aviation and the British Aircraft Corporation (BAC). Studies started in 1954, and France and the United Kingdom signed a treaty establishing the development project on 29 November 1962, as the programme cost was estimated at £70 million . Construction of the six prototypes began in February 1965, and the first flight took off from Toulouse on 2 March 1969. The market was predicted for 350 aircraft, and the manufacturers received up to 100 option orders from many major airlines. On 9 October 1975, it received its French Certificate of Airworthiness, and from the UK CAA on 5 December.

The Tupolev Tu-144 is a Soviet supersonic passenger airliner designed by Tupolev in operation from 1968 to 1999.

A delta wing is a wing shaped in the form of a triangle. It is named for its similarity in shape to the Greek uppercase letter delta (Δ).
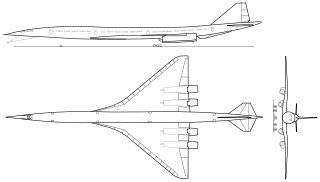
The Boeing 2707 was an American supersonic passenger airliner project during the 1960s. After winning a competition for a government-funded contract to build an American supersonic airliner, Boeing began development at its facilities in Seattle, Washington. The design emerged as a large aircraft with seating for 250 to 300 passengers and cruise speeds of approximately Mach 3. It was intended to be much larger and faster than competing supersonic transport (SST) designs such as Concorde.

The North American Aviation XB-70 Valkyrie is a retired prototype version of the planned B-70 nuclear-armed, deep-penetration supersonic strategic bomber for the United States Air Force Strategic Air Command. Designed in the late 1950s by North American Aviation (NAA) to replace the B-52 Stratofortress and B-58 Hustler, the six-engined, delta-winged Valkyrie could cruise for thousands of miles at Mach 3+ while flying at 70,000 feet (21,000 m).

A supersonic transport (SST) or a supersonic airliner is a civilian supersonic aircraft designed to transport passengers at speeds greater than the speed of sound. To date, the only SSTs to see regular service have been Concorde and the Tupolev Tu-144. The last passenger flight of the Tu-144 was in June 1978 and it was last flown in 1999 by NASA. Concorde's last commercial flight was in October 2003, with a November 26, 2003 ferry flight being its last flight.

Convair, previously Consolidated Vultee, was an American aircraft-manufacturing company that later expanded into rockets and spacecraft. The company was formed in 1943 by the merger of Consolidated Aircraft and Vultee Aircraft. In 1953, it was purchased by General Dynamics, and operated as their Convair Division for most of its corporate history.
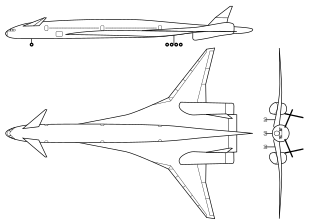
The Boeing Sonic Cruiser was a concept jet airliner with a delta wing–canard configuration. It was distinguished from conventional airliners by its delta wing and high-subsonic/transonic cruising speed of up to Mach 0.98. Boeing first proposed it in 2001, but airlines generally preferred lower operating costs over higher speed. Boeing ended the Sonic Cruiser project in December 2002 and shifted to the slower but more fuel-efficient 7E7 airliner.

The Convair B-58 Hustler, designed and produced by American aircraft manufacturer Convair, was the first operational bomber capable of Mach 2 flight.

Tupolev, officially Public Joint Stock Company Tupolev, is a Russian aerospace and defence company headquartered in Basmanny District, Moscow.

The General Electric J79 is an axial-flow turbojet engine built for use in a variety of fighter and bomber aircraft and a supersonic cruise missile. The J79 was produced by General Electric Aircraft Engines in the United States, and under license by several other companies worldwide. Among its major uses was the Lockheed F-104 Starfighter, Convair B-58 Hustler, McDonnell Douglas F-4 Phantom II, North American A-5 Vigilante and IAI Kfir.

The Hughes AIM-47 Falcon, originally GAR-9, was a very long-range high-performance air-to-air missile that shared the basic design of the earlier AIM-4 Falcon. It was developed in 1958 along with the new Hughes AN/ASG-18 radar fire-control system intended to arm the Mach 3 XF-108 Rapier interceptor aircraft and, after that jet's cancellation, the YF-12A. It was never used operationally, but was a direct predecessor of the AIM-54 Phoenix used on the Grumman F-14 Tomcat.

A supersonic aircraft is an aircraft capable of supersonic flight, that is, flying faster than the speed of sound. Supersonic aircraft were developed in the second half of the twentieth century. Supersonic aircraft have been used for research and military purposes, but only two supersonic aircraft, the Tupolev Tu-144 and the Concorde, ever entered service for civil use as airliners. Fighter jets are the most common example of supersonic aircraft.

An escape crew capsule is an escape capsule that allows one or more occupants of an aircraft or spacecraft to escape from the craft while it is subjected to extreme conditions, such as high speed or altitude. The occupant remains encapsulated and protected until such time as the external environment is suitable for direct exposure or the capsule reaches the ground.

The Tupolev Tu-244 was a proposed supersonic transport (SST) aircraft, developed from the Tu-144. It implemented novel features such as cryogenic fuel to enable flight distances of up to 10,000 km (6,200 mi) and would have carried up to 300 passengers. The project was cancelled in 1993.

The Convair Kingfish reconnaissance aircraft design was the ultimate result of a series of proposals designed at Convair as a replacement for the Lockheed U-2. Kingfish competed with the Lockheed A-12 for the Project Oxcart mission, and lost to that design in 1959.

The High Virgo, also known as Weapons System 199C (WS-199C), was a prototype air-launched ballistic missile (ALBM) jointly developed by Lockheed and the Convair division of General Dynamics during the late 1950s. The missile proved moderately successful and aided in the development of the later GAM-87 Skybolt ALBM. It was also used in early tests of anti-satellite weapons.
Douglas Aircraft Company's Model 2229 was a proposed supersonic transport (SST) originally started as a private study. The design progressed as far as making mock-ups of the cockpit area and wind-tunnel models of the overall layout. After studying the design, Douglas concluded that the SST would not work economically, and declined to enter the Model 2229 in the National Supersonic Transport (NST) program in 1963.

The Boom Overture is a proposed supersonic airliner under development by Boom Technology. Its design will be capable of traveling Mach 1.7, with 64–80 passengers depending on configuration, and 4,250 nmi of range. The Overture is planned to be introduced in 2029. The company claims that with 500 viable routes, there could be a market for up to 1,000 supersonic airliners with fares similar to business class. The aircraft is planned to have a delta wing configuration, but will be built with composite materials. Following a redesign revealed in 2022, it is intended to be powered by four dry (non-afterburning) 35,000 lbf (160 kN) turbofans.


















